Chemistry:Propanidid
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epontol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
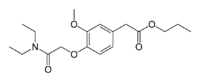
| Formula | C18H27NO5 |
| Molar mass | 337.416 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Propanidid is an ultra short-acting phenylacetate general anesthetic. It was originally introduced by Bayer in 1963[1] but anaphylactic reactions caused it to be withdrawn shortly afterwards.
Even though Cremophor EL has been shown to cause anaphylactic reactions in humans in several cases (both when given intravenously and orally), it is still debated whether propanidid itself may have contributed to the reactions.
It has been argued that the toxic effects or reactions to propanidid (and Althesin) were due to the drugs themselves.[2] Several cases of negative reactions have been recorded for different drugs using Cremophor EL as solubilizer, suggesting that the negative reactions were mainly caused by Cremophor and not by the drug substances themselves.
References
- ↑ Hiltmann R, Wollweber H, Hoffmeister F, Wirth W, "3-Methoxy-4-Carbamidomethoxy-Phenylacetic Acid Esters", US patent 3086978, issued 1963-04-23, assigned to Bayer
- ↑ "Proceedings: A new steroid anaesthetic-althesin". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 66 (10): 1027–1030. October 1973. doi:10.1177/003591577306601023. PMID 4148526.
External links
- "[Anesthesia with propanidid in a liposomal preparation. An experimental study in swine]". Der Anaesthesist 44 (8): 573–580. August 1995. doi:10.1007/s001010050191. PMID 7573906.
- "[Anesthesiologic efficacy of propanidid as a liposome dispersion. An experimental study with rats]". Der Anaesthesist 41 (8): 448–456. August 1992. PMID 1524155.
- "[Propanidid and etomidate identification from the blood by thin-layer chromatography]". Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica 49 (5–6): 15–17. 1992. PMID 16092193.
- "Anaphylactoid reactions in children receiving high-dose intravenous cyclosporine for reversal of tumor resistance: the causative role of improper dissolution of Cremophor EL". Journal of Clinical Oncology 13 (10): 2508–2516. October 1995. doi:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.10.2508. PMID 7595701.
- "IgE-mediated anaphylaxis after first intravenous infusion of cyclosporine". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology 87 (3): 243–245. September 2001. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62234-X. PMID 11570623.
 |
