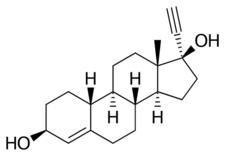
Chemistry:Etynodiol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ethynodiol; 3β-Hydroxynorethisterone; 17α-Ethynylestr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol |
| Drug class | Progestin; Progestogen |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Etynodiol, or ethynodiol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was never marketed.[1][2][3] A diacylated derivative, etynodiol diacetate, is used as a hormonal contraceptive.[1][2] Etynodiol is sometimes used as a synonym for etynodiol diacetate.
It was patented in 1955.[4]
Pharmacology
Etynodiol is a prodrug of norethisterone, and is converted immediately and completely into norethisterone.[5][6][7] Etynodiol is an intermediate in the conversion of the prodrug lynestrenol into norethisterone.[8]
| Compound | Typea | PR | AR | ER | GR | MR | SHBG | CBG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norethisterone | – | 67–75 | 15 | 0 | 0–1 | 0–3 | 16 | 0 |
| 5α-Dihydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 25 | 27 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| 3α,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 1 | 0 | 0–1 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| 3α,5β-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | ? | 0 | 0 | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 3β,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone | Metabolite | 1 | 0 | 0–8 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| Ethinylestradiol | Metabolite | 15–25 | 1–3 | 112 | 1–3 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 |
| Norethisterone acetate | Prodrug | 20 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Norethisterone enanthate | Prodrug | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Noretynodrel | Prodrug | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Etynodiol | Prodrug | 1 | 0 | 11–18 | 0 | ? | ? | ? |
| Etynodiol diacetate | Prodrug | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Lynestrenol | Prodrug | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ? | ? |
| Notes: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were promegestone for the PR, metribolone for the AR, estradiol for the ER, dexamethasone for the GR, aldosterone]] for the MR, dihydrotestosterone for SHBG, and cortisol for CBG. Footnotes: a = Active]] or inactive metabolite, prodrug, or neither of norethisterone. Sources: See template. | ||||||||
Chemistry
Etynodiol is a 19-nortestosterone derivative. Structurally, it is almost identical to norethisterone and lynestrenol, differing only in its C3 substituent. Whereas norethisterone has a ketone at C3 and lynestrenol has no substituent at C3, etynodiol has a hydroxyl group at the position.
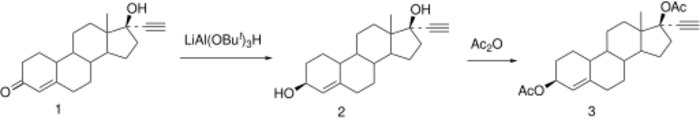
Synthesis
Society and culture
Generic names
Etynodiol is the generic name of the drug and its INN, while ethynodiol is its BAN.[1][2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. 1997. p. 1454. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=A0THacd46ZsC&pg=PA1454. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 422. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA422. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ↑ "Classification and pharmacology of progestins". Maturitas 46 (Suppl 1): S7–S16. December 2003. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2003.09.014. PMID 14670641.
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 478. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA478.
- ↑ Contraception. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 21–. ISBN 978-1-4612-2730-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=cpDhBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA21.
- ↑ Bhattacharya (1 January 2003). Pharmacology, 2/e. Elsevier India. pp. 378–. ISBN 978-81-8147-009-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=X3cCZQCrrjcC&pg=PA378.
- ↑ IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer (2007). Combined Estrogen-progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-progestogen Menopausal Therapy. World Health Organization. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-92-832-1291-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=aGDU5xibtNgC&pg=PA146.
- ↑ "Prodrugs: advantage or disadvantage?". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 163 (6 Pt 2): 2198–203. December 1990. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(90)90561-K. PMID 2256526.
- ↑ "The synthesis of 3beta-hydroxyestr-4-en-17-one and 3beta-hydroxyandrost-4-en-17-one". Steroids 10 (4): 411–24. October 1967. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(67)90119-5. PMID 6064262.
- ↑ "Synthesis of 3β-hydroxy analogues of steroidal hormones, a biologically active class of compounds". Tetrahedron 5: 15–26. 1959. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(59)80066-1.
 |
