Chemistry:Linopirdine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
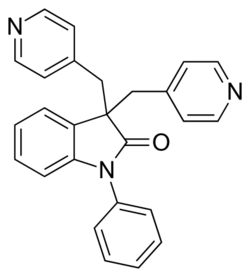
| Formula | C26H21N3O |
| Molar mass | 391.474 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Linopirdine is a putative cognition-enhancing drug with a novel mechanism of action. Linopirdine blocks the KCNQ2\3 heteromer M current with an IC50 of 2.4 micromolar[1] disinhibiting acetylcholine release, and increasing hippocampal CA3-schaffer collateral mediated glutamate release onto CA1 pyramidal neurons.[2] In a murine model linopirdine is able to nearly completely reverse the senescence-related decline in cortical c-FOS, an effect which is blocked by atropine and MK-801, suggesting Linopirdine can compensate for the age related decline in acetylcholine release.[3] Linopirdine also blocks homomeric KCNQ1 and KCNQ4 voltage gated potassium channels which contribute to vascular tone with substantially less selectivity than KCNQ2/3.[1] Linopirdine also acts as a glycine receptor antagonist in concentrations typical for Kv7 studies in the brain.[4]
Synthesis
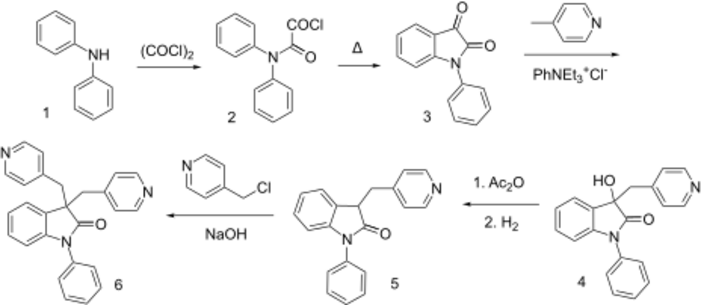
The amide formation between diphenylamine (1) and oxalyl chloride [79-37-8] gives intermediate, CID:11594101 (2). Haworth type intramolecular cyclization of the acid chloride occurs on heating to afford 1-phenylisatin [723-89-7] (3). The reaction with 4-picoline (4) under PTC with a Quat. salt afforded the carbinol, CID:10358387 (5). Dehydration of the alcohol using acetic anhydride gives [33546-08-6] (6). The reduction of the olefin then afforded the indolone, CID:10470081 (7). The 3 position is now activated by the adjacent benzene ring on one side and the carbonyl group on the other. Alkylation with 4-picolylchloride [10445-91-7] (8) proceeds with hydroxide as the base to afford Linopirdine (9).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Selectivity of linopirdine (DuP 996), a neurotransmitter release enhancer, in blocking voltage-dependent and calcium-activated potassium currents in hippocampal neurons". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 286 (2): 709–717. August 1998. PMID 9694925.
- ↑ "M-type potassium channels modulate Schaffer collateral-CA1 glutamatergic synaptic transmission". The Journal of Physiology 590 (16): 3953–3964. August 2012. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.235820. PMID 22674722.
- ↑ "The acetylcholine release enhancer linopirdine induces Fos in neocortex of aged rats". Neurobiology of Aging 22 (3): 485–494. 2001. doi:10.1016/s0197-4580(00)00252-9. PMID 11378256.
- ↑ "Kv7 channel antagonists block glycine receptors" (in en). bioRxiv. 2022-03-02. doi:10.1101/2022.03.02.482705.
- ↑ "A Large Scale Preparation of the Cognitive Enhancer Linopirdine". Synthetic Communications 23 (11): 1617–1625. 1993. doi:10.1080/00397919308011258.
- ↑ "Microwave-Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Neurotransmitter Release Enhancer Linopiridine and Its New Analogues". Synthetic Communications 33 (18): 3115–3121. 2003. doi:10.1081/SCC-120023425.
- ↑ Bryant III WM, Huhn GF, US patent 4806651, issued 1989, assigned to E.I. Du Pont De Nemours and Company
- ↑ Earl RA, Myers MJ, Nickolson VJ, US patent 5173489, issued 1992, assigned to The Dupont Merck Pharmaceutical Co.
 |
