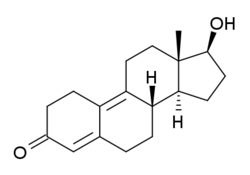
Chemistry:Dienolone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | RU-3118; Nordienolone |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H24O2 |
| Molar mass | 272.388 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dienolone (developmental code name RU-3118; online product names Trenazone,[1] Dienazone), or nordienolone, also known as 19-nor-δ9(10)-testosterone, δ9(10)-nandrolone, or estra-4,9(10)-dien-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) of the 19-nortestosterone group that was never marketed.[2] It has been found to possess slightly lower affinity for the androgen receptor (AR) and progesterone receptor (PR) relative to nandrolone in rat and rabbit tissue bioassays, whereas trenbolone was found to possess the same affinity for the AR as dienolone but several-fold increased affinity for the PR.[3] Dienedione (the 17-keto analogue of dienolone, also known as 19-nor-4,9-androstadienedione) is thought to be a prohormone of dienolone,[4] while methyldienolone and ethyldienolone are orally active 17α-alkylated AAS derivatives of dienolone.[5][6] In contrast, dienogest, the 17α-cyanomethyl derivative of dienolone, is a potent progestogen and antiandrogen.[7]
See also
- Trenbolone (trienolone)
References
- ↑ "A simple method for the small scale synthesis and solid-phase extraction purification of steroid sulfates". Steroids 92: 74–80. December 2014. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2014.09.006. PMID 25286236.
- ↑ https://isomerdesign.com/Cdsa/HC/StatusDecisions/A-2013-00235%20-%20PDFs/C-Dienolone-2011-08-12.pdf [bare URL PDF]
- ↑ "Towards the mapping of the progesterone and androgen receptors". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 27 (1–3): 255–269. 1987. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(87)90317-7. PMID 3695484.
- ↑ "2009 - Final Rule: Classification of Three Steroids as Schedule III Anabolic Steroids Under the Controlled Substances Act". https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/rules/2009/fr1204.htm.
- ↑ "Synthetic Anabolic Agents: Steroids and Nonsteroidal Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators". Doping in Sports. Springer Science & Business Media. 18 December 2009. pp. 103, 157, 162–164. ISBN 978-3-540-79088-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=R-hIC-caIn8C&pg=PA103.
- ↑ "Dissociation of the androgenic and other hormonal activities from the protein anabolic effects of steroids". Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 380–381. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66353-6_11. ISBN 978-3-642-66353-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=3-LrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA380.
- ↑ "Dienogest". Drugs 56 (5): 825–33; discussion 834–5. November 1998. doi:10.2165/00003495-199856050-00007. PMID 9829156.
 |
