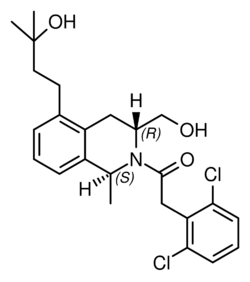
Chemistry:Mevidalen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LY-3154207; LY3154207 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H29Cl2NO3 |
| Molar mass | 450.40 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Mevidalen (developmental code name LY-3154207) is a dopaminergic drug which is under development for the treatment of Lewy body disease, including those with Parkinson's disease.[1][2][3][4][5] It acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the dopamine D1 receptor.[1][6] The drug is orally active and crosses the blood–brain barrier.[6] It is a tetrahydroisoquinoline and is a close analogue of DETQ, another D1 receptor PAM.[2][3][6] Mevidalen has been found to have wakefulness-promoting effects in sleep-deprived humans.[7][8] Side effects of mevidalen have been reported to include increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, nervousness, fatigue, headaches, palpitations, and contact dermatitis, as well as falls in those with dementia.[6][5][8] As of March 2022, mevidalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of Lewy body disease.[1] Besides for movement disorders and dementia, D1 receptor PAMs like mevidalen might have value in the treatment of certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, excessive somnolence, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Mevidalen - Eli Lilly and Company". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800042093.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Positive allosteric modulators of the dopamine D1 receptor: A new mechanism for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders". Advances in Pharmacology. Advances in Pharmacology. 86. San Diego, Calif.: Elsevier. 2019. pp. 273–305. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2019.06.001. ISBN 9780128166680.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Synthesis and Preclinical Characterization of LY3154885, a Human Dopamine D1 Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulator with an Improved Nonclinical Drug-Drug Interaction Risk Profile". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 65 (5): 3786–3797. March 2022. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01887. PMID 35175768.
- ↑ "Safety and Efficacy of Mevidalen in Lewy Body Dementia: A Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial". Movement Disorders 37 (3): 513–524. March 2022. doi:10.1002/mds.28879. PMID 34859493.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Mevidalen (LY3154207), a Centrally Acting Dopamine D1 Receptor-Positive Allosteric Modulator, in Patients With Parkinson Disease". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development 11 (3): 324–332. March 2022. doi:10.1002/cpdd.1039. PMID 34664427.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Mevidalen (LY3154207), a Centrally Acting Dopamine D1 Receptor-Positive Allosteric Modulator (D1PAM), in Healthy Subjects". Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development 10 (4): 393–403. April 2021. doi:10.1002/cpdd.874. PMID 33029934.
- ↑ "The Signaling and Pharmacology of the Dopamine D1 Receptor". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 15: 806618. 2021. doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.806618. PMID 35110997.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "The Dopamine D1 Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulator Mevidalen (LY3154207) Enhances Wakefulness in the Humanized D1 Mouse and in Sleep-Deprived Healthy Male Volunteers". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 380 (3): 143–152. March 2022. doi:10.1124/jpet.121.000719. PMID 34893551.
 |

