Chemistry:Homocysteic acid
From HandWiki
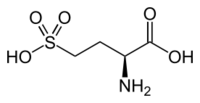 L-Homocysteic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-4-sulfobutanoic acid
| |
| Other names
Homocysteate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9NO5S | |
| Molar mass | 183.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white or colorless solid |
| Melting point | 261 °C (502 °F; 534 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Homocysteic acid is the organosulfur compound with the formula HO
3SCH
2CH
2CH(NH
2)CO
2H. A white solid, it is sulfonic acid-containing non-proteinogenic amino acid. It is aanalog of glutamic acid and is a potent NMDA receptor agonist.[1][2] It is related to homocysteine, a by-product of methionine metabolism.
Homocysteic acid is prepared by the oxidation of homocystine with aqueous bromine.[3]
References
- ↑ Grandes, P; Kq, KQD; Morino, P; Cuénod, M; Streit, P (1991). "Homocysteate, an Excitatory Transmitter Candidate Localized in Glia". The European Journal of Neuroscience 3 (12): 1370–1373. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00070.x. PMID 12106235.
- ↑ Yuzaki, M; Connor, JA (1999). "Characterization of L-homocysteate-induced currents in Purkinje cells from wild-type and NMDA receptor knockout mice". Journal of Neurophysiology 82 (5): 2820–6. doi:10.1152/jn.1999.82.5.2820. PMID 10561449.
- ↑ Watkins, J. C. (1962). "The Synthesis of Some Acidic Amino Acids Possessing Neuropharmacological Activity". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry 5 (6): 1187–1199. doi:10.1021/jm01241a010. PMID 14056452.
 |

