Chemistry:Guangxitoxin
| Guangxitoxin-1E | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
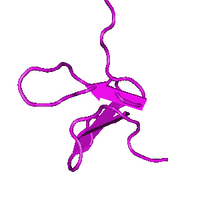 Schematic diagram of the three-dimensional Solution Structure of GxTX-1E. | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Organism | |||||||
| Symbol | N/A | ||||||
| UniProt | P84835 | ||||||
| |||||||
Guangxitoxin, also known as GxTX, is a peptide toxin found in the venom of the tarantula Plesiophrictus guangxiensis. It primarily inhibits outward voltage-gated Kv2.1 potassium channel currents, which are prominently expressed in pancreatic β-cells, thus increasing insulin secretion.[1][2]
Sources
Guangxitoxin is found in the venom of the tarantula Plesiophrictus guangxiensis, which lives mainly in Guangxi province of southern China.[2]
Chemistry
Subtypes
Guangxitoxin consists of multiple subtypes, including GxTX-1D, GxTX-1E and GxTX-2.[1] GxTX-2 shows sequence similarities with Hanatoxin (HaTX), Stromatoxin-1 (ScTx1), and Scodra griseipes toxin (SGTx) peptides.[1][3][4][5] GxTX-1 shows sequence similarities with Jingzhaotoxin-III (JZTX-III), Grammostola spatulata mechanotoxin-4 (GsMTx-4), and Voltage-sensor toxin-1 (VSTX1) peptides.[1][6][7][8] GxTX-1 consists of two variants, GxTX-1D and GxTX-1E, of which GxTX-1E is a more potent inhibitor of Kv2.1.[1]
Sequence
GxTX-1D and GxTX-1E consist of 36 amino acids, differing only a single amino acid at the NH2-terminal, aspartate or glutamate, respectively:[1]
Asp/Glu-Gly-Glu-Cys-Gly-Gly-Phe-Trp-Trp-Lys-Cys-Gly-Ser-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Cys-Cys-Pro-Lys-Tyr-Val-Cys-Ser-Pro-Lys-Trp-Gly-Leu-Cys-Asn-Phe-Pro-Met-Pro
GxTX-2 consists of 33 amino acids, which has only 9 identical amino acids in corresponding sequence compared to GxTX-1D and GxTX-1E:[1]
Glu-Cys-Arg-Lys-Met-Phe-Gly-Gly-Cys-Ser-Val-Asp-Ser-Asp-Cys-Cys-Ala-His-Leu-Gly-Cys-Lys-Pro-Thr-Leu-Lys-Tyr-Cys-Ala-Trp-Asp-Gly-Thr
Structure
The three-dimensional NMR structure of the toxin reveals an amphipathic part and an inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) motif.[9] The amphipathic part is composed of a large cluster characterized by solvent-exposed hydrophobic residues which is enclosed by acidic and basic residues.[9] The ICK motif contains three disulfide bonds stabilizing the toxin structure.[9] The conserved amphipathic structure assists in binding the toxin and can be explained since similar toxins allocate into lipid membranes effectively with the help of this structure and interact with Kv channels from within the membrane.[10][11][12][13] Differences in distribution of acidic and basic residues compared to SGTx-1 may contribute to the difference in affinity of GxTX-1E for the Kv2.1 channel.[9] Dissimilarities in orientation of loops and turns compared to JZTX-III may contribute to the discrepancy in selectivity of GxTX-1E to the Kv2.1 channel.[9]
Target
GxTX-1E inhibits voltage-gated Kv2.1 channels by modifying its voltage-dependent gating,.[1][14] mutations in the S3b-S4 paddle motif of the voltage-sensing domain of Kv2.1 reduce affinity for tarantula toxins.[13] Two other voltage-gated potassium channels inhibited by GxTX-1 are the Kv2.2 and Kv4.3 channels.[1] Kv2.2 is located predominantly in δ-cells of primate islets.[15] Kv4.3 is mainly of importance in the heart.[16]
The Kv2.1 channel is predominantly expressed in pancreatic β-cells[17] and in the central nervous system.[18][19] In pancreatic β-cells, Kv2.1 comprises 60% of the currents mediated by Kv channels.[20] Furthermore, the Kv2.1 channel shows similar biophysical properties to the delayed rectifier K+ current (IDR) of the β-cells.[21] This makes GxTX appropriate to study the physiological role of the aforementioned current as it inhibits 90% of the β-cell IDR.[1] The IDR is thought to play an important role in repolarization of action potentials.[22] Both the Kv2.2 and Kv4.3 channels are believed not to contribute significantly to the β-cell IDR.[1]
GxTX-1E has no effect on voltage-gated Na+ or Ca2+ channels.[1]
Mode of action
Inhibition of Kv2.1 by GxTX-1E causes a shift in voltage-dependency of activation toward more positive potentials of almost 100 mV.[2] Moreover, GxTX-1E also exhibits properties of decreasing the velocity of hKv2.1 channel opening and increasing the velocity of Kv2.1 channel closing approximately sixfold.[2] By inhibiting Kv2.1 potassium channels, GxTX-1E boosts action potentials of pancreatic β-cells causing mainly increased glucose-stimulated intracellular calcium oscillations which in turn intensifies glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.[1][2] How GxTX-1E is able to generate distinctive calcium oscillations in different cells remains unclear (broader oscillations, increased frequency or restoration of oscillations), however, the specificity of GxTX-1E points in the direction of IDR inhibition causing these effects.[2] Notably, GxTX-1E stimulated insulin secretion is specifically glucose dependent, considering that IDR is only active above -20mV membrane potentials which is only seen in raised glucose levels.[2]
Therapeutic use
Unlike KATP channel blockers, GxTX-1 primarily blocks IDR and demonstrates a potential target for future drugs in diabetes mellitus type 2 treatment, since a blockade of IDR should not provoke hypoglycaemia.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 "Blockers of the delayed-rectifier potassium current in pancreatic beta-cells enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion". Diabetes 55 (4): 1034–42. April 2006. doi:10.2337/diabetes.55.04.06.db05-0788. PMID 16567526.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "Gating modifier peptides as probes of pancreatic beta-cell physiology". Toxicon 49 (2): 231–8. February 2007. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.012. PMID 17101164.
- ↑ "An inhibitor of the Kv2.1 potassium channel isolated from the venom of a Chilean tarantula". Neuron 15 (4): 941–9. October 1995. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(95)90184-1. PMID 7576642.
- ↑ "Novel tarantula toxins for subtypes of voltage-dependent potassium channels in the Kv2 and Kv4 subfamilies". Molecular Pharmacology 62 (1): 48–57. July 2002. doi:10.1124/mol.62.1.48. PMID 12065754.
- ↑ "Solution structure and functional characterization of SGTx1, a modifier of Kv2.1 channel gating". Biochemistry 43 (4): 890–7. February 2004. doi:10.1021/bi0353373. PMID 14744131.
- ↑ "Jingzhaotoxin-III, a novel spider toxin inhibiting activation of voltage-gated sodium channel in rat cardiac myocytes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (25): 26220–6. June 2004. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401387200. PMID 15084603.
- ↑ "Identification of a peptide toxin from Grammostola spatulata spider venom that blocks cation-selective stretch-activated channels". The Journal of General Physiology 115 (5): 583–98. May 2000. doi:10.1085/jgp.115.5.583. PMID 10779316.
- ↑ "Functional analysis of an archaebacterial voltage-dependent K+ channel". Nature 422 (6928): 180–5. March 2003. doi:10.1038/nature01473. PMID 12629550. Bibcode: 2003Natur.422..180R.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 "Solution structure of GxTX-1E, a high-affinity tarantula toxin interacting with voltage sensors in Kv2.1 potassium channels". Biochemistry 49 (25): 5134–42. June 2010. doi:10.1021/bi100246u. PMID 20509680.
- ↑ "A membrane-access mechanism of ion channel inhibition by voltage sensor toxins from spider venom". Nature 430 (6996): 232–5. July 2004. doi:10.1038/nature02632. PMID 15241419. Bibcode: 2004Natur.430..232L.
- ↑ "Voltage-sensor activation with a tarantula toxin as cargo". Nature 436 (7052): 857–60. August 2005. doi:10.1038/nature03873. PMID 16094370. Bibcode: 2005Natur.436..857R.
- ↑ "Tarantula toxins interact with voltage sensors within lipid membranes". The Journal of General Physiology 130 (5): 497–511. November 2007. doi:10.1085/jgp.200709869. PMID 17938232.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Interactions between lipids and voltage sensor paddles detected with tarantula toxins". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 16 (10): 1080–5. October 2009. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1679. PMID 19783984.
- ↑ "A KV2.1 gating modifier binding assay suitable for high throughput screening". Channels 3 (6): 437–47. November 2009. doi:10.4161/chan.3.6.10201. PMID 21150283.
- ↑ "Expression of voltage-gated potassium channels in human and rhesus pancreatic islets". Diabetes 53 (3): 597–607. March 2004. doi:10.2337/diabetes.53.3.597. PMID 14988243.
- ↑ "The molecular physiology of the cardiac transient outward potassium current (I(to)) in normal and diseased myocardium". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 33 (5): 851–72. May 2001. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2001.1376. PMID 11343410.
- ↑ "Voltage-dependent K(+) channels in pancreatic beta cells: role, regulation and potential as therapeutic targets". Diabetologia 46 (8): 1046–62. August 2003. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1159-8. PMID 12830383.
- ↑ "A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning". Nature 340 (6235): 642–5. August 1989. doi:10.1038/340642a0. PMID 2770868. Bibcode: 1989Natur.340..642F.
- ↑ "Kv2.1: a voltage-gated k+ channel critical to dynamic control of neuronal excitability". Neurotoxicology 26 (5): 743–52. October 2005. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2005.02.003. PMID 15950285.
- ↑ "Members of the Kv1 and Kv2 voltage-dependent K(+) channel families regulate insulin secretion". Molecular Endocrinology 15 (8): 1423–35. August 2001. doi:10.1210/mend.15.8.0685. PMID 11463864.
- ↑ "Expression and function of pancreatic beta-cell delayed rectifier K+ channels. Role in stimulus-secretion coupling". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 271 (50): 32241–6. December 1996. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.50.32241. PMID 8943282.
- ↑ "Delayed rectifying and calcium-activated K+ channels and their significance for action potential repolarization in mouse pancreatic beta-cells". The Journal of General Physiology 95 (6): 1041–59. June 1990. doi:10.1085/jgp.95.6.1041. PMID 2197368.
 |

