Chemistry:Baicalin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
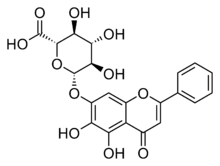
| IUPAC name
5,6-Dihydroxy-4-oxoflav-2-en-7-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-[(5,6-Dihydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Baicalein 7-O-glucuronide; 5,6-Dihydroxy-4-oxygen-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-7-β-D-glucopyranose acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 70480 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H18O11 | |
| Molar mass | 446.364 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 202 to 205 °C (396 to 401 °F; 475 to 478 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
As baicalin is a flavone glycoside, it is a flavonoid. It is the glucuronide of baicalein.
Natural occurrences
Baicalin is found in several species in the genus Scutellaria, including Scutellaria baicalensis,[1] and Scutellaria lateriflora. There are 10 mg/g baicalin in Scutellaria galericulata leaves.[2] It is also present in the bark isolate of the Oroxylum indicum tree.
Medical uses
Baicalin is one of the chemical ingredients of at least two herbal supplements: Shuanghuanglian[1] and Sho-Saiko-To, which is a Chinese classic herbal formula, and listed in Japan as Kampo medicine.[citation needed]
Baicalin, along with its aglycone baicalein, is a positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site and/or a non-benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.[3][4][5] In mice, baicalin produces anxiolytic effects without sedative or myorelaxant effects.[6][7] It is thought that baicalin, along with other flavonoids, may underlie the anxiolytic effects of S. baicalensis and S. lateriflora.[8][9]
Baicalin is a known prolyl endopeptidase inhibitor.[10] It induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Su, Hai-xia; Yao, Sheng; Zhao, Wen-Feng; Li, Min-jun; Liu, Jia; Shang, Wei-Juan; Xie, Hang; Ke, Chang-Qiang et al. (2020). "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities in vitro of Shuanghuanglian preparations and bioactive ingredients". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 41 (9): 1167–1177. doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0483-6. PMID 32737471.
- ↑ P.H. and Horhammer, L., Hager's Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, Vols. 2-6, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1969-1979
- ↑ "Two flavones from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and their binding affinities to the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor complex". Pharmazie 57 (12): 857–8. 2002. PMID 12561253.
- ↑ "Interaction of flavones from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis with the benzodiazepine site". Planta Med. 66 (1): 91–3. 2000. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1243121. PMID 10705749. http://www.thieme-connect.com/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0029-1243121.
- ↑ Edwin Lowell Cooper; Nobuo Yamaguchi (1 January 2004). Complementary and Alternative Approaches to Biomedicine. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 188–. ISBN 978-0-306-48288-5. https://archive.org/details/springer_10.1007-978-1-4757-4820-8.
- ↑ "Anxiolytic-Like Effect of baicalin and its additivity with other anxiolytics". Planta Med. 72 (2): 189–92. 2006. doi:10.1055/s-2005-873193. PMID 16491459. http://www.thieme-connect.com/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-2005-873193.
- ↑ "Anxiolytic-like effects of baicalein and baicalin in the Vogel conflict test in mice". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 464 (2–3): 141–6. 2003. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01422-5. PMID 12620506.
- ↑ "Phytochemical and biological analysis of skullcap (Scutellaria lateriflora L.): a medicinal plant with anxiolytic properties". Phytomedicine 10 (8): 640–9. 2003. doi:10.1078/0944-7113-00374. PMID 14692724.
- ↑ Stefanie Schwartz (9 January 2008). Psychoactive Herbs in Veterinary Behavior Medicine. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 139–. ISBN 978-0-470-34434-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZP6QVep-x24C&pg=PA139.
- ↑ Tarragó, T; Kichik, N; Claasen, B; Prades, R; Teixidó, M; Giralt, E (2008). "Baicalin, a prodrug able to reach the CNS, is a prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitor". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16 (15): 7516–24. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.067. PMID 18650094.
- ↑ "Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells". Biochim Biophys Acta 1813 (8): 1465–1474. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.05.003. PMID 21596068.
 |
