Chemistry:Dihydrexidine
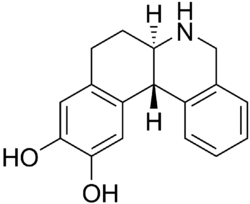 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 267.328 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dihydrexidine (DAR-0100) is a moderately selective full agonist at the dopamine D1 and D5 receptors.[1] It has approximately 10-fold selectivity for D1 and D5 over the D2 receptor.[2] Although dihydrexidine has some affinity for the D2 receptor, it has functionally selective (highly biased) D2 signaling,[3] thereby explaining why it lacks D2 agonist behavioral qualities.[4]
Dihydrexidine has shown impressive antiparkinson effects in the MPTP-primate model,[5] and has been investigated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.[6] In an early clinical trial the drug was given intravenously and led to profound hypotension so development was halted.[7] The drug was resurrected when it was shown that smaller subcutaneous doses were safe.[8] This led to a pilot study in schizophrenia[9] and current clinical trials to assess its efficacy in improving the cognitive and working memory deficits in schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder.
There have been several reviews of relevance to the compound.[10][11][12]
References
- ↑ "Dihydrexidine, a novel selective high potency full dopamine D-1 receptor agonist.". Eur J Pharmacol 166 (1): 111–113. 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(89)90690-0. PMID 2572425.
- ↑ "Dihydrexidine, a novel full efficacy D1 dopamine receptor agonist.". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262 (1): 383–393. 1992. PMID 1352553.
- ↑ Kilts, JD. (2002). "Functional selectivity of dopamine receptor agonists. II. Actions of dihydrexidine in D2L receptor-transfected MN9D cells and pituitary lactotrophs.". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301 (3): 1179–89. doi:10.1124/jpet.301.3.1179. PMID 12023553.
- ↑ "Behavioral effects in the rat of dihydrexidine, a high-potency, full-efficacy D1 dopamine receptor agonist.". Neuropsychopharmacology 5 (3): 187–195. 1991. PMID 1684499.
- ↑ "Dihydrexidine, a full dopamine D1 agonist, reduces MPTP-induced parkinsonism in monkeys.". Eur J Pharmacol 199 (3): 389–391. 1991. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(91)90508-N. PMID 1680717.
- ↑ "Dopamine D1 receptor agonists as antiparkinson drugs.". Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19 (7): 255–256. 1998. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(98)01219-X. PMID 9703756.
- ↑ "Effects of the full dopamine D1 receptor agonist dihydrexidine in Parkinson's disease.". Clin. Neuropharmacol. 21 (6): 339–343. 1998. PMID 9844789.
- ↑ "A single 20 mg dose of dihydrexidine (DAR-0100), a full dopamine D1 agonist, is safe and tolerated in patients with schizophrenia.". Schizophr. Res. 93 (1–3): 42–50. 2007. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2007.03.011. PMID 17467956.
- ↑ "A single 20 mg dose of the full D1 dopamine agonist dihydrexidine (DAR-0100) increases prefrontal perfusion in schizophrenia.". Schizophr. Res. 94 (1–3): 332–341. 2007. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2007.03.033. PMID 17596915.
- ↑ "Parkinson's disease and D1 dopamine receptors.". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs 2 (11): 1582–1591. 2001. PMID 11763161.
- ↑ "Dihydrexidine--the first full dopamine D1 receptor agonist.". CNS Drug Rev. 10 (3): 230–242. 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00024.x. PMID 15492773.
- ↑ "Dopamine D1 receptor ligands: where are we now and where are we going.". Med Res Rev 29 (2): 272–294. 2009. doi:10.1002/med.20130. PMID 18642350.
 |
