Chemistry:Homotaurine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
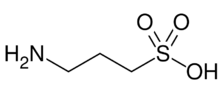
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Aminopropane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
Tramiprosate; Alzhemed; 3-APS
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 139.17 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 293 °C (559 °F; 566 K) (decomposition) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Homotaurine (also known as tramiprosate (INN), 3-amino-1-propanesulfonic acid, or 3-APS) is a natural sulfonic acid found in seaweed.[3] It is analogous to taurine, but with an extra carbon in its chain. It has GABAergic activity, apparently by mimicking GABA, which it resembles.[4]
Homotaurine was investigated in a Phase III clinical trial as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD) that did not show efficacy. However, post-hoc analyses have shown positive and significant effects of homotaurine on secondary endpoints and subgroups of patients, including a reduction in hippocampal volume loss and lower decline in memory function in the overall cohort, as well as a reduction in global cognitive decline in APOE4 allele carriers, suggesting a disease-modifying effect.[5] A study in cognitive impairment done in 2018 did show positive benefits.[6]
Homotaurine is currently in a phase 3 study with expected FDA approval as the first disease modifying drug for AD.[7][8]
Medical use
Acamprosate (N-acetyl homotaurine) was approved by the FDA in 2004 to treat alcohol dependence.[4]
Biochemical properties
In preclinical studies it had been found to bind to soluble amyloid beta and inhibit the formation of neurotoxic aggregates.[5][9] Homotaurine has also shown anticonvulsant activities, reduction in skeletal muscle tonus, and hypothermic activity.[10]
Homotaurine has been reported as a GABA antagonist,[4] as well as a GABA agonist.[10][11] In vitro studies have found that homotaurine is a GABAA partial agonist[12] as well as a GABAB receptor partial agonist with low efficacy, becoming an antagonist and displacing the full agonists GABA and baclofen at this receptor.[13] In a study in rats, homotaurine reversed the catatonia induced by baclofen (the prototypical GABAB agonist),[14] and was able to produce analgesia via the GABAB receptor, an effect that was abolished when CGP-35348, a GABAB receptor antagonist was applied.[15][16]
In a human study homotaurine selectively and fully inhibits the formation of Aβ42 oligomers at the clinical dose, without evidence of vasogenic edema.[7]
One study in rats showed that homotaurine suppressed ethanol-stimulated dopamine release, as well as ethanol intake and preference in rats in a way similar to the N-acetyl derivative of homotaurine, acamprosate.[17]
References
- ↑ "Homotaurine". Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/A76109.
- ↑ "Tramiprosate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/1646#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Martorana, Alessandro; Di Lorenzo, Francesco; Manenti, Guglielmo; Semprini, Roberta; Koch, Giacomo (23 September 2014). "Homotaurine Induces Measurable Changes of Short Latency Afferent Inhibition in a Group of Mild Cognitive Impairment Individuals". Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 6: 254. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2014.00254. PMID 25295005.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lednicer, Daniel (2008). The Organic Chemistry of Drug Synthesis (7th ed.). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-470-18066-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=N6OAhuiHqiIC&pg=PA15.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Caltagirone, C; Ferrannini, L; Marchionni, N; Nappi, G; Scapagnini, G; Trabucchi, M (December 2012). "The potential protective effect of tramiprosate (homotaurine) against Alzheimer's disease: a review". Aging Clinical and Experimental Research 24 (6): 580–587. doi:10.3275/8585. PMID 22961121.
- ↑ Martorana, A.; Motta, C; Koch, G.; Massaia, M.; Mondino, S.; Raniero, I.; Vacca, A.; Di Lorenzo, F. et al. (15 March 2018). "Effect of homotaurine in patients with cognitive impairment: results from an Italian observational retrospective study". Journal of Gerontology and Geriatrics 66: 15–20. http://www.jgerontology-geriatrics.com/article/view/97.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Tolar, Martin; Abushakra, Susan; Hey, John A.; Porsteinsson, Anton; Sabbagh, Marwan (December 2020). "Aducanumab, gantenerumab, BAN2401, and ALZ-801—the first wave of amyloid-targeting drugs for Alzheimer's disease with potential for near term approval". Alzheimer's Research & Therapy 12 (1): 95. doi:10.1186/s13195-020-00663-w. PMID 32787971.
- ↑ Abushakra, S.; Porsteinsson, A.; Scheltens, P.; Sadowsky, C.; Vellas, B.; Cummings, J.; Gauthier, S.; Hey, J. A. et al. (1 September 2017). "Clinical effects of tramiprosate in apoe4/4 homozygous patients with mild alzheimer's disease suggest disease modification potential". Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease 4 (3): 149–156. doi:10.14283/jpad.2017.26. PMID 29182706.
- ↑ Aisen, Paul; Gauthier, Serge; Vellas, Bruno; Briand, Richard; Saumier, Daniel; Laurin, Julie; Garceau, Denis (1 September 2007). "Alzhemed: A Potential Treatment for Alzheimers Disease". Current Alzheimer Research 4 (4): 473–478. doi:10.2174/156720507781788882. PMID 17908052.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Lajtha, Abel (2013). Metabolism in the Nervous System. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 520. ISBN 978-1-4684-4367-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=du_TBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA520.
- ↑ Tashjian, Armen H.; Armstrong, Ehrin J. (2011). Principles of Pharmacology: The Pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 308. ISBN 978-1-4511-1805-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=kjCCMZHInigC&pg=PA308.
- ↑ Reyes-Haro, Daniel; Cabrera-Ruíz, Elizabeth; Estrada-Mondragón, Argel; Miledi, Ricardo; Martínez-Torres, Ataúlfo (November 2014). "Modulation of GABA-A receptors of astrocytes and STC-1 cells by taurine structural analogs". Amino Acids 46 (11): 2587–2593. doi:10.1007/s00726-014-1813-0. PMID 25119985.
- ↑ Giotti, A.; Luzzi, S.; Spagnesi, S.; Zilletti, L. (August 1983). "Homotaurine: a GABAB antagonist in guinea-pig ileum.". British Journal of Pharmacology 79 (4): 855–862. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10529.x. PMID 6652358.
- ↑ Mehta, A; Ticku, M (September 1987). "Baclofen induces catatonia in rats". Neuropharmacology 26 (9): 1419–1423. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(87)90108-0. PMID 2823166.
- ↑ Serrano, M.Isabel; Serrano, Jose S.; Fernández, Ana; Asadi, Ihklas; Serrano-Martino, M.Carmen (March 1998). "GABAB Receptors and Opioid Mechanisms Involved in Homotaurine-Induced Analgesia". General Pharmacology: The Vascular System 30 (3): 411–415. doi:10.1016/s0306-3623(97)00279-6. PMID 9510095.
- ↑ Serrano, Maria Isabel; Serrano, Jose S.; Asadi, Ikhlas; Fernandez, Ana; Serrano-Martino, Maria Carmen (16 June 2001). "Role of K+-channels in homotaurine-induced analgesia". Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology 15 (3): 167–173. doi:10.1046/j.1472-8206.2001.00026.x. PMID 11468027.
- ↑ Olive, M.Foster; Nannini, Michelle A; Ou, Christine J; Koenig, Heather N; Hodge, Clyde W (February 2002). "Effects of acute acamprosate and homotaurine on ethanol intake and ethanol-stimulated mesolimbic dopamine release". European Journal of Pharmacology 437 (1–2): 55–61. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(02)01272-4. PMID 11864639.
{{Navbox | name = GABA receptor modulators | title = GABA receptor modulators | state = collapsed | bodyclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Ionotropic | list1 = {{Navbox|subgroup | groupstyle = text-align:center | groupwidth = 5em
| group1 = GABAA | list1 =
- Agonists: (+)-Catechin
- Bamaluzole
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- BL-1020
- DAVA
- Dihydromuscimol
- GABA
- Gabamide
- GABOB
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- Homotaurine (tramiprosate, 3-APS)
- Ibotenic acid
- iso-THAZ
- iso-THIP
- Isoguvacine
- Isomuscimol
- Isonipecotic acid
- Kojic amine
- Lignans (e.g., honokiol)
- Methylglyoxal
- Monastrol
- Muscimol
- Nefiracetam
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone)
- Org 20599
- PF-6372865
- Phenibut
- Picamilon
- P4S
- Progabide
- Propofol
- Quisqualamine
- SL-75102
- TACA
- TAMP
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- ZAPA
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)<!--PMID: 9776662-->
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, [[Chemistry:Cholecholesterol]], THDOC)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., [[abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, [[Chemistry:Diethyl diethyl ether, Parparaldehyde]], sevoflurane)
- Antagonists: Bicuculline
- Coriamyrtin
- Dihydrosecurinine
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Hydrastine
- Hyenachin (mellitoxin)
- PHP-501
- Pitrazepin
- Securinine
- Sinomenine
- SR-42641
- SR-95103
- Thiocolchicoside
- Tutin
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., [[apalutamide, [[Chemistry:Bicalutbicalutamide, Enzalutenzalutamide, Chemistry:Flutamide|flut]]amide]], nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
| group2 = GABAA-ρ | list2 =
- Agonists: BL-1020
- CACA
- CAMP
- Homohypotaurine
- GABA
- GABOB
- Ibotenic acid
- Isoguvacine
- Muscimol
- N4-Chloroacetylcytosine arabinoside
- Picamilon
- Progabide
- TACA
- TAMP
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- Positive modulators: Allopregnanolone
- Alphaxolone
- ATHDOC
- Lanthanides
- Antagonists: (S)-2-MeGABA
- (S)-4-ACPBPA
- (S)-4-ACPCA
- 2-MeTACA
- 3-APMPA
- 4-ACPAM
- 4-GBA
- cis-3-ACPBPA
- CGP-36742 (SGS-742)
- DAVA
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- I4AA
- Isonipecotic acid
- Loreclezole
- P4MPA
- P4S
- SKF-97541
- SR-95318
- SR-95813
- TPMPA
- trans-3-ACPBPA
- ZAPA
- Negative modulators: 5α-Dihydroprogesterone
- Bilobalide
- Loreclezole
- Picrotoxin (picrotin, picrotoxinin)
- Pregnanolone
- ROD-188
- THDOC
- Zinc
}}
| group2 = Metabotropic
| list2 =
| below =
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- GABAA receptor positive modulators
- GABA metabolism/transport modulators
}}
 |
