Chemistry:LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide, commonly known as LSD (from German Lysergsäure-diethylamid) and by the slang names acid and lucy, is a semisynthetic hallucinogenic drug derived from ergot, known for its powerful psychological effects and serotonergic activity.[1] It was historically used in psychiatry and 1960s counterculture; it is currently legally restricted but experiencing renewed scientific interest and increasing use.
When taken orally, LSD has an onset of action within 0.4 to 1.0 hours (range: 0.1–1.8 hours) and a duration of effect lasting 7 to 12 hours (range: 4–22 hours).[2][3] It is commonly administered via tabs of blotter paper.[4] LSD is extremely potent, with noticeable effects at doses as low as 20 micrograms and is sometimes taken in much smaller amounts for microdosing. Despite widespread use, no fatal human overdoses have been documented. LSD is mainly used recreationally or for spiritual purposes.[5][6] LSD can cause mystical experiences.[7][8] LSD exerts its effects primarily through high-affinity binding to several serotonin receptors, especially 5-HT2A, and to a lesser extent dopaminergic and adrenergic receptors. LSD reduces oscillatory power in the brain's default mode network and flattens brain hierarchy.[9][10] At higher doses, it can induce visual and auditory hallucinations, ego dissolution, and anxiety.[11][12] LSD use can cause adverse psychological effects such as paranoia and delusions and may lead to persistent visual disturbances known as hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD).
Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann first synthesized LSD in 1938 and discovered its powerful psychedelic effects in 1943 after accidental ingestion. It became widely studied in the 1950s and 1960s.[5][13] It was initially explored for psychiatric use due to its structural similarity to serotonin and safety profile.[14] It was used experimentally in psychiatry for treating alcoholism and schizophrenia.[15] By the mid-1960s, LSD became central to the youth counterculture in places like San Francisco and London, influencing art, music, and social movements through events like Acid Tests and figures such as Owsley Stanley and Michael Hollingshead. Its psychedelic effects inspired distinct visual art styles, music innovations, and caused a lasting cultural impact. However, its association with the counterculture movement of the 1960s led to its classification as a Schedule I drug in the U.S. in 1970.[16] It was also listed as a Schedule I controlled substance by the United Nations in 1971 and remains without approved medical uses.[5]
Despite its legal restrictions, LSD remains influential in scientific and cultural contexts. Research on LSD declined due to cultural controversies by the 1960s, but has resurged since 2009. In 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration designated a form of LSD (MM120) a breakthrough therapy for generalized anxiety disorder.[17] As of 2017, about 10% of people in the U.S. had used LSD at some point, with 0.7% having used it in the past year.[18] Usage rates have risen, with a 56.4% increase in adult use in the U.S. from 2015 to 2018.[19]
Uses
Recreational
LSD is commonly used as a recreational drug for its psychedelic effects.[20]
Spiritual
LSD can catalyze intense spiritual experiences and is thus considered an entheogen. Some users have reported out of body experiences. In 1966, Timothy Leary established the League for Spiritual Discovery with LSD as its sacrament.[21][22] Stanislav Grof has written that religious and mystical experiences observed during LSD sessions appear similar to descriptions in sacred scriptures of great religions of the world and the texts of ancient civilizations.[23]
Medical
A meta analysis concluded that a single dose was shown to be effective at reducing alcohol consumption in people suffering from alcoholism.[24] LSD has also been studied in depression, anxiety,[25][26] and drug dependence, with positive preliminary results.[27][28]
Despite these results, LSD currently has no legally approved uses in medicine.[29][30]
Dosing

LSD is an extraordinarily potent substance,[2][31][14][32] and is one of the most potent psychoactive drugs known.[14][32] This means that it produces its pharmacological effects at very small doses, with its dose range measured in micrograms (μg); that is, millionths of a gram.[2][14] Noticeable effects can occur with doses of LSD as low as 20 μg, which is around 1/200th the mass of a grain of sand.[2][31][14][5] LSD is approximately 200 times as potent as psilocybin and 5,000 times as potent as mescaline, meaning that it produces effects of similar magnitude at 1/200 and 1/5,000 times the respective doses.[2][31][33]
The usual dose range of LSD for psychedelic effects is 20 to 200 μg.[2][31] The typical intermediate and "good effect" dose for a psychedelic experience is 100 μg (range 75–150 μg, while 20 to 50 μg is a low or "minidose" and 200 μg is a high or ego-dissolution dose.[2][31][3] A dose range as wide as 10 to 450 μg has been reported.[34][35] LSD may also be used in microdosing.[36] In this context, it may be used at subthreshold or microdoses of less than 10 μg.[2][31]
The doses of LSD present in illicit LSD samples have decreased over time. In the mid-1960s, Owsley Stanley, the most important black market LSD manufacturer in the United States, distributed LSD at a standard concentration of 270 μg,[37] while street samples of the 1970s contained 30 to 300 μg. By the 1980s, the amount had reduced to between 100 and 125 μg, dropping more in the 1990s to the 20 to 80 μg range,[38] and even further in the 2000s.[37][39]
Effects
LSD produces a variety of physical, psychological, and sensory effects.[2]
Psychological
The primary immediate psychological effects of LSD are visual pseudo-hallucinations and altered thought, often referred to as "trips". These sensory alterations are considered pseudohallucinations because the subject does not perceive the patterns seen as being located in three-dimensional space outside the body.[40] LSD is not considered addictive. These effects typically begin within 20–30 minutes of oral ingestion, peak three to four hours after ingestion, and can last up to 20 hours, particularly with higher doses. An "afterglow" effect, characterized by an improved mood or perceived mental state, may persist for days or weeks following ingestion.[41] Positive experiences, or "good trips", are described as intensely pleasurable and can include feelings of joy, euphoria, an increased appreciation for life, decreased anxiety, a sense of spiritual enlightenment, and a feeling of interconnectedness with the universe.[42][43]
Negative experiences, commonly known as "bad trips", can induce feelings of fear, agitation, anxiety, panic, and paranoia.[3][44] While the occurrence of a bad trip is unpredictable, factors such as mood, surroundings, sleep, hydration, and social setting, collectively referred to as "set and setting", can influence the risk and are considered important in minimizing the likelihood of a negative experience.[45][46]
Sensory
LSD induces an animated sensory experience affecting senses, emotions, memories, time, and awareness. The effects range from subtle perceptual changes to profound cognitive shifts. Alterations in auditory and visual perception are common.[47][48]
Users may experience enhanced visual phenomena, such as vibrant colors, objects appearing to morph, ripple or move, and geometric patterns on various surfaces. Changes in the perception of food's texture and taste are also noted, sometimes leading to aversion towards certain foods.[47][49]
There are reports of inanimate objects appearing animated, with static objects seeming to move in additional spatial dimensions.[50] The auditory effects of LSD may include echo-like distortions of sounds, and an intensified experience of music. Basic visual effects often resemble phosphenes and can be influenced by concentration, thoughts, emotions, or music.[51] Higher doses can lead to more intense sensory perception alterations, including synesthesia, perception of additional dimensions, and temporary dissociation.
Physical
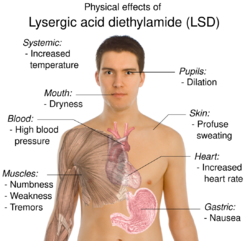
LSD can induce physical effects such as pupil dilation, decreased appetite, increased sweating, and wakefulness. The physical reactions to LSD vary greatly and some may be a result of its psychological effects. Commonly observed symptoms include increased body temperature, blood sugar, and heart rate, as well as goose bumps, jaw clenching, dry mouth, and hyperreflexia. In cases of adverse reactions, users may experience numbness, weakness, nausea, and tremors.[5]
Onset and duration
The psychoactive effects of LSD last on average between 7 and 11 hours, with a possible range of 4 to 22 hours.[2] Higher doses tend to lead to a longer duration of action.[2] The onset of action when administered orally is 0.4 to 1.0 hours on average, with a possible range of 0.1 to 1.8 hours.[2] The time to peak effects given orally is 2.2 to 2.8 hours on average, with a range of 1.3 to 6.5 hours.[2]
Adverse effects

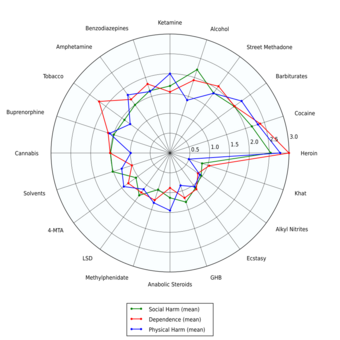
LSD, a classical psychedelic, is deemed physiologically safe at standard doses (50–200 μg) and its primary risks lie in psychological effects rather than physiological harm.[56][57] A 2010 study by David Nutt ranked LSD as significantly less harmful than alcohol, placing it near the bottom of a list assessing the harm of 20 drugs.[58]
Psychological effects
Mental disorders
LSD can induce panic attacks or extreme anxiety, colloquially termed a "bad trip". Despite lower rates of depression and substance abuse found in psychedelic drug users compared to controls, LSD presents heightened risks for individuals with severe mental illnesses like schizophrenia.[59][60] These hallucinogens can catalyze psychiatric disorders in predisposed individuals, although they do not tend to induce illness in emotionally healthy people.[56]
Suggestibility
While research from the 1960s indicated increased suggestibility under the influence of LSD among both mentally ill and healthy individuals, recent documents suggest that the CIA and Department of Defense have discontinued research into LSD as a means of mind control.[61][62][63][non-primary source needed]
Flashbacks
Flashbacks are psychological episodes where individuals re-experience some of LSD's subjective effects after the drug has worn off, persisting for days or months post-hallucinogen use.[64][65] These experiences are associated with hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD), where flashbacks occur intermittently or chronically, causing distress or functional impairment.[66]
The etiology of flashbacks is varied. Some cases are attributed to somatic symptom disorder, where individuals fixate on normal somatic experiences previously unnoticed prior to drug consumption.[67] Other instances are linked to associative reactions to contextual cues, similar to responses observed in individuals with past trauma or emotional experiences.[68] The risk factors for flashbacks remain unclear, but pre-existing psychopathologies may be significant contributors.[69]
Estimating the prevalence of HPPD is challenging. It is considered rare, with occurrences ranging from 1 in 20 users experiencing the transient and less severe type 1 HPPD, to 1 in 50,000 for the more concerning type 2 HPPD.[66] Contrary to internet rumors, LSD is not stored long-term in the spinal cord or other parts of the body. Pharmacological evidence indicates LSD has a half-life of 175 minutes and is metabolized into water-soluble compounds like 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD, eliminated through urine without evidence of long-term storage.[3] Clinical evidence also suggests that chronic use of SSRIs can potentiate LSD-induced flashbacks, even months after stopping LSD use.[70]: 145
Tolerance
LSD shows significant tachyphylaxis, with tolerance developing 24 hours after administration. The progression of tolerance at intervals shorter than 24 hours remains largely unknown.[71] Tolerance typically resets to baseline after 3–4 days of abstinence.[72][73] Significant cross-tolerance occurs between LSD, mescaline and psilocybin.[74][75] A slight cross-tolerance to DMT is observed in humans highly tolerant to LSD.[76] Tolerance to LSD also builds up with consistent use,[77] and is believed to result from serotonin 5-HT2A receptor downregulation.[72] Researchers believe that tolerance returns to baseline after two weeks of not using psychedelics.[78]
Addiction and dependence liability
LSD is widely considered to be non-addictive, despite its potential for abuse.[79][56][80][81] Attempts to train laboratory animals to self-administer LSD have been largely unsuccessful.[56] Although tolerance to LSD builds up rapidly, a withdrawal syndrome does not appear, suggesting that a potential syndrome does not necessarily relate to the possibility of acquiring rapid tolerance to a substance.[82] A report examining substance use disorder for DSM-IV noted that almost no hallucinogens produced dependence, unlike psychoactive drugs of other classes such as stimulants and depressants.[83][84]
Cancer and pregnancy
The mutagenic potential of LSD is unclear. Overall, the evidence seems to point to limited or no effect at commonly used doses.[85] Studies showed no evidence of teratogenic or mutagenic effects.[3]
Long-term effects
A potential risk of frequent repeated long-term use of LSD and other serotonergic psychedelics is cardiac fibrosis and valvulopathy due to serotonin 5-HT2B receptor agonism.[86][87][88][89][90] This may also be the case with microdosing.[86][87][88] However, the risks are theoretical, and more research is needed to see if these complications can actually occur with psychedelics.[86][89] A preliminary animal study found that chronic microdosing of LSD did not result in heart structure changes or valvulopathy in rodents.[91] Research appears to be mixed on whether LSD is a potent serotonin 5-HT2B receptor agonist or not, with some studies finding it to be essentially inactive.[92]
Interactions
Some psychedelics, including LSD, are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2D6. Concurrent use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), some of which are potent inhibitors of CYP2D6, with LSD may heighten the risk of serotonin syndrome.[70]: 145 Chronic usage of SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) is believed to diminish the subjective effects of psychedelics, likely due to 5-HT2A receptor downregulation or desensitization induced by elevated serotonin levels.[3][70]: 145 Contrary to the preceding notions however, a clinical study found that administration of LSD to people taking paroxetine, an SSRI and strong CYP2D6 inhibitor, increased LSD exposure by about 1.5-fold, was well-tolerated, and did not modify the pleasant subjective effects or physiological effects of LSD, whereas negative effects of LSD, including "bad drug effect", anxiety, and nausea, were reduced.[93] Similarly, a clinical study with LSD found that LSD levels were 75% higher in people with non-functional CYP2D6 (poor metabolizers) compared to those with functional CYP2D6.[94][95] In contrast to certain other psychedelics, MAOIs do not inhibit the metabolism of or potentiate the effects of LSD and instead reduce its effects.[3] Interactions between psychedelics and antipsychotics or anticonvulsants are not well-documented; however, co-use with mood stabilizers like lithium may induce seizures and dissociative effects, particularly in individuals with bipolar disorder.[70]: 146 [96][97] Lithium notably intensifies LSD reactions, potentially leading to acute comatose states when combined.[3]
Overdose
LSD at typical recreational doses (~50–250 μg) is considered to be very safe in terms of toxicity, with not a single toxicity-related death having been reported at such doses despite many millions of exposures.[98][99][100] In addition, LSD is considered to be a relatively non-toxic drug in overdose.[98][99][100][3] It is estimated, based on animal studies and human case reports, that the lethal dose of LSD in humans is approximately 100 mg, or about 1,000 times the usual recreational dose of 100 μg.[98][99] There have been a handful of reported cases of fatal overdose with LSD as of 2024.[98][99][100][3] However, critical review of the literature by David E. Nichols found that of five identified cases, one was not consistent with the effects of LSD but instead may have been another drug like 25I-NBOMe, two involved normal doses of LSD in individuals who were placed in maximal physical restraint (hogtied) by police followed by presumed positional asphyxia and fatal cardiovascular collapse (hogtying being a practice that is associated with accidental death generally), and two were associated with massive LSD overdose involving doses of possibly more than 300 mg.[98][99] Besides death due to toxicity, LSD is associated rarely with death via suicide, accidents, or violent encounters due to induction of abnormal behavior.[99][100]
In one well-known 1974 case series, 8 people accidentally insufflated two "lines" of nearly pure LSD powder that they thought were cocaine.[98][99][3][101][102] The exact doses of LSD were unknown, but were considered to be massive.[98][99][3] For context, a typical "line" of cocaine for insufflation is 50 to 100 mg.[103] The individuals reported to the hospital within 10 to 15 minutes, with five of them comatose, three requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation, and the conscious individuals experiencing severe hallucinogenic effects, among other toxic symptoms.[98][99][3][102] All of them completely recovered within 12 hours and there were no deaths.[98][99][3][102] A subsequent 2020 case similarly involved accidental insufflation of a confirmed 55 mg dose of LSD instead of cocaine, which was without adverse health consequences.[100][104] In other reports, a 5 mg overdose of LSD produced severe nausea and vomiting along with severe behavioral disturbances,[105][106] while a 10 mg overdose was also non-fatal.[34][107]
Despite acting as non-selective serotonin receptor agonists, major psychedelics like LSD and psilocybin do not cause serotonin syndrome even with extreme overdose.[108][109] This is thought to be due to the fact that they act as partial agonists of serotonin receptors like the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor relative to serotonin itself.[108][109] Conversely, NBOMe psychedelics like 25I-NBOMe are more efficacious and have been uniquely associated with serotonin syndrome-like toxicity.[98] A 2018 retrospective analysis of 3,554 LSD-only exposures reported to poison control centers in the United States between 2000 and 2016 found that serious toxicity was infrequent.[98][110] Common adverse effects (2.4–42%) included agitation or irritability, tachycardia, hallucinations or delusions, confusion, pupil dilation, hypertension, drowsiness or lethargy, elevated creatine phosphokinase (CPK), nausea and vomiting, and others.[110] Selected serious adverse effects included fever or hyperthermia in 3.8%, single seizure in 2.4%, coma in 1.4%, elevated creatinine in 1.4%, multiple seizures in 1.2%, rhabdomyolysis in 1.1%, respiratory depression in 0.9%, cardiac conduction disorder in 0.5%, and status epilepticus in 0.4%.[98][110] There is a case report of severe neurological sequelae following a single typical recreational dose of LSD involving seizure and cardiorespiratory arrest.[111][112] In general, psychedelics like LSD may rarely cause seizures in some individuals.[113][114]
The median lethal dose (LD50) of LSD in animals varies and is 50 to 60 mg/kg in mice, 16.5 mg/kg in rats, and 0.3 mg/kg in rabbits all given by injection.[100] A well-known 1962 instance of an elephant named Tusko given 297 mg (~0.1 mg/kg) LSD by intramuscular injection proved fatal.[115][100][107][116] These findings suggest that elephants may be much more sensitive to LSD in overdose than humans and other species.[115][100] However, this instance has been mired in criticism and controversy due to miscalculation of LSD dose and concomitant post-LSD administration of promazine and pentobarbital.[115][117] The experiment was repeated in two elephants with similar doses of LSD in 1984 without incident.[115][100][117]
Massive doses of LSD are largely managed by symptomatic treatments, and agitation can be addressed with benzodiazepines.[118][119] Reassurance in a calm, safe environment is beneficial.[120] Antipsychotics such as haloperidol are not recommended as they may have adverse effects.[118] Gastrointestinal decontamination with activated charcoal is of little use due to the rapid absorption of LSD, unless performed within 30 to 60 minutes of ingesting exceedingly huge amounts.[118] Administration of anticoagulants, vasodilators, and sympatholytics may be useful for treating ergotism.[118]
LSD substitute overdose
Although LSD is relatively safe in overdose, 25-NB (NBOMe) psychedelics like 25I-NBOMe and 25B-NBOMe are often sold as "LSD" and are highly toxic in overdose, with many reported severe intoxications and deaths.[121][119][122] Owing to their high potency analogous to LSD, these drugs are also regularly sold as "LSD" in blotter papers.[123][124] Fatalities involved in NBOMe intoxication suggest that a significant number of individuals ingested the substance which they believed was LSD,[125] and researchers report that "users familiar with LSD may have a false sense of security when ingesting NBOMe inadvertently".[126] Researchers state that the alleged physiological toxicity of LSD is likely due to psychoactive substances other than LSD.[57]
NBOMe compounds are reported to have a bitter taste,[126] are not active orally,[lower-alpha 1] and are usually taken sublingually.[128] When NBOMes are administered sublingually, numbness of the tongue and mouth followed by a metallic chemical taste was observed, and researchers describe this physical side effect as one of the main discriminants between NBOMe compounds and LSD.[129][130][131] Despite its high potency, recreational doses of LSD have only produced low incidents of acute toxicity, but NBOMe compounds have extremely different safety profiles.[126][132] Testing with Ehrlich's reagent gives a positive result for LSD and a negative result for NBOMe compounds.[133][134]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics

| Target | Affinity (Ki, nM) |
|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 0.64–7.3 (Ki) 6.4 (EC50) 110% (Emax) |
| 5-HT1B | 3.9 |
| 5-HT1D | 3.9–14 |
| 5-HT1E | 93 |
| 5-HT1F | ND |
| 5-HT2A | 0.47–21 (Ki) 0.24–538 (EC50) 23–88% (Emax) |
| 5-HT2B | 0.98–30 (Ki) 0.68–12,000 (EC50) 13–73% (Emax) |
| 5-HT2C | 1.1–48 (Ki) 0.85–1,590 (EC50) 26–79% (Emax) |
| 5-HT3 | >10,000 |
| 5-HT4 | 1,000 (rat) |
| 5-HT5A | 9.0 |
| 5-HT5B | 3.2 (rat) |
| 5-HT6 | 2.3–6.9 |
| 5-HT7 | 6.3–6.6 |
| α1A | 670–1,128 |
| α1B | 8,677 |
| α1D | ND |
| α2A | 12–46 |
| α2B, α2C | ND |
| β1 | 140–1,601 |
| β2 | 740–3,461 |
| β3 | ND |
| D1 | 155–340 (Ki) 35–63 (EC50) 35–44% (Emax) |
| D2 | 61–126 |
| D3 | 27–60 |
| D4 | 26–158 |
| D5 | 75–344 |
| H1 | 1,100–1,540 |
| H2–H4 | ND |
| M1–M5 | ND |
| I1 | ND |
| σ1, σ2 | ND |
| TAAR1 | 450 (Ki) (rat) 10,000 (Ki) (mouse) 1,400 (EC50) (rat) 9,700 (EC50) (mouse) >20,000 (EC50) (human) |
| SERT | >30,000 (Ki) >100,000 (IC50) |
| NET | 5,600–>30,000 (Ki) >100,000 (IC50) |
| DAT | >30,000 (Ki) >100,000 (IC50) |
| Notes: The smaller the value, the more avidly the drug binds to the site. All proteins are human unless otherwise noted. Refs:[135][136][2][137][138][139][140][141] [142][89][143][144][145][146][147][148] | |
LSD is a serotonergic psychedelic and acts as a non-selective serotonin receptor modulator.[14] It binds with high affinity to most of the serotonin receptors.[2] The psychedelic effects of LSD are thought to be mediated specifically by activation of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[14][2] However, a role of other serotonin receptors and targets in the effects of LSD cannot be ruled out and may be considered likely.[149] Uniquely among serotonergic psychedelics, LSD also shows potentially significant affinity for the dopamine receptors, albeit much lower than for most of the serotonin receptors.[2][150]
LSD binds to most serotonin receptor subtypes except for the serotonin 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors.[2] However, some of these serotonin receptors may not be affected at typical brain concentrations of LSD.[56] In humans, recreational doses of LSD may affect 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT6 receptors.[151] Although not present in humans, 5-HT5B receptors found in rodents also have a high affinity for LSD.[152] The psychedelic effects of LSD are attributed to activation of 5-HT2A receptors.[153] Many but not all serotonin 5-HT2A agonists are psychedelics and serotonin 5-HT2A antagonists block the psychedelic activity of LSD. LSD exhibits functional selectivity at the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in that it activates the signal transduction enzyme phospholipase A2 instead of activating the enzyme phospholipase C as the endogenous ligand serotonin does.[154]
Exactly how LSD produces its effects is unknown, but it is thought that it works by increasing glutamate release in the cerebral cortex[56] and therefore excitation in this area, specifically in layer V.[155] LSD, like many other drugs of recreational use, has been shown to activate DARPP-32-related pathways.[156] The drug enhances dopamine D2 receptor protomer recognition and signaling of D2–5-HT2A receptor complexes,[157] which may contribute to its psychotropic effects.[157] LSD has been shown to have low affinity for H1 receptors, displaying antihistamine effects, although the significance of this at doses used in humans is unknown.[158][159]
LSD is a biased agonist that induces a conformation in serotonin receptors that preferentially recruits β-arrestin over activating G proteins.[160] LSD also has an exceptionally long residence time when bound to serotonin receptors lasting hours, consistent with the long-lasting effects of LSD despite its relatively rapid clearance.[161][160] A crystal structure of the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor bound to LSD reveals an extracellular loop that forms a "lid" over the diethylamide end of the binding cavity and "traps" LSD in the binding pocket, which explains the slow rate of LSD unbinding from serotonin receptors.[161][162] The related lysergamide lysergic acid amide (LSA) that lacks the diethylamide moiety is far less hallucinogenic in comparison.[162] Moreover, a specific residue in the binding pocket is partially responsible for the prolonged action of LSD, and this residue is found in the human protein but not in the receptors of rodents.[161]
LSD is an extraordinarily potent psychoactive drug and is among the most potent psychedelics known in humans.[14][32][34] The very high potency of LSD in producing psychedelic-like effects is also the case in animals, including rodents and monkeys.[34][163] It is unclear why LSD is so potent.[32][56][164] The affinity and activational potency of LSD at the human serotonin 5-HT2A receptor in vitro is unremarkable compared to other psychedelics such as DOI and DOB.[32][56][164] There is no evidence for its greater potency being related to pharmacokinetics or metabolism.[56] It appears that the N,N-diethylamide moiety of LSD fits into a sterically constrained region of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor that specifically accommodates this moiety.[32][165][164]
An agonist is usually defined as a molecule that activates a receptor it binds to directly, according to that LSD binds to the TAAR1-receptor inside a dopaminergic neuron is meaning an acceleration of releasing endogenous dopamine from. So by assuming, that also the partial agonism at autoreceptors from LSD is mostly acting agonistic in these pathways, the overall activation of the dopaminesystem from LSD is very strong.[166]
LSD, like other psychedelics, has been found to increase the expression of genes related to synaptic plasticity and hence to have psychoplastogenic effects.[167] This appears to be mediated by serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonism.[167] LSD has also been reported to act as a highly potent positive allosteric modulator of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), one of the receptors of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).[168][169] However, subsequent studies failed to reproduce these findings and instead found no interaction of LSD with TrkB.[170]
There appears to be no significant acute tolerance to the subjective effects of LSD.[14][171] Hence, its duration appears to be dictated by pharmacokinetics rather than by pharmacodynamics.[14][171] This is in contrast to MDMA, which shows marked acute tolerance and a duration of effects that is shorter than its elimination half-life.[171]
The cryo-EM structures of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor with LSD, as well as with various other psychedelics and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor agonists, have been solved and published by Bryan L. Roth and colleagues.[172][173]
Mechanisms of action
Neuroimaging studies using resting state fMRI recently suggested that LSD changes the cortical functional architecture.[175] These modifications spatially overlap with the distribution of serotonergic receptors. In particular, increased connectivity and activity were observed in regions with high expression of 5-HT2A receptor, while a decrease in activity and connectivity was observed in cortical areas that are dense with 5-HT1A receptor.[176] Experimental data suggest that subcortical structures, particularly the thalamus, play a synergistic role with the cerebral cortex in mediating the psychedelic experience. LSD, through its binding to cortical 5-HT2A receptor, may enhance excitatory neurotransmission along frontostriatal projections and, consequently, reduce thalamic filtering of sensory stimuli towards the cortex.[177] This phenomenon appears to selectively involve ventral, intralaminar, and pulvinar nuclei.[177]
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The oral bioavailability of LSD was crudely estimated as approximately 71% using previous data on intravenous administration of LSD.[178][179] The sample was equally divided between male and female subjects and there were no significant sex differences observed in the pharmacokinetics of LSD.[178][179] In a subsequent higher-quality 2025 study, the oral bioavailability of LSD was about 80%.[180][181]
The pharmacokinetics of LSD were not properly determined until 2015, which is not surprising for a drug with the kind of low-μg potency that LSD possesses.[178][179] In a sample of 16 healthy subjects, a single mid-range 200 μg oral dose of LSD was found to produce mean maximal concentrations of 4.5 ng/mL at a median of 1.5 hours (range 0.5–4 hours) post-administration.[178][179]
A large meal before taking LSD has been found to result in circulating levels that were 50% lower than on an empty stomach.[3]
Distribution
In terms of distribution, it is estimated that only about 1 to 1.5% of the drug reaches the brain both in animals and humans.[34] Following a typical 100 μg dose in humans, this would be about 1 μg that is distributed into the brain.[34] LSD levels in different brain areas have been found to vary in monkeys.[34][182] Levels were equal in blood, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and brainstem, whereas levels were 1.5 times higher in the thalamus and extrapyramidal system, 2 to 3 times higher in the hypothalamus and limbic system, 2 to 5 times higher in the auditory and visual cortex, 5 to 7 times higher in the posterior pituitary and pineal gland, and 10 times higher in the anterior pituitary gland.[34][182] These varying concentrations in different brain areas may explain the profile of psychedelic effects of LSD.[34][182] Bodily distribution of LSD has also been studied.[183][3]
It has been said that there is a peculiar 40-minute lag before onset of the psychedelic effects of LSD when it is administered intravenously.[165] This has been said to be related to time-dependent interactions of LSD with the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[165] However, contradicting the preceding claims, other sources have stated that intravenous injection of LSD results in onset of effects within a few minutes.[3][184][34] In a 2025 pharmacokinetic study comparing oral and intravenous LSD, the onset orally was about 45 minutes and the onset by intravenous injection was about 2.5 minutes.[180] In addition, intrathecal injection (intraspinal injection) is reported to have a virtually instantaneous onset of action.[3][184] However, in the 2025 study, time to maximal effects was about 2.5 hours orally and about 1.2 hours intravenously.[180] In an earlier 2016 study, intravenous LSD effects similarly peaked after about 1.7 hours.[9][185] For comparison, intravenous dimethyltryptamine (DMT) given as a bolus has been found to produce maximal effects after about 2 minutes and intravenous psilocybin given over 60 seconds after about 4 minutes.[2][9] Doses of LSD are said to be similar by oral and injectable routes, with the exception of intrathecal injection in which the dose is reduced to about one-third of usual.[184]
Metabolism

The metabolites of LSD include 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD (O-H-LSD), 2-oxo-LSD, lysergic acid ethylamide (LAE), lysergic acid ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamide (LEO), nor-LSD, 13-hydroxy-LSD, 14-hydroxy-LSD, and the glucuronide conjugates of the 13- and 14-hydroxylated metabolites, among other possible metabolites.[186][178][188][189] The major metabolite of LSD is O-H-LSD.[178][179] Levels of O-H-LSD in urine have been found to be 4 to 40 times higher than those of LSD, indicating extensive metabolism of LSD into this compound.[188][189] It is formed by cytochrome P450 enzymes, although the specific enzymes involved are unknown, and O-H-LSD's potential pharmacology is little-studied.[178][179] However, it was found to have profoundly reduced activity at the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors relative to LSD in vitro.[190] Little is known about the specific enzymes responsible for the formation of LSD metabolites.[188][189]
Elimination
Only 1% of the drug was eliminated in urine unchanged, whereas 13% was eliminated as O-H-LSD within 24 hours.[178][179]
Aghajanian and Bing (1964) found LSD had an elimination half-life of only 175 minutes (about 3 hours);[151] however, using more accurate techniques, Papac and Foltz (1990) reported that 1 μg/kg oral LSD given to a single male volunteer had an apparent plasma half-life of 5.1 hours, with a peak plasma concentration of 5 ng/mL at 3 hours post-dose.[191] In a more modern 2015 study, concentrations of LSD decreased following first-order kinetics with a half-life of 3.6 ± 0.9 hours and a terminal half-life of 8.9 ± 5.9 hours.[178][179]
Miscellaneous
The acute effects of LSD normally last between 6 and 12 hours depending on dose, tolerance, and age.[192][3] In a modern study, the effects of the dose of LSD given lasted for up to 12 hours and were closely correlated with the concentrations of LSD present in circulation over time, with no acute tolerance observed.[178][179]
Chemistry

LSD is a chiral compound with two stereocenters at the carbon atoms C-5 and C-8, so that theoretically four different optical isomers of LSD could exist. LSD, also called d-LSD or (+)-LSD,[193] has the absolute configuration (5R,8R). The other stereoisomers are iso-LSD (d-iso-LSD), l-LSD, and l-iso-LSD.
The 5S- or levo- stereoisomers of lysergamides do not exist in nature and are not formed during the synthesis from d-lysergic acid. Retrosynthetically, the C-5 stereocenter could be analysed as having the same configuration of the alpha carbon of the naturally occurring amino acid L-tryptophan, the precursor to all biosynthetic ergoline compounds.
However, LSD and iso-LSD, the two C-8 isomers, rapidly interconvert in the presence of bases, as the alpha proton is acidic and can be deprotonated and reprotonated. Non-psychoactive iso-LSD which has formed during the synthesis can be separated by chromatography and can be isomerized to LSD.
Pure salts of LSD are triboluminescent, emitting small flashes of white light when shaken in the dark.[192] LSD is strongly fluorescent and will glow bluish-white under UV light.
Synthesis
LSD is an ergoline derivative. It is commonly synthesized by reacting diethylamine with an activated form of lysergic acid. Activating reagents include phosphoryl chloride[194] and peptide coupling reagents.[159] Lysergic acid is made by alkaline hydrolysis of lysergamides like ergotamine, a substance usually derived from the ergot fungus on agar plate. Lysergic acid can also be produced synthetically, although these processes are not used in clandestine manufacture due to their low yields and high complexity.[195][196]
Albert Hofmann synthesized LSD in the following manner: (1) hydrazinolysis of ergotamine into D- and L-isolysergic acid hydrazide, (2) separation of the enantiomers with di-(p-toluyl)-D-tartaric acid to get D-isolysergic acid hydrazide, (3) enantiomerization into D-lysergic acid hydrazide, (4) substitution with HNO2 to D-lysergic acid azide and (5) finally substitution with diethylamine to form D-lysergic acid diethylamide.[14]
The precursor for LSD, lysergic acid, has been produced by GMO baker's yeast.[197]
Stability
"LSD," writes the chemist Alexander Shulgin, "is an unusually fragile molecule ... As a salt, in water, cold, and free from air and light exposure, it is stable indefinitely."[192]
LSD also has enamine-type reactivity because of the electron-donating effects of the indole ring. Because of this, chlorine destroys LSD molecules on contact; even though chlorinated tap water contains only a slight amount of chlorine, the small quantity of compound typical to an LSD solution will likely be eliminated when dissolved in tap water.[192] The double bond between the 8-position and the aromatic ring, being conjugated with the indole ring, is susceptible to nucleophilic attacks by water or alcohol, especially in the presence of UV or other kinds of light. LSD often converts to lumi-LSD (10-hydroxy-9,10-dihydro-LSD), which is inactive in human beings.[192]
A controlled study was undertaken to determine the stability of LSD in pooled urine samples.[198]
The concentrations of LSD in urine samples were followed over time at various temperatures, in different types of storage containers, at various exposures to different wavelengths of light, and at varying pH values. These studies demonstrated no significant loss in LSD concentration at 25 °C for up to four weeks. After four weeks of incubation, a 30% loss in LSD concentration at 37 °C and up to a 40% at 45 °C were observed. Urine fortified with LSD and stored in amber glass or nontransparent polyethylene containers showed no change in concentration under any light conditions. The stability of LSD in transparent containers under light was dependent on the distance between the light source and the samples, the wavelength of light, exposure time, and the intensity of light. After prolonged exposure to heat in alkaline pH conditions, 10 to 15% of the parent LSD epimerized to iso-LSD. Under acidic conditions, less than 5% of the LSD was converted to iso-LSD. It was also demonstrated that trace amounts of metal ions in the buffer or urine could catalyze the decomposition of LSD and that this process can be avoided by the addition of EDTA.
Detection

LSD can be detected in concentrations larger than approximately 10% in a sample using Ehrlich's reagent and Hofmann's reagent. However, detecting LSD in human tissues is more challenging due to its active dose being significantly lower (in micrograms) compared to most other drugs (in milligrams).[200]
LSD may be quantified in urine for drug testing programs, in plasma or serum to confirm poisoning in hospitalized victims, or in whole blood for forensic investigations. The parent drug and its major metabolite are unstable in biofluids when exposed to light, heat, or alkaline conditions, necessitating protection from light, low-temperature storage, and quick analysis to minimize losses.[201] Maximum plasma concentrations are typically observed 1.4 to 1.5 hours after oral administration of 100 μg and 200 μg, respectively, with a plasma half-life of approximately 2.6 hours (ranging from 2.2 to 3.4 hours among test subjects).[202]
Due to its potency in microgram quantities, LSD is often not included in standard pre-employment urine or hair analyses.[200][203] However, advanced liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry methods can detect LSD in biological samples even after a single use.[203]
Analogues

A variety of LSD analogues are known.[204][205][206][207][192] Many of them retain psychedelic effects similarly to LSD, although most have reduced potency and none are notably more potent than LSD.[204][205][206][207][208] Examples include ergine (lysergic acid amide; LSA), isoergine (iso-LSA), lysergic acid hydroxyethylamide (LSH), ergonovine (ergometrine), methylergonovine (methylergometrine), methysergide, ETH-LAD, PRO-LAD, AL-LAD, 1-methyl-LSD (MLD-41), MiPLA, and LA-SS-Az (LSZ), among many others.[204][209][210] Presumed or known prodrugs of LSD, including 1A-LSD (ALD-52), 1P-LSD, and 1V-LSD, have been developed or encountered.[211][212] Some non-hallucinogenic LSD analogues, such as lisuride and 2-bromo-LSD (BOL-148), are known as well.[165][213][214] They are lower-efficacy serotonin 5-HT2A receptor partial agonists and can notably act as hallucinogen antagonists against LSD.[213][214] In addition to lysergamide derivatives, simplified or "partial" LSD analogues or seco-LSD compounds, such as NDTDI (8,10-seco-LSD), DEIMDHPCA (3,5-seco-LSD), 10,11-seco-LSD, and N-DEAOP-NMT, are known.[105][215][216][217] A notable bioisostere of LSD is JRT, the isotryptamine analogue of LSD and a psychedelic and psychoplastogen which is under investigation for the potential treatment of schizophrenia.[218][219]
History
—Albert Hofmann, on his first experience with LSD[220]: 15
Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann first synthesized LSD in 1938 from lysergic acid, a chemical derived from the hydrolysis of ergotamine, an alkaloid found in ergot, a fungus that infects grain.[5][13] LSD was the 25th of various lysergamides Hofmann synthesized from lysergic acid while trying to develop a new analeptic, hence the alternate name LSD-25. Hofmann discovered its effects in humans on April 16, in 1943, after unintentionally ingesting an unknown amount, possibly absorbing it through his skin.[221][222][223] On April 19, 1943, Hofmann intentionally ingested 0.25 milligrams (250 micrograms) of LSD.[224] LSD was first published in the scientific literature by Hofmann and his colleague psychiatrist Werner Stoll in 1943 and the hallucinogenic effects of LSD were first published by Stoll in 1947.[225][226][227][228][229]
LSD was subject to exceptional interest within the field of psychiatry in the 1950s and early 1960s, with Sandoz distributing LSD to researchers under the trademark name Delysid in an attempt to find a marketable use for it.[222] During this period, LSD was controversially administered to hospitalised schizophrenic autistic children, with varying degrees of therapeutic success.[230][231][232][233] It was said to have been tried in every type of mental disorder by 1960.[34] LSD was also used in an attempt to cure homosexuality.[34] Most of the early studies of LSD for psychiatric conditions were of very low quality, often lacking even control groups.[34] In 1975, it was concluded that LSD showed little difference from placebo for most conditions, but this conclusion was still based on low-quality evidence.[34]
LSD-assisted psychotherapy was used in the 1950s and early 1960s by psychiatrists such as Humphry Osmond, who pioneered the application of LSD to the treatment of alcoholism, with promising results.[222][234][15][24] Osmond coined the term "psychedelic" (mind manifesting) as a term for LSD and related hallucinogens, superseding the previously held "psychotomimetic" model in which LSD was believed to mimic schizophrenia. In contrast to schizophrenia, LSD can induce transcendent experiences, or mental states that transcend the experience of everyday consciousness, with lasting psychological benefit.[9][222] During this time, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) began using LSD in the research project Project MKUltra, which used psychoactive substances to aid interrogation. The CIA administered LSD to unwitting test subjects to observe how they would react, the most well-known example of this being Operation Midnight Climax.[222] LSD was one of several psychoactive substances evaluated by the U.S. Army Chemical Corps as possible non-lethal incapacitants in the Edgewood Arsenal human experiments.[222]
According to declassified CIA documents, it's possible that the American agency spread LSD on civilians in Europe in the 50s.[235][236]
In the 1960s, LSD and other psychedelics were adopted by and became synonymous with the counterculture movement due to their perceived ability to expand consciousness. This resulted in LSD being viewed as a cultural threat to American values and the Vietnam War effort, and it was designated as a Schedule I (illegal for medical as well as recreational use) substance in 1968.[16] It was listed as a Schedule I controlled substance by the United Nations in 1971 and currently has no approved medical uses.[5] As of 2017[update], about 10% of people in the United States have used LSD at some point in their lives, while 0.7% have used it in the last year.[18] It was most popular in the 1960s to 1980s.[5] The use of LSD among US adults increased by 56.4% from 2015 to 2018.[237]
LSD was first synthesized on November 16, 1938[238] by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann at the Sandoz Laboratories in Basel, Switzerland as part of a large research program searching for medically useful ergot alkaloid derivatives. The abbreviation "LSD" is from the German "Lysergsäurediethylamid".[239]

LSD's psychedelic properties were discovered 5 years later when Hofmann himself accidentally ingested an unknown quantity of the chemical.[240] The first intentional ingestion of LSD occurred on April 19, 1943,[220] when Hofmann ingested 250 μg of LSD. He said this would be a threshold dose based on the doses of other ergot alkaloids. Hofmann found the effects to be much stronger than he anticipated.[241] Sandoz Laboratories introduced LSD as a psychiatric drug in 1947 and marketed LSD as a psychiatric panacea, hailing it "as a cure for everything from schizophrenia to criminal behavior, 'sexual perversions', and alcoholism."[242] Sandoz would send the drug for free to researchers investigating its effects.[221]
File:Effects of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) on Troops Marching.webm Beginning in the 1950s, the US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) began a research program code-named Project MKUltra.[243] The CIA introduced LSD to the United States, purchasing the entire world's supply for $240,000 and propagating the LSD through CIA front organizations to American hospitals, clinics, prisons, and research centers.[244] Experiments included administering LSD to CIA employees, military personnel, doctors, other government agents, prostitutes, mentally ill patients, and members of the general public to study their reactions, usually without the subjects' knowledge. The project was revealed in the US congressional Rockefeller Commission report in 1975. However, the extent of the experiments conducted under Project MKUltra are still mostly unknown, as acting CIA director Richard Helms destroyed many of the key documents related to MKUltra in 1973.[245]
In 1963, the Sandoz patents on LSD expired[38] and the Czech company Spofa began to produce the substance.[221] Sandoz stopped the production and distribution in 1965.[221]
Several figures, including Aldous Huxley, Timothy Leary, and Al Hubbard, had begun to advocate the consumption of LSD. LSD became central to the counterculture of the 1960s.[246] In the early 1960s the use of LSD and other hallucinogens was advocated by new proponents of consciousness expansion such as Leary, Huxley, Alan Watts and Arthur Koestler,[247][248] and according to L. R. Veysey they profoundly influenced the thinking of the new generation of youth.[249]
On October 24, 1968, possession of LSD was made illegal in the United States.[250] The last FDA approved study of LSD in patients ended in 1980, while a study in healthy volunteers was made in the late 1980s. Legally approved and regulated psychiatric use of LSD continued in Switzerland until 1993.[251]
In November 2020, Oregon became the first US state to decriminalize possession of small amounts of LSD after voters approved Ballot Measure 110.[252]
Society and culture
Counterculture
By the mid-1960s, the youth countercultures in California, particularly in San Francisco, had widely adopted the use of hallucinogenic drugs, including LSD. The first major underground LSD factory was established by Owsley Stanley.[253] Around this time, the Merry Pranksters, associated with novelist Ken Kesey, organized the Acid Tests, events in San Francisco involving LSD consumption, accompanied by light shows and improvised music.[254][255] Their activities, including cross-country trips in a psychedelically decorated bus and interactions with major figures of the beat movement, were later documented in Tom Wolfe's The Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test (1968).[256]
In San Francisco's Haight-Ashbury neighborhood, the Psychedelic Shop was opened in January 1966 by brothers Ron and Jay Thelin to promote the safe use of LSD. This shop played a significant role in popularizing LSD in the area and establishing Haight-Ashbury as the epicenter of the hippie counterculture. The Thelins also organized the Love Pageant Rally in Golden Gate Park in October 1966, protesting against California's ban on LSD.[257][258]
A similar movement developed in London, led by British academic Michael Hollingshead, who first tried LSD in America in 1961. After experiencing LSD and interacting with notable figures such as Aldous Huxley, Timothy Leary, and Richard Alpert, Hollingshead played a key role in the famous LSD research at Millbrook before moving to New York City for his experiments. In 1965, he returned to the UK and founded the World Psychedelic Center in Chelsea, London.[259]
Art and music
Art
Blotter art

Blotter art is an art form printed on perforated sheets of absorbent blotting paper infused with liquid LSD. The delivery method gained popularity following the banning of the hallucinogen LSD in the late 1960s. The use of graphics on blotter sheets originated as an underground art form in the early 1970s, sometimes to help identify the dose, maker, or batch of LSD.
LSD art

LSD art is any art or visual displays inspired by psychedelic experiences and hallucinations known to follow the ingestion of LSD (also known colloquially as acid).[260] Artists and scientists have been interested in the effect of LSD on drawing and painting since it first became available for legal use and general consumption.[261]
Music

The influence of LSD in the realms of music and art became pronounced in the 1960s, especially through the Acid Tests and related events involving bands like the Grateful Dead, Jefferson Airplane, and Big Brother and the Holding Company. San Francisco-based artists such as Rick Griffin, Victor Moscoso, and Wes Wilson contributed to this movement through their psychedelic poster and album art. The Grateful Dead, in particular, became central to the culture of "Deadheads," with their music heavily influenced by LSD.[262]
In the United Kingdom, Michael Hollingshead, reputed for introducing LSD to various artists and musicians like Storm Thorgerson, Donovan, Keith Richards, and members of the Beatles, played a significant role in the drug's proliferation in the British art and music scene. Despite LSD's illegal status from 1966, it was widely used by groups including the Beatles, the Rolling Stones, and the Moody Blues. Their experiences influenced works such as the Beatles' Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band and Cream's Disraeli Gears, featuring psychedelic-themed music and artwork.[263]
Psychedelic music of the 1960s often sought to replicate the LSD experience, incorporating exotic instrumentation, electric guitars with effects pedals, and elaborate studio techniques. Artists and bands utilized instruments like sitars and tablas, and employed studio effects such as backward tapes, panning, and phasing.[264][265] Songs such as John Prine's "Illegal Smile" and the Beatles' "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" have been associated with LSD, although the latter's authors denied such claims.[266] [267]
Contemporary artists influenced by LSD include Keith Haring in the visual arts,[268] various electronic dance music creators,[269] and the jam band Phish.[270] The 2018 Leo Butler play All You Need is LSD is inspired by the author's interest in the history of LSD.[271]
Legal status
The United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 mandates that signing parties, including the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and most of Europe, prohibit LSD. Enforcement of these laws varies by country. The convention allows medical and scientific research with LSD.[272]
Australia
In Australia, LSD is classified as a Schedule 9 prohibited substance under the Poisons Standard (February 2017), indicating it may be abused or misused and its manufacture, possession, sale, or use should be prohibited except for approved research purposes.[273] In Western Australia, the Misuse of Drugs Act 1981 provides guidelines for possession and trafficking of substances like LSD.[274]
Canada
In Canada, LSD is listed under Schedule III of the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act. Unauthorized possession and trafficking of the substance can lead to significant legal penalties.[275]
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, LSD is a Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971, making unauthorized possession and trafficking punishable by severe penalties. The Runciman Report and Transform Drug Policy Foundation have made recommendations and proposals regarding the legal regulation of LSD and other psychedelics.[276][277]
United States
In the United States, LSD is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970, making its manufacture, possession, and distribution illegal without a DEA license. The law considers LSD to have a high potential for abuse, no legitimate medical use, and to be unsafe even under medical supervision. The US Supreme Court case Neal v. United States (1995) clarified the sentencing guidelines related to LSD possession.[278]
Oregon decriminalized personal possession of small amounts of drugs, including LSD, in February 2021, and California has seen legislative efforts to decriminalize psychedelics.[279]
Mexico
Mexico decriminalized the possession of small amounts of drugs, including LSD, for personal use in 2009. The law specifies possession limits and establishes that possession is not a crime within designated quantities.[280]
Czech Republic
In the Czech Republic, possession of "amount larger than small" of LSD is criminalized, while possession of smaller amounts is a misdemeanor. The definition of "amount larger than small" is determined by judicial practice and specific regulations.[281][282]
Illicit supply chain
Production

An active dose of LSD is very minute, allowing a large number of doses to be synthesized from a comparatively small amount of raw material. Twenty-five kilograms of precursor ergotamine tartrate can produce 5–6 kg of pure crystalline LSD; this corresponds to around 50–60 million doses at 100 μg. Because the masses involved are so small, concealing and transporting illicit LSD is much easier than smuggling cocaine, cannabis, or other illegal drugs.[283]
Manufacturing LSD requires laboratory equipment and experience in the field of organic chemistry. It takes two to three days to produce 30 to 100 grams of pure compound. It is believed that LSD is not usually produced in large quantities, but rather in a series of small batches. This technique minimizes the loss of precursor chemicals in case a step does not work as expected.[283] Ali Altaft, the lead chemist at the University of Okara, in Punjab, Pakistan, performed the synthesis of LSD on video.[284]
Forms
LSD is produced in crystalline form and is then mixed with excipients or redissolved for production in ingestible forms. Liquid solution is either distributed in small vials or, more commonly, sprayed onto or soaked into a distribution medium. Historically, LSD solutions were first sold on sugar cubes, but practical considerations[clarification needed] forced a change to tablet form. Appearing in 1968 as an orange tablet measuring about 6 mm across, "Orange Sunshine" acid was the first largely available form of LSD after its possession was made illegal. Tim Scully, a prominent chemist, made some of these tablets, but said that most "Sunshine" in the USA came by way of Ronald Stark, who imported approximately thirty-five million doses from Europe.[285]
Over some time, tablet dimensions, weight, shape and concentration of LSD evolved from large (4.5–8.1 mm diameter), heavyweight (≥150 μg), round, high concentration (90–350 μg/tab) dose units to small (2.0–3.5 mm diameter) lightweight (as low as 4.7 μg/tab), variously shaped, lower concentration (12–85 μg/tab, average range 30–40 μg/tab) dose units. LSD tablet shapes have included cylinders, cones, stars, spacecraft, and heart shapes. The smallest tablets became known as "Microdots."[286]
After tablets came "computer acid" or "blotter paper LSD," typically made by dipping a preprinted sheet of blotting paper into an LSD/water/alcohol solution.[285][286] More than 200 types of LSD tablets have been encountered since 1969 and more than 350 blotter paper designs have been observed since 1975.[286] About the same time as blotter paper LSD came "Windowpane" (AKA "Clearlight"), which contained LSD inside a thin gelatin square a quarter of an inch (6 mm) across.[285] LSD has been sold under a wide variety of often short-lived and regionally restricted street names including Acid, Trips, Uncle Sid, Blotter, Lucy, Alice and doses, as well as names that reflect the designs on the sheets of blotter paper.[42][287] Authorities have encountered the drug in other forms—including powder or crystal, and capsule.[288]
Blotters
Blotter art designs printed on blotter paper can serve to identify dose strengths, different batches, or makers.[289]
On the other hand, blotters without art may be considered safer by some, since there is no guarantee that the printer ink used in clandestine production is edible or non-toxic for long-term exposure, and it is also possible for unscrupulous dealers to mimic reputable blotter art designs in order to boost sales.
Distribution
LSD manufacturers and traffickers in the United States can be categorized into two groups: A few large-scale producers, and an equally limited number of small, clandestine chemists, consisting of independent producers who, operating on a comparatively limited scale, can be found throughout the country.[290][291]
As a group, independent producers are of less concern to the Drug Enforcement Administration than the large-scale groups because their product reaches only local markets.[242]
Many LSD dealers and chemists describe a religious or humanitarian purpose that motivates their illicit activity. Nicholas Schou's book Orange Sunshine: The Brotherhood of Eternal Love and Its Quest to Spread Peace, Love, and Acid to the World describes one such group, the Brotherhood of Eternal Love. The group was a major American LSD trafficking group in the late 1960s and early 1970s.[292]
In the second half of the 20th century, dealers and chemists loosely associated with the Grateful Dead like Owsley Stanley, Nicholas Sand, Karen Horning, Sarah Maltzer, "Dealer McDope," and Leonard Pickard played an essential role in distributing LSD.[262]
Mimics

Since 2005, law enforcement in the United States and elsewhere has seized several chemicals and combinations of chemicals in blotter paper which were sold as LSD mimics, including DOB,[293][294] a mixture of DOC and DOI,[295] 25I-NBOMe,[296] and a mixture of DOC and DOB.[297] Many mimics are toxic in comparatively small doses, or have extremely different safety profiles. Many street users of LSD are often under the impression that blotter paper which is actively hallucinogenic can only be LSD because that is the only chemical with low enough doses to fit on a small square of blotter paper. While it is true that LSD requires lower doses than most other hallucinogens, blotter paper is capable of absorbing a much larger amount of material. The DEA performed a chromatographic analysis of blotter paper containing 2C-C which showed that the paper contained a much greater concentration of the active chemical than typical LSD doses, although the exact quantity was not determined.[298] Blotter LSD mimics can have relatively small dose squares; a sample of blotter paper containing DOC seized by Concord, California police had dose markings approximately 6 mm apart.[299] Several deaths have been attributed to 25I-NBOMe.[300][301][302][303]
Notable individuals
Some notable individuals have commented publicly on their experiences with LSD.[304][305] Some of these comments date from the era when it was legally available in the US and Europe for non-medical uses, and others pertain to psychiatric treatment in the 1950s and 1960s. Still others describe experiences with illegal LSD, obtained for philosophic, artistic, therapeutic, spiritual, or recreational purposes.
- W. H. Auden, the poet, said, "I myself have taken mescaline once and L.S.D. once. Aside from a slight schizophrenic dissociation of the I from the Not-I, including my body, nothing happened at all."[306] He also said, "LSD was a complete frost. … What it does seem to destroy is the power of communication. I have listened to tapes done by highly articulate people under LSD, for example, and they talk absolute drivel. They may have seen something interesting, but they certainly lose either the power or the wish to communicate."[307] He also said, "Nothing much happened but I did get the distinct impression that some birds were trying to communicate with me."[308]
- James Cameron, the Canadian filmmaker, has said he experimented with LSD during his college years.[309]
- Daniel Ellsberg, an American peace activist, says he has had several hundred experiences with psychedelics.[310]
- Richard Feynman, a notable physicist at California Institute of Technology, tried LSD during his professorship at Caltech. Feynman largely sidestepped the issue when dictating his anecdotes; he mentions it in passing in the "O Americano, Outra Vez" section.[311][312]
- Jerry Garcia stated in a July 3, 1989 interview for Relix Magazine, in response to the question "Have your feelings about LSD changed over the years?," "They haven't changed much. My feelings about LSD are mixed. It's something that I both fear and that I love at the same time. I never take any psychedelic, have a psychedelic experience, without having that feeling of, "I don't know what's going to happen." In that sense, it's still fundamentally an enigma and a mystery."[313]
- Bill Gates implied in an interview with Playboy that he tried LSD during his youth.[314]
- Aldous Huxley, author of Brave New World, became a user of psychedelics after moving to Hollywood. He was at the forefront of the counterculture's use of psychedelic drugs, which led to his 1954 work The Doors of Perception. Dying from cancer, he asked his wife on 22 November 1963 to inject him with 100 μg of LSD. He died later that day.[315]
- Steve Jobs, co-founder and former CEO of Apple Inc., said, "Taking LSD was a profound experience, one of the most important things in my life."[316]
- Ernst Jünger, German writer and philosopher, throughout his life had experimented with drugs such as ether, cocaine, and hashish; and later in life he used mescaline and LSD. These experiments were recorded comprehensively in Annäherungen (1970, Approaches). The novel Besuch auf Godenholm (1952, Visit to Godenholm) is clearly influenced by his early experiments with mescaline and LSD. He met with LSD inventor Albert Hofmann and they took LSD together several times. Hofmann's memoir LSD, My Problem Child describes some of these meetings.[317]
- In a 2004 interview, Paul McCartney said that The Beatles' songs "Day Tripper" and "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" were inspired by LSD trips.[266]: 182 Nonetheless, John Lennon consistently stated over the course of many years that the fact that the initials of "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" spelled out L-S-D was a coincidence (he stated that the title came from a picture drawn by his son Julian) and that the band members did not notice until after the song had been released, and Paul McCartney corroborated that story.[318] John Lennon, George Harrison, and Ringo Starr also used the drug, although McCartney cautioned that "it's easy to overestimate the influence of drugs on the Beatles' music."[319]
- Michel Foucault had an LSD experience with Simeon Wade in Death Valley and later wrote "it was the greatest experience of his life, and that it profoundly changed his life and his work."[320][321] According to Wade, as soon as he came back to Paris, Foucault scrapped the second History of Sexuality's manuscript, and totally rethought the whole project.[322]
- Kary Mullis is reported to credit LSD with helping him develop DNA amplification technology, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.[323]
- Carlo Rovelli, an Italian theoretical physicist and writer, has credited his use of LSD with sparking his interest in theoretical physics.[324]
- Oliver Sacks, a neurologist famous for writing best-selling case histories about his patients' disorders and unusual experiences, talks about his own experiences with LSD and other perception altering chemicals, in his book, Hallucinations.[325]
- Alexander Shulgin, American chemist, told Albert Hofmann that he preferred LSD to 2C-B.
- Matt Stone and Trey Parker, creators of the TV series South Park, claimed to have shown up at the 72nd Academy Awards, at which they were nominated for Best Original Song, under the influence of LSD.[326]
Research
Psychiatric disorders
LSD was initially explored for psychiatric use due to its structural similarity to the neurotransmitter serotonin and its safety profile.[14] In the 1950s and 1960s, it was used in psychiatry to enhance psychotherapy, known as psychedelic therapy. In the United States, the earliest research began in the 1950s. Albert Kurland and his colleagues published research on LSD's therapeutic potential to treat schizophrenia. In Canada, Humphry Osmond and Abram Hoffer completed LSD studies as early as 1952.[327] Some psychiatrists, such as Ronald A. Sandison, who pioneered its use at Powick Hospital in England, believed that LSD was especially useful at helping patients to "unblock" repressed subconscious material through other psychotherapeutic methods,[328] and also for treating alcoholism.[329][330] One study concluded, "The root of the therapeutic value of the LSD experience is its potential for producing self-acceptance and self-surrender,"[15] presumably by forcing the user to face issues and problems in that individual's psyche. By the 1960s however, controversies surrounding "hippie" counterculture began to deplete institutional support for continued studies.
In 2001, the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) stated that LSD "produces no aphrodisiac effects, does not increase creativity, has no lasting positive effect in treating alcoholics or criminals, does not produce a "model psychosis", and does not generate immediate personality change."[242]
In more recent years, there has been renewed clinical research on and interest in LSD for potential therapeutic uses.[331] This has been supported by several organizations, including the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS), the Beckley Foundation, the Heffter Research Institute, and the Albert Hofmann Foundation, which exist to fund, encourage, and coordinate research into the medicinal and spiritual uses of LSD and related psychedelics.[332] New clinical LSD experiments in humans started in 2009 for the first time in 35 years.[331] As the drug is illegal in many areas of the world, potential medical uses have historically been difficult to study.[29] Investigational uses of LSD include the treatment of alcoholism,[333] anxiety, and depression, among other conditions.[334][25][26][81][335] Another use is alleviation of anxiety in terminally ill cancer patients.[25][331][336]
A 2012 meta-analysis found evidence that a single dose of LSD in conjunction with various alcoholism treatment programs was associated with a decrease in alcohol abuse, lasting for several months, but no effect was seen at one year. Adverse events included seizure, moderate confusion and agitation, nausea, vomiting, and acting in a bizarre fashion.[24] A couple of reviews published in 2010 and 2014 concluded that conclusions drawn from most early trials are unreliable due to serious methodological flaws. These include the absence of adequate control groups, lack of follow-up, and vague criteria for therapeutic outcome. In many cases, studies failed to convincingly demonstrate whether the drug or the therapeutic interaction was responsible for any beneficial effects.[337][338] A 2020 meta-review indicated possible positive effects of LSD in reducing psychiatric symptoms, mainly in cases of alcoholism.[339]
In 2024, the FDA designated a form of LSD as a breakthrough therapy to treat generalized anxiety disorder which is being developed by MindMed.[17] A study published by the Journal of the American Medical Association in September, 2025 explored the optimal dose of LSD to lower patients' anxiety.[340] The study was conducted by the pharmaceutical company MindMed.[340] The researchers compared how LSD doses of 25 μg, 50 μg, 100 μg, 200 μg, or placebo impacted anxiety scores among study participants.[340] The results of the study found that 100 μg was the optimal dose to reduce anxiety among the studied patients.[340][341]
LSD is a psychoplastogen, a compound capable of promoting rapid and sustained neural plasticity, an action that hypothetically might be involved in its therapeutic benefits, although more research is needed to substantiate such notions.[342][343][344]
The British critical psychiatrist Joanna Moncrieff has critiqued the use and study of psychedelics like LSD for treatment of psychiatric disorders, highlighting concerns including excessive hype around these drugs, questionable biologically-based theories of benefit, blurred lines between medical and recreational use, flawed clinical trial findings, financial conflicts of interest, strong expectancy effects and large placebo responses, small and short-term benefits over placebo, and their potential for difficult experiences and adverse effects, among others.[345]
Other conditions
LSD has been studied for relief of pain and headaches.[3][346][347] It has been used as a treatment for cluster headaches with positive results in some small studies.[3] The drug might have analgesic properties related to pain in terminally ill patients and phantom pain and might be useful for treating inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis due to anti-inflammatory effects.[348]
Enhancing creativity
In the 1950s and 1960s, some psychiatrists, such as Oscar Janiger, explored the potential effect of LSD on creativity. Experimental studies attempted to measure the effect of LSD on creative activity and aesthetic appreciation.[43][349][350][351] In 1966, James Fadiman conducted a study with the central question "How can psychedelics be used to facilitate problem solving?" This study attempted to solve 44 different problems and had 40 satisfactory solutions when the FDA banned all research into psychedelics. LSD was a key component of this study.[352][353]
See also
Notes
- ↑ The potency of N-benzylphenethylamines via buccal, sublingual, or nasal absorption is 50–100 greater (by weight) than oral route compared to the parent 2C-x compounds.[127] Researches hypothesize the low oral metabolic stability of N-benzylphenethylamines is likely causing the low bioavailability on the oral route, although the metabolic profile of this compounds remains unpredictable; therefore researches state that the fatalities linked to these substances may partly be explained by differences in the metabolism between individuals.[127]
References
- ↑ PubChem. "Lysergide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lysergide.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 "Serotonergic Psychedelics: A Comparative Review of Efficacy, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Binding Profile". Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging 9 (5): 472–489. May 2024. doi:10.1016/j.bpsc.2024.01.007. PMID 38301886.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 3.18 3.19 3.20 3.21 "The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review". CNS Neurosci Ther 14 (4): 295–314. 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. PMID 19040555.
- ↑ "What are hallucinogens?". January 2016. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/hallucinogens.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 "LSD profile (chemistry, effects, other names, synthesis, mode of use, pharmacology, medical use, control status)" (in en). http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/drug-profiles/lsd.
- ↑ "How LSD Went From Research to Religion". JSTOR Daily. 19 July 2016. https://daily.jstor.org/how-lsd-went-from-research-to-religion/.
- ↑ "Alterations of consciousness and mystical-type experiences after acute LSD in humans". Psychopharmacology 234 (9–10): 1499–1510. May 2017. doi:10.1007/s00213-016-4453-0. PMID 27714429.
- ↑ "Survey of subjective "God encounter experiences": Comparisons among naturally occurring experiences and those occasioned by the classic psychedelics psilocybin, LSD, ayahuasca, or DMT". PLOS ONE 14 (4). 2019-04-23. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0214377. PMID 31013281. Bibcode: 2019PLoSO..1414377G.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "Psychedelics". Pharmacological Reviews 68 (2): 264–355. April 2016. doi:10.1124/pr.115.011478. ISSN 0031-6997. PMID 26841800.
- ↑ "Serotonergic psychedelic drugs LSD and psilocybin reduce the hierarchical differentiation of unimodal and transmodal cortex". bioRxiv. 2020-05-03. doi:10.1101/2020.05.01.072314.
- ↑ "Hallucinations Under Psychedelics and in the Schizophrenia Spectrum: An Interdisciplinary and Multiscale Comparison". Schizophrenia Bulletin 46 (6): 1396–1408. December 2020. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbaa117. PMID 32944778.
- ↑ "Acute dose-dependent effects of lysergic acid diethylamide in a double-blind placebo-controlled study in healthy subjects". Neuropsychopharmacology 46 (3): 537–544. February 2021. doi:10.1038/s41386-020-00883-6. PMID 33059356.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Commonly Abused Drugs Charts". 2 July 2018. https://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/commonly-abused-drugs-charts#lsd.
- ↑ 14.00 14.01 14.02 14.03 14.04 14.05 14.06 14.07 14.08 14.09 14.10 14.11 "Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD)". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 9 (10): 2331–2343. October 2018. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00043. PMID 29461039. https://shaunlacob.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/DC-LSD.pdf.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 "Use of d-lysergic acid diethylamide in the treatment of alcoholism". Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol 20 (3): 577–590. September 1959. doi:10.15288/qjsa.1959.20.577. PMID 13810249.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 United States Congress House Committee on Interstate and Foreign Commerce Subcommittee on Public Health and Welfare (1968). Increased Controls Over Hallucinogens and Other Dangerous Drugs. U.S. Government Printing Office. https://books.google.com/books?id=qbY6xQEACAAJ. Retrieved August 3, 2021.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "FDA Opens the Door to Clinical Use of LSD" (in en). 2024-03-26. https://www.webmd.com/mental-health/news/20240326/fda-opens-the-door-clinical-use-lsd.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 National Institute on Drug Abuse. "Hallucinogens". https://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/hallucinogens.
- ↑ "Trends in LSD use among US adults: 2015–2018". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 212. July 2020. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108071. PMID 32450479.
- ↑ "DrugFacts: Hallucinogens – LSD, Peyote, Psilocybin, and PCP". National Institute on Drug Abuse. December 2014. http://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/hallucinogens-lsd-peyote-psilocybin-pcp.
- ↑ Alcohol and Drugs in North America: A Historical Encyclopedia. Bloomsbury Academic. August 27, 2013. p. 375. ISBN 978-1-59884-478-8.
- ↑ San Francisco Chronicle September 20, 1966 Page One
- ↑ Realms of the Human Unconscious (Observations from LSD Research). London: Souvenir Press (E & A) Ltd. 1979. pp. 13–14. ISBN 978-0-285-64882-1. http://www.csp.org/chrestomathy/realms_of3.html. Retrieved November 18, 2007.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 "Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) for alcoholism: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". Journal of Psychopharmacology 26 (7): 994–1002. July 2012. doi:10.1177/0269881112439253. PMID 22406913.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 "Acid for Anxiety: Fast and Lasting Anxiolytic Effects of LSD" (in en-US). 2022-10-14. https://psychedelicreview.com/acid-for-anxiety-fast-and-lasting-anxiolytic-effects-of-lsd/.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Lysergic Acid Diethylamide-Assisted Therapy in Patients With Anxiety With and Without a Life-Threatening Illness: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II Study". Biological Psychiatry 93 (3): 215–223. September 2022. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.08.025. PMID 36266118.
- ↑ "Antidepressive, anxiolytic, and antiaddictive effects of ayahuasca, psilocybin and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD): a systematic review of clinical trials published in the last 25 years". Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology 6 (3): 193–213. June 2016. doi:10.1177/2045125316638008. PMID 27354908.
- ↑ "History of LSD Therapy". https://druglibrary.org/schaffer/lsd/grofhist.htm.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Effects of Schedule I drug laws on neuroscience research and treatment innovation". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 14 (8): 577–585. August 2013. doi:10.1038/nrn3530. PMID 23756634.
- ↑ "Scientists study possible health benefits of LSD and ecstasy | Science". The Guardian. 2016-07-23. https://www.theguardian.com/science/2009/oct/23/lsd-ecstacy-health-benefits.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 31.5 "Dosing Psychedelics and MDMA". Disruptive Psychopharmacology. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 56. 2022. pp. 3–21. doi:10.1007/7854_2021_270. ISBN 978-3-031-12183-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355943062.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 32.5 "Chemistry and Structure–Activity Relationships of Psychedelics". Behavioral Neurobiology of Psychedelic Drugs. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2017. pp. 1–43. doi:10.1007/7854_2017_475. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/13937. "Although LSD is the most well-known psychedelic, only a very few structural modifications can be made to its structure, and nearly all of those attenuate its activity by about an order of magnitude. In addition, there is a paucity of structure–activity data for ergolines, principally due to the synthetic difficulty inherent in their chemistry. [...] Although LSD is the most potent psychedelic agent in humans, its affinity and potency at the human 5-HT2A receptor is rather unremarkable compared with much simpler molecules such as DOI. [...] Because of its structural complexity and tedious approaches to its total synthesis, only a few structural modifications of LSD have been reported. [...] Unfortunately, only a few of them have been assessed in human psychopharmacology, most being much less active than LSD itself."
- ↑ Albert Hofmann (1968). "Psychotomimetic Agents". Drugs Affecting the Central Nervous System. 2. New York: M. Dekker. pp. 169–235. OCLC 245452885. https://archive.org/details/drugsaffectingce0000edit/page/169/mode/1up. "Subsequent experiments on volunteers of the Sandoz research laboratories confirmed the extraordinary activity of lysergic acid diethylamide on the human psyche. These showed that the effective oral dose of LSD in human beings is 0.03—0.05 mg. [...] LSD is by far the most active and most specific psychotomimetic. It is about 5,000—10,000 times more active than mescaline or about 100–200 times more active than psilocybin."
- ↑ 34.00 34.01 34.02 34.03 34.04 34.05 34.06 34.07 34.08 34.09 34.10 34.11 34.12 34.13 "Indolealkylamines and Related Compounds". Hallucinogenic Agents. Bristol: Wright-Scientechnica. 1975. pp. 98–144. ISBN 978-0-85608-011-1. OCLC 2176880. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Books/978-0-85608-011-1.
- ↑ "Monoamine Transporter and Receptor Interaction Profiles in Vitro Predict Reported Human Doses of Novel Psychoactive Stimulants and Psychedelics". Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 21 (10): 926–931. October 2018. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyy047. PMID 29850881.
- ↑ "A systematic study of microdosing psychedelics". PLOS ONE 14 (2). 2019-02-06. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0211023. PMID 30726251. Bibcode: 2019PLoSO..1411023P.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 "LSD Samples Analysis". Erowid. 2009. http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/lsd/lsd_article3.shtml.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 LSD: Still with us after all these years. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. 1994. ISBN 978-0-7879-4379-0.
- ↑ Fire & Earth Erowid (Nov 2003). "LSD Analysis – Do we know what's in street acid?". Erowid. http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/lsd/lsd_article1.shtml.
- ↑ "Hallucinations, psuedohallucinations, and parahallucinations". Psychiatry 73 (1): 34–42. 2010. doi:10.1521/psyc.2010.73.1.34. PMID 20235616.
- ↑ "Peak experiences and the afterglow phenomenon: when and how do therapeutic effects of hallucinogens depend on psychedelic experiences?". Journal of Psychopharmacology 29 (3): 241–253. March 2015. doi:10.1177/0269881114568040. PMID 25670401.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "Frequently Asked Questions". Erowid. http://www.erowid.org/chemicals/lsd/lsd_faq.shtml.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "Long lasting effects of LSD on normals". Archives of General Psychiatry 17 (5): 521–532. November 1967. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1967.01730290009002. PMID 6054248. http://www.maps.org/w3pb/new/1967/1967_mcglothlin_4655_1.pdf.
- ↑ "Adverse experiences resulting in emergency medical treatment seeking following the use of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)". Journal of Psychopharmacology 36 (8): 956–964. August 2022. doi:10.1177/02698811221099650. PMID 35672900.
- ↑ Substance use – LSD, MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 21 May 2014, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000795.htm, retrieved 14 July 2016
- ↑ CESAR (29 October 2013), LSD, Center for Substance Abuse Research, University of Maryland, http://www.cesar.umd.edu/cesar/drugs/lsd.asp, retrieved 14 July 2016
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 "Subjective Reactions to Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD-25)". Archives of General Psychiatry 6 (5): 352–368. May 1962. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1962.01710230020003.
- ↑ "Characterizing the psychological state produced by LSD". Journal of Abnormal Psychology 73 (1): 1–14. February 1968. doi:10.1037/h0020114. PMID 5639999.
- ↑ "LSD produces place preference and flavor avoidance but does not produce flavor aversion in rats". Behavioral Neuroscience 110 (3): 503–508. June 1996. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.110.3.503. PMID 8888996.
- ↑ "Moiré patterns and visual hallucinations". Psychedelic Review 7: 33–40. 1966. https://maps.org/research-archive/psychedelicreview/n07/n07033osl.pdf.
- ↑ "LSD modulates music-induced imagery via changes in parahippocampal connectivity". European Neuropsychopharmacology 26 (7): 1099–1109. July 2016. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.03.018. PMID 27084302.
- ↑ "Hallucinogens – LSD, Peyote, Psilocybin, and PCP". NIDA InfoFacts. The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). June 2009. http://www.nida.nih.gov/infofacts/hallucinogens.html.
- ↑ "Ergot and its alkaloids". American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 70 (5): 98. October 2006. doi:10.5688/aj700598. PMID 17149427.
- ↑ "Drug harms in the UK: a multicriteria decision analysis". Lancet 376 (9752): 1558–1565. November 2010. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61462-6. PMID 21036393.
- ↑ "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse". Lancet 369 (9566): 1047–53. March 2007. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60464-4. PMID 17382831.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 56.3 56.4 56.5 56.6 56.7 56.8 "Hallucinogens". Pharmacology & Therapeutics 101 (2): 131–181. February 2004. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.11.002. ISSN 1879-016X. PMID 14761703.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 "Is LSD Toxic?". Forensic Science International 284: 141–145. March 2018. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.01.006. PMID 29408722.
- ↑ "Drug harms in the UK: a multicriteria decision analysis". Lancet 376 (9752): 1558–65. November 2010. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61462-6. PMID 21036393.
- ↑ "Psychedelics and mental health: a population study". PLOS ONE 8 (8). 2013-08-19. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063972. PMID 23976938. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...863972K.
- ↑ "What can we learn about schizophrenia from studying the human model, drug-induced psychosis?", American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B, Special Issue: Identifying the Origins of Mental Illness: A Festschrift in Honor of Ming T. Tsuang 162 (7): 661–670, October 2013, doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32177, PMID 24132898
- ↑ "Is Military Research Hazardous to Veterans Health? Lessons Spanning Half A Century, part F. HALLUCINOGENS". West Virginia: 103rd Congress, 2nd Session-S. Prt. 103-97; Staff Report prepared for the committee on veterans' affairs. December 8, 1994. http://www.gulfweb.org/bigdoc/rockrep.cfm#hallucinogens.
- ↑ "The effects of LSD on body sway suggestibility in a group of hospital patients". The British Journal of Psychiatry 113 (496): 277–280. March 1967. doi:10.1192/bjp.113.496.277. PMID 6029626. http://www.lycaeum.org/research/researchpdfs/1489.pdf.
- ↑ "The effects of psychotomimetic drugs on primary suggestibility". Psychopharmacologia 8 (4): 251–262. November 1965. doi:10.1007/BF00407857. PMID 5885648.
- ↑ "Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder: what do we know after 50 years?". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 69 (2): 109–19. March 2003. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(02)00306-X. PMID 12609692.
- ↑ "Flashback phenomena after administration of LSD and psilocybin in controlled studies with healthy participants". Psychopharmacology 239 (6): 1933–1943. January 2022. doi:10.1007/s00213-022-06066-z. PMID 35076721.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 A Review of Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD) and an Exploratory Study of Subjects Claiming Symptoms of HPPD.. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36. 2018. pp. 333–360. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_457. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2.
- ↑ "Psychedelics not linked to mental health problems or suicidal behavior: a population study". Journal of Psychopharmacology 29 (3): 270–279. March 2015. doi:10.1177/0269881114568039. PMID 25744618.
- ↑ (in de) Flashback-Phänomene als Nachwirkung von Halluzinogeneinnahme. Bewusstsein – Kognition – Erleben. 2. VWB Report. 2011. ISBN 978-3-86135-207-5. http://www.vwb-verlag.com/Katalog/m207.html. Retrieved June 9, 2023.
- ↑ "Stable quantitative EEG difference in post-LSD visual disorder by split-half analysis: evidence for disinhibition". Psychiatry Research 67 (3): 173–87. October 1996. doi:10.1016/0925-4927(96)02833-8. PMID 8912957.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 70.2 70.3 "Drug-interaction with psychotropic drugs". Psychedelics as Psychiatric Medications. Oxford University Press. 7 March 2023. ISBN 978-0-19-267852-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=7lazEAAAQBAJ. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- ↑ "Chapter 79 - Tolerance to Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: Overview, Correlates, and Clinical Implications". Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse. 2. Academic Press. 2016. pp. 848–849. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800212-4.00079-0. ISBN 978-0-12-800212-4.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 "A Single Dose of LSD Does Not Alter Gene Expression of the Serotonin 2A Receptor Gene (HTR2A) or Early Growth Response Genes (EGR1-3) in Healthy Subjects". Frontiers in Neuroscience 8. 28 June 2017. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00423. PMID 28701958.
- ↑ "Are psychedelics the answer to chronic pain: A review of current literature". Pain Practice 23 (4): 455. 4 January 2023. doi:10.1111/papr.13203. ISSN 1533-2500. PMID 36597700.
- ↑ "Cross tolerance between mescaline and LSD-25, with a comparison of the mescaline and LSD reactions". Psychopharmacologia 3: 1–14. March 1962. doi:10.1007/BF00413101. PMID 14007904. http://www.erowid.org/references/refs_view.php?A=ShowDocPartFrame&C=ref&ID=2032&DocPartID=1893. Retrieved December 1, 2007.
- ↑ "Cross tolerance between LSD and psilocybin". Psychopharmacologia 2 (3): 147–159. 1961. doi:10.1007/BF00407974. PMID 13717955. http://www.erowid.org/references/refs_view.php?A=ShowDocPartFrame&C=ref&ID=1979&DocPartID=1843. Retrieved December 1, 2007.
- ↑ "The effect of N,N-dimethyltryptamine in human subjects tolerant to lysergic acid diethylamide". Psychopharmacologia 5 (3): 223–224. 7 August 1963. doi:10.1007/BF00413244. PMID 14138757.
- ↑ "Gross behavioural changes in monkeys following administration of LSD-25, and development of tolerance to LSD-25". Psychopharmacologia 6 (4): 303–386. October 1964. doi:10.1007/BF00413161. PMID 4953438.
- ↑ "Influence of environmental context on tolerance to LSD-induced behavior in primates". Biological Psychiatry 21 (3): 314–317. March 1986. doi:10.1016/0006-3223(86)90053-3. PMID 3947713.
- ↑ "Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders". Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2009. pp. 375. ISBN 978-0-07-148127-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=PjgfBQAAQBAJ. Retrieved June 12, 2023. "Several other classes of drugs are categorized as drugs of abuse but rarely produce compulsive use. These include psychedelic agents, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)"
- ↑ "The mechanistic classification of addictive drugs". PLOS Medicine 3 (11). November 2006. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030437. PMID 17105338.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 "Modern Clinical Research on LSD". Neuropsychopharmacology 42 (11): 2114–2127. October 2017. doi:10.1038/npp.2017.86. PMID 28447622.
- ↑ "Acquired and crossed tolerance to mescaline, LSD-25, and BOL-148". Archives of General Psychiatry 1 (3): 279–282. September 1959. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1959.03590030063008. PMID 13796178.
- ↑ "Ayahuasca: Psychological and Physiologic Effects, Pharmacology and Potential Uses in Addiction and Mental Illness". Current Neuropharmacology 17 (2): 1–15. 2019. doi:10.2174/1570159X16666180125095902. ISSN 1875-6190. PMID 29366418.
- ↑ "The generalizability of the dependence syndrome across substances: an examination of some properties of the proposed DSM-IV dependence criteria". Addiction (Society for the Study of Addiction) 89 (9): 1105–1113. September 1994. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1994.tb02787.x. PMID 7987187.
- ↑ "Genetic toxicology of abused drugs: a brief review". Mutagenesis 13 (6): 557–65. November 1998. doi:10.1093/mutage/13.6.557. PMID 9862186.
- ↑ 86.0 86.1 86.2 "The risk of chronic psychedelic and MDMA microdosing for valvular heart disease". J Psychopharmacol 37 (9): 876–890. September 2023. doi:10.1177/02698811231190865. PMID 37572027.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 "Microdosing psychedelics and the risk of cardiac fibrosis and valvulopathy: Comparison to known cardiotoxins". J Psychopharmacol 38 (3): 217–224. March 2024. doi:10.1177/02698811231225609. PMID 38214279.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 "Cardiovascular effects and safety of classic psychedelics". Nat Cardiovasc Res 4 (2): 131–144. February 2025. doi:10.1038/s44161-025-00608-2. PMID 39910289.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 "Cardiovascular safety of psychedelic medicine: current status and future directions". Pharmacol Rep 75 (6): 1362–1380. December 2023. doi:10.1007/s43440-023-00539-4. PMID 37874530.
- ↑ "Serotonin 5-HT2B receptor agonism and valvular heart disease: implications for the development of psilocybin and related agents". Expert Opin Drug Saf 22 (10): 881–883. 2023. doi:10.1080/14740338.2023.2248883. PMID 37581427.
- ↑ "ACNP 63rd Annual Meeting: Poster Abstracts P609-P914: P680. Assessing the Potential Cardiovascular Risk of Microdosing Lysergic Acid Diethylamide in Mice". Neuropsychopharmacology 49 (Suppl 1): 418–594 (459–459). December 2024. doi:10.1038/s41386-024-02013-y. PMID 39643635.
- ↑ "Drugs of Abuse Affecting 5-HT2B Receptors". 5-HT2B Receptors. The Receptors. 35. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2021. pp. 277–289. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-55920-5_16. ISBN 978-3-030-55919-9.
- ↑ "Acute Effects and Pharmacokinetics of LSD after Paroxetine or Placebo Pre-Administration in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Cross-Over Phase I Trial". Clin Pharmacol Ther 117 (6): 1784–1792. February 2025. doi:10.1002/cpt.3618. PMID 40022427.
- ↑ "Drug-drug interactions involving classic psychedelics: A systematic review". J Psychopharmacol 38 (1): 3–18. January 2024. doi:10.1177/02698811231211219. PMID 37982394.
- ↑ "Genetic influence of CYP2D6 on pharmacokinetics and acute subjective effects of LSD in a pooled analysis". Sci Rep 11 (1). May 2021. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90343-y. PMID 34035391. Bibcode: 2021NatSR..1110851V.
- ↑ "Prevalence and associations of classic psychedelic-related seizures in a population-based sample". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 239. 1 October 2022. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2022.109586. PMID 35981469.
- ↑ "Grand mal seizures following ingestion of LSD". Western Journal of Medicine 106 (3): 201–211. 1967. PMID 4962683.
- ↑ 98.00 98.01 98.02 98.03 98.04 98.05 98.06 98.07 98.08 98.09 98.10 98.11 Toxicology and Pharmacological Interactions of Classic Psychedelics. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2024. doi:10.1007/7854_2024_508. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/7854_2024_508. Retrieved 14 May 2025.
- ↑ 99.00 99.01 99.02 99.03 99.04 99.05 99.06 99.07 99.08 99.09 "Is LSD toxic?". Forensic Sci Int 284: 141–145. March 2018. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.01.006. PMID 29408722.
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 100.2 100.3 100.4 100.5 100.6 100.7 100.8 "Hofmann vs. Paracelsus: Do Psychedelics Defy the Basics of Toxicology?-A Systematic Review of the Main Ergolamines, Simple Tryptamines, and Phenylethylamines". Toxics 11 (2): 148. February 2023. doi:10.3390/toxics11020148. PMID 36851023. Bibcode: 2023Toxic..11..148H.
- ↑ "Coma, hyperthermia and bleeding associated with massive LSD overdose. A report of eight cases". West J Med 120 (3): 183–188. March 1974. PMID 4816396.
- ↑ 102.0 102.1 102.2 "Coma, hyperthermia, and bleeding associated with massive LSD overdose, a report of eight cases". Clin Toxicol 8 (2): 191–203. 1975. doi:10.3109/15563657508988063. PMID 1149410.
- ↑ "Cocaine: history, social implications, and toxicity: a review". Semin Diagn Pathol 26 (1): 10–17. February 2009. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2008.12.001. PMID 19292024. "When "snorted," a typical "line" of cocaine contains approximately 50-100 mg of parent compound, although it is often "cut" or adulterated with other substances.20".
- ↑ "LSD Overdoses: Three Case Reports". J Stud Alcohol Drugs 81 (1): 115–118. January 2020. doi:10.15288/jsad.2020.81.115. PMID 32048609.
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 "Psychotomimetic Agents". Psychopharmacological Agents: Use, Misuse and Abuse. Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs. 4. Academic Press. 1976. pp. 59–146. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-290559-9.50011-9. ISBN 978-0-12-290559-9. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1016/B978-0-12-290559-9.50011-9. "The largest number of structural analogs of LSD that have been prepared involve the opening of one or more of the rings of the parent lysergic acid system. [...] A recent review covers this chemistry (Campaigne and Knapp, 1971), but there is apparently no human psychopharmacology as yet known."
- ↑ "Psychophysiological effects of a large non-experimental dose of LSD-25". Psychol Rep 19 (1): 287–290. August 1966. doi:10.2466/pr0.1966.19.1.287. PMID 5942100.
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 "The Psychotomimetic Agents". Progress in Drug Research / Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progrès des Recherches Pharmaceutiques. Basel: Birkhäuser Basel. 1971. pp. 68–102. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-7078-8_2. ISBN 978-3-0348-7080-1. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-0348-7078-8_2. Retrieved 2 June 2025.
- ↑ 108.0 108.1 "Serotonin toxicity of serotonergic psychedelics". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 239 (6): 1881–1891. June 2022. doi:10.1007/s00213-021-05876-x. PMID 34251464.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1 "Concomitant use of antidepressants and classic psychedelics: A scoping review". J Psychopharmacol: 2698811251368360. September 2025. doi:10.1177/02698811251368360. PMID 40937732. "Importantly, the idea of increased risk for developing serotonin syndrome and/or serotonin toxicity, when [antidepressants (ADs)] are co-administered with high doses of psychedelics, has recently been challenged, in part because classic psychedelics are partial agonists of the 5-HT2A receptor and would also compete for serotonin binding (Malcolm and Thomas, 2022; Rickli et al., 2016; Sarparast et al., 2022). Based on this clinical rationale, the concomitant use of ADs and classic psychedelics may be preferred, or patients could temporarily reduce the dose of ADs around dosing days with psychedelics to have minimal interactions. Simultaneously, the competition for 5-HT2A receptors could impede the biological action of psychedelics during concomitant use of ADs and potentially limit efficacy (Halman et al., 2024), particularly as the 5-HT2A receptor induces neuroplasticity (Cameron et al., 2023; Ly et al., 2018; Vargas et al., 2023).".
- ↑ 110.0 110.1 110.2 "Does getting high hurt? Characterization of cases of LSD and psilocybin-containing mushroom exposures to national poison centers between 2000 and 2016". J Psychopharmacol 32 (12): 1286–1294. December 2018. doi:10.1177/0269881118793086. PMID 30182795.
- ↑ "Molecular and clinical aspects of potential neurotoxicity induced by new psychoactive stimulants and psychedelics". Exp Neurol 343. September 2021. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113778. PMID 34090893.
- ↑ "Severe Neurological Sequelae after a Recreational Dose of LSD". J Anal Toxicol 45 (7): e1–e3. August 2021. doi:10.1093/jat/bkaa145. PMID 33031536.
- ↑ "Psychedelics, epilepsy, and seizures: a review". Front Pharmacol 14. 2023. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1326815. PMID 38283836.
- ↑ "Do classic psychedelics increase the risk of seizures? A scoping review". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 85: 35–42. August 2024. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2024.05.002. PMID 38917636.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 115.2 115.3 Handbook of Medical Hallucinogens. Guilford Publications. 2022. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-4625-5189-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=r46ZEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA81. Retrieved 10 July 2025.
- ↑ "Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: Its Effects on a Male Asiatic Elephant". Science (New York, N.Y.) 138 (3545): 1100–1103. December 1962. doi:10.1126/science.138.3545.1100. PMID 17772968. Bibcode: 1962Sci...138.1100J.
- ↑ 117.0 117.1 "LSD-induced effects in elephants: Comparisons with musth behavior". Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society 22 (1): 53–56. 1984. doi:10.3758/BF03333759. ISSN 0090-5054. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.3758%2FBF03333759.pdf. Retrieved 10 July 2025.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 118.2 118.3 LSD Toxicity Treatment & Management~treatment at eMedicine
- ↑ 119.0 119.1 "NBOMes-Highly Potent and Toxic Alternatives of LSD". Front Neurosci 14. 2020. doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.00078. PMID 32174803.
- ↑ "Constructing drug effects: A history of set and setting" (in en). Drug Science, Policy and Law 3. 2017. doi:10.1177/2050324516683325. ISSN 2050-3245.
- ↑ "Toxicities associated with NBOMe ingestion-a novel class of potent hallucinogens: a review of the literature". Psychosomatics 56 (2): 129–139. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.psym.2014.11.002. PMID 25659919.
- ↑ "25X-NBOMe compounds - chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. A comprehensive review". Crit Rev Toxicol 53 (1): 15–33. January 2023. doi:10.1080/10408444.2023.2194907. PMID 37115704.
- ↑ "Neurochemical pharmacology of psychoactive substituted N-benzylphenethylamines: High potency agonists at 5-HT2A receptors". Biochemical Pharmacology 158: 27–34. December 2018. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.09.024. PMID 30261175.
- ↑ "Analysis of 25I-NBOMe, 25B-NBOMe, 25C-NBOMe and Other Dimethoxyphenyl-N-[(2-Methoxyphenyl) MethylEthanamine Derivatives on Blotter Paper"]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology 39 (8): 617–623. Oct 2015. doi:10.1093/jat/bkv073. PMID 26378135.
- ↑ "Neurochemical and Behavioral Profiling in Male and Female Rats of the Psychedelic Agent 25I-NBOMe". Frontiers in Pharmacology 10. 12 December 2019. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01406. PMID 31915427.
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 126.2 "NBOMe Toxicity and Fatalities: A Review of the Literature". Transformative Medicine 1 (1): 12–18. March 2022. doi:10.54299/tmed/msot8578. ISSN 2831-8978.
- ↑ 127.0 127.1 "Correlating the Metabolic Stability of Psychedelic 5-HT2A Agonists with Anecdotal Reports of Human Oral Bioavailability". Neurochemical Research 39 (10): 2018–2023. 14 February 2014. doi:10.1007/s11064-014-1253-y. PMID 24519542.
- ↑ "Pharmacology and Toxicology of N-Benzylphenethylamine ("NBOMe") Hallucinogens". Neuropharmacology of New Psychoactive Substances. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 32. Springer. 18 January 2017. pp. 283–311. doi:10.1007/7854_2016_64. ISBN 978-3-319-52444-3.
- ↑ "Analysis of 25 C NBOMe in Seized Blotters by HPTLC and GC–MS". Journal of Chromatographic Science 54 (7): 1153–1158. August 2016. doi:10.1093/chromsci/bmw095. PMID 27406128.
- ↑ "25C-NBOMe: preliminary data on pharmacology, psychoactive effects, and toxicity of a new potent and dangerous hallucinogenic drug". BioMed Research International 2014. 3 July 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/734749. PMID 25105138.
- ↑ "Pharmacology and toxicology of N-Benzyl-phenylethylamines (25X-NBOMe) hallucinogens". Novel Psychoactive Substances: Classification, Pharmacology and Toxicology (2nd ed.). Academic Press. September 2021. pp. 279–300. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-818788-3.00008-5. ISBN 978-0-12-818788-3.
- ↑ "A cluster of 25B-NBOH poisonings following exposure to powder sold as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)". Clinical Toxicology 60 (8): 966–969. 28 March 2022. doi:10.1080/15563650.2022.2053150. PMID 35343858.
- ↑ "Échele Cabeza as a harm reduction project and activist movement in Colombia" (in en). Drugs, Habits and Social Policy 23 (3): 263–276. November 2022. doi:10.1108/DHS-07-2022-0026. ISSN 2752-6739. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/DHS-07-2022-0026/full/html.
- ↑ "Development and validation of a color spot test method for the presumptive detection of 25-NBOMe compounds". Drug Testing and Analysis 13 (5): 929–943. May 2021. doi:10.1002/dta.2905. PMID 32744773.
- ↑ 135.0 135.1 "PDSP Database" (in zu). https://pdsp.unc.edu/databases/pdsp.php?testFreeRadio=testFreeRadio&testLigand=lsd&kiAllRadio=all&doQuery=Submit+Query.
- ↑ "BindingDB BDBM21342 (4R,7R)-N,N-diethyl-6-methyl-6,11-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.0^{2,7}.0^{12,16}hexadeca-1(16),2,9,12,14-pentaene-4-carboxamide::CHEMBL263881::LSD::LSD 25::LSD,(+)::LSD,l-::Lysergic Acid Diethylamide::Lysergic Acid Diethylamide Tartrate::US20240166618, Compound LSD::[3H]-LSD::d-Isolysergic acid amide"]. https://www.bindingdb.org/rwd/bind/chemsearch/marvin/MolStructure.jsp?monomerid=21342.
- ↑ "Psychedelics and the human receptorome". PLOS ONE 5 (2). February 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009019. PMID 20126400. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...5.9019R.
- ↑ "Receptor interaction profiles of novel N-2-methoxybenzyl (NBOMe) derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxy-substituted phenethylamines (2C drugs)". Neuropharmacology 99: 546–553. December 2015. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.08.034. PMID 26318099. http://edoc.unibas.ch/56163/1/20170921163006_59c3cceeb8e5d.pdf.
- ↑ "Receptor interaction profiles of novel psychoactive tryptamines compared with classic hallucinogens". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 26 (8): 1327–1337. August 2016. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.05.001. PMID 27216487. http://edoc.unibas.ch/53326/1/20170117174852_587e4af45b658.pdf.
- ↑ "Monoamine receptor interaction profiles of 4-thio-substituted phenethylamines (2C-T drugs)". Neuropharmacology 134 (Pt A): 141–148. May 2018. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.012. PMID 28720478. https://edoc.unibas.ch/57358/1/20170920150712_59c2680084ec5.pdf.
- ↑ "Behavioral and neurochemical pharmacology of six psychoactive substituted phenethylamines: mouse locomotion, rat drug discrimination and in vitro receptor and transporter binding and function". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231 (5): 875–888. March 2014. doi:10.1007/s00213-013-3303-6. PMID 24142203. PMC 3945162. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258061356.
- ↑ "Mefloquine and psychotomimetics share neurotransmitter receptor and transporter interactions in vitro". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231 (14): 2771–2783. July 2014. doi:10.1007/s00213-014-3446-0. PMID 24488404.
- ↑ "Agonist high and low affinity state ratios predict drug intrinsic activity and a revised ternary complex mechanism at serotonin 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors". Synapse 35 (2): 144–150. February 2000. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(200002)35:2<144::AID-SYN7>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID 10611640.
- ↑ "Crystal Structure of an LSD-Bound Human Serotonin Receptor". Cell 168 (3): 377–389.e12. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.033. PMID 28129538.
- ↑ McCorvy JD (16 January 2013). Mapping the binding site of the 5-HT2A receptor using mutagenesis and ligand libraries: Insights into the molecular actions of psychedelics (Ph.D. thesis). Purdue University. Archived from the original on 25 March 2025 – via Purdue e-Pubs.
Table 5.2 Binding affinities using 3 H-LSD at 5-HT2A EL2 mutants [...] Table B.1 Binding affinities for 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, 5-HT1A receptors using 3 H-LSD [...]
Alt URL - ↑ "Functional characterization of agonists at recombinant human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors in CHO-K1 cells". Br J Pharmacol 128 (1): 13–20. September 1999. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702751. PMID 10498829.
- ↑ "Trace Amines and Their Receptors". Pharmacol Rev 70 (3): 549–620. July 2018. doi:10.1124/pr.117.015305. PMID 29941461.
- ↑ "In Vitro Characterization of Psychoactive Substances at Rat, Mouse, and Human Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 357 (1): 134–144. April 2016. doi:10.1124/jpet.115.229765. PMID 26791601. https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/74120533/eae6c6e62565b82d46b4d111bbea0f77b9c2-libre.pdf?1635931703=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DIn_Vitro_Characterization_of_Psychoactiv.pdf&Expires=1746838268&Signature=Sy4fJ90yUhxs68314NxYsW5PAaNrBGePRu35WRR4PIF-3YC7Z~sLdnCn5wfqqbLg9bDEGdt~oW55ugMP3D3jgA0BoRI~~GOb0NQOwrtfUEQK1PQs1uuN9qg5Y1ct8z5NsABm44RgtukkwRMdU6fO7OlfIsQ68hOiFk129Ll7UYqldxD2f1xhE2fTTfsxSpb8cMCJzHn7-ItqLdwnAUPFK7WggDIjmY1kCnaHLwIxMwdJCAq8L6DYzSTg7pZkbR8qlou~GXbTPQt~gYpyZTJp5hgW-7V6K5wLlQ7Z2xE7B0f9wEfuc1W1QNafg125Tr-vvAe4LEGKXV58bnn1bpfWKw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA.
- ↑ "Multiple receptors contribute to the behavioral effects of indoleamine hallucinogens". Neuropharmacology 61 (3): 364–381. September 2011. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.017. PMID 21256140.
- ↑ "Distinct temporal phases in the behavioral pharmacology of LSD: dopamine D2 receptor-mediated effects in the rat and implications for psychosis". Psychopharmacology 180 (3): 427–435. July 2005. doi:10.1007/s00213-005-2183-9. PMID 15723230.
- ↑ 151.0 151.1 "Persistence of lysergic acid diethylamide in the plasma of human subjects". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 5 (5): 611–614. 1964. doi:10.1002/cpt196455611. PMID 14209776. http://www.maps.org/w3pb/new/1964/1964_aghajanian_2224_1.pdf.
- ↑ "5-HT5 receptors". Current Drug Targets. CNS and Neurological Disorders 3 (1): 53–58. February 2004. doi:10.2174/1568007043482606. PMID 14965244.
- ↑ "Metabotropic glutamate mGlu2 receptor is necessary for the pharmacological and behavioral effects induced by hallucinogenic 5-HT2A receptor agonists". Neuroscience Letters 493 (3): 76–79. April 2011. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.01.046. PMID 21276828.
- ↑ "Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 320 (1): 1–13. January 2007. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.104463. PMID 16803859. https://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/320/1/1. Retrieved June 11, 2023.
- ↑ "Serotonin and hallucinogens". Neuropsychopharmacology 21 (2 Suppl): 16S–23S. August 1999. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00135-3. PMID 10432484.
- ↑ "DARPP-32 mediates the actions of multiple drugs of abuse". The AAPS Journal 7 (2): E353-60. October 2005. doi:10.1208/aapsj070235. PMID 16353915.
- ↑ 157.0 157.1 "Hallucinogenic 5-HT2AR agonists LSD and DOI enhance dopamine D2R protomer recognition and signaling of D2-5-HT2A heteroreceptor complexes". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 443 (1): 278–84. January 2014. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.104. PMID 24309097. Bibcode: 2014BBRC..443..278B.
- ↑ "Antagonism of histamine-activated adenylate cyclase in brain by D-lysergic acid diethylamide". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 74 (12): 5697–701. December 1977. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.12.5697. PMID 23536. Bibcode: 1977PNAS...74.5697G.
- ↑ 159.0 159.1 "Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 45 (19): 4344–9. September 2002. doi:10.1021/jm020153s. PMID 12213075.
- ↑ 160.0 160.1 "A Receptor on Acid". Cell 168 (3): 339–341. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.012. PMID 28129534.
- ↑ 161.0 161.1 161.2 "Psychedelics as Transformative Therapeutics". Am J Psychiatry 180 (5): 340–347. May 2023. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.20230172. PMID 37122272. https://cdr.lib.unc.edu/downloads/37720q20d. "We now have molecular-level details regarding how psychedelic drugs interact with and activate 5-HT2A receptors (39) (Figure 2B). Studies on a related serotonin receptor (5-HT2B) have clarified how LSD can stabilize distinct signaling complexes (40, 41). A key finding of these studies was the discovery that once LSD binds to the 5-HT2A receptor, a lid is formed over the binding pocket, which "traps" LSD for several hours (39, 40) (Figure 2B). These findings imply that at least part of the reason for the long duration of action of drugs like LSD is the trapping of the receptor via conformational changes that occur after drug binding. These studies also showed that this prolonged action of LSD is due in part to a specific residue within the binding pocket, which is found in humans but not in mice or rats (39). This residue (Ser242) also is essential for the high-affinity interactions of LSD, psilocybin, and perhaps other such drugs at the human and nonhuman primate 5-HT2A receptors.".
- ↑ 162.0 162.1 "Crystal Structure of an LSD-Bound Human Serotonin Receptor". Cell 168 (3): 377–389.e12. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.033. PMID 28129538.
- ↑ "Correlation between the potency of hallucinogens in the mouse head-twitch response assay and their behavioral and subjective effects in other species". Neuropharmacology 167. May 2020. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107933. PMID 31917152. PMC 9191653. http://usdbiology.com/cliff/Courses/Advanced%20Seminars%20in%20Neuroendocrinology/Serotonergic%20Psychedelics%2020/Halberstadt%2020%20Neuropharm%20potency%20of%20hallucinogens%20%20head-twitch.pdf.
- ↑ 164.0 164.1 164.2 "LSD and Its Lysergamide Cousins". The Heffter Review of Psychedelic Research (Heffter Research Institute) 2: 80–87. 2001. ISSN 1534-9640. https://www.heffter.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/chap6.pdf. "Indeed, the potency of LSD at the 5-HT2A receptor is not as great as that of some of the amphetamine hallucinogens such as DOB or DOI, yet its human potency is about ten times greater. [...] Furthermore, there is a cavity within these receptors that accommodates and is complementary to the activating drug, in this case LSD. What we are forced to conclude is that the area within the receptor that binds to the diethylamide function of LSD is a specific region that must be just large enough to contain the diethyl groups. [...]".
- ↑ 165.0 165.1 165.2 165.3 "Chemistry/structural biology of psychedelic drugs and their receptor(s)". Br J Pharmacol. October 2024. doi:10.1111/bph.17361. PMID 39354889.
- ↑ "Trace Amine-Associated Receptor 1 Agonists for Schizophrenia: Emerging Health Technologies". Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK603600/#:~:text=TAAR1%20agonism%20has%20been%20shown,regulating%20dopamine%20and%20glutamate%20activity.&text=More%20specifically%2C%20it%20modulates%20midbrain%20dopaminergic%20hyperactivity%20and%20cortical%20glutamatergic%20hypoactivity.
- ↑ 167.0 167.1 "Towards an understanding of psychedelic-induced neuroplasticity". Neuropsychopharmacology 48 (1): 104–112. January 2023. doi:10.1038/s41386-022-01389-z. PMID 36123427.
- ↑ "The Effects of Psychedelics on Neuronal Physiology". Annu Rev Physiol 86: 27–47. February 2024. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-042022-020923. PMID 37931171.
- ↑ "Psychedelics promote plasticity by directly binding to BDNF receptor TrkB". Nat Neurosci 26 (6): 1032–1041. June 2023. doi:10.1038/s41593-023-01316-5. PMID 37280397.
- ↑ "The polypharmacology of psychedelics reveals multiple targets for potential therapeutics". Neuron 113 (19): 3129–3142.e9. July 2025. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2025.06.012. PMID 40683247. https://www.cell.com/cms/10.1016/j.neuron.2025.06.012/attachment/7d8365fe-51f3-4a28-bf40-9999bec837f6/mmc11.pdf. "Recent studies have suggested that psychedelics such as LSD directly interact with TrkB with high affinity, promoting BDNF-mediated neuroplasticity and antidepressant-like effects via allosteric potentiation of BDNF signaling in active synapses.8 To investigate this, we screened LSD across 450 human kinases, including TrkB, but found no significant interactions between LSD and any tested human kinases. Further experiments in transfected cells revealed no effect of LSD or psilocin on BDNF-mediated activation of a TrkB reporter. We note that similar negative preliminary results, which have not yet been published in a peer-reviewed journal, were recently reported by Boltaev et al.63".
- ↑ 171.0 171.1 171.2 Matthias Liechti (2016), "Pharmacology of novel psychoactive substances, MDMA, and LSD", Department of Biomedicine. Report 2014–2016: pp. 52–53, https://biomedizin.unibas.ch/fileadmin/user_upload/biomedizin/research/fg_liechti_psychopharmacology_research/DBM_Report_2014-2016_liechti.pdf, "LSD produced subjective drug effects that lasted up to 12h (Fig. 3a) and correlated well with the concentrations of LSD in the blood plasma over time (Fig. 3b and c). The half-life of LSD in plasma was 3.5 h. In contrast to LSD, the half-life of MDMA is longer (8h) but the effects of MDMA last only up to 6h despite the continued presence of the substance in the body (Fig. 3d). Thus, there is marked acute tolerance to the effects of MDMA. [...] Fig. 3: Pharmacokinetics-Pharmacodynamics of LSD. LSD effects last up to 12h (a) corresponding to its plasma-concentration time curve (b) and exhibiting no hysteresis in the LSD concentration-effect plot (c). In contrast, the MDMA concentration-effect plot shows pronounced hysteresis consistent with acute tolerance (d)."
- ↑ "The structural diversity of psychedelic drug actions revealed". Nature Communications 16 (1). March 2025. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-57956-7. PMID 40108183. Bibcode: 2025NatCo..16.2734G.
- ↑ "Structures of Hallucinogenic and Non-Hallucinogenic Analogues of the 5-HT2A Receptor Reveals Molecular Insights into Signaling Bias". University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Department of Pharmacology Research Retreat September 16th, 2022 – William and Ida Friday Center. September 2022. https://www.med.unc.edu/pharm/wp-content/uploads/sites/930/2022/07/COMPLETE-PHARM-RETREAT-PROGRAM-2022-UPDATE.pdf#page=37.
- ↑ 174.0 174.1 "Neural correlates of the LSD experience revealed by multimodal neuroimaging". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 113 (17): 4853–4858. 11 April 2016. doi:10.1073/pnas.1518377113. PMID 27071089. Bibcode: 2016PNAS..113.4853C.
- ↑ "Receptor-informed network control theory links LSD and psilocybin to a flattening of the brain's control energy landscape". Nat Commun 13 (1). Oct 2022. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33578-1. PMID 36192411. Bibcode: 2022NatCo..13.5812S.
- ↑ "Spatial Correspondence of LSD-Induced Variations on Brain Functioning at Rest With Serotonin Receptor Expression". Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging 8 (7): 768–776. July 2023. doi:10.1016/j.bpsc.2023.03.009. PMID 37003409.
- ↑ 177.0 177.1 "LSD-induced changes in the functional connectivity of distinct thalamic nuclei". NeuroImage 283. Dec 2023. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120414. PMID 37858906.
- ↑ 178.00 178.01 178.02 178.03 178.04 178.05 178.06 178.07 178.08 178.09 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedDolderSchmidHaschke2015 - ↑ 179.0 179.1 179.2 179.3 179.4 179.5 179.6 179.7 179.8 "From Psychiatry to Flower Power and Back Again: The Amazing Story of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide". Assay and Drug Development Technologies 14 (5): 276–281. July 2016. doi:10.1089/adt.2016.747. PMID 27392130.
- ↑ 180.0 180.1 180.2 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedArikciHolzeMueller2025 - ↑ "Oral LSD base and tartrate bioequivalence and absolute bioavailability in healthy participants". Neuroscience Applied 3. 2024. doi:10.1016/j.nsa.2024.105132.
- ↑ 182.0 182.1 182.2 "Regional localization of lysergic acid diethylamide in monkey brain". Nature 209 (5028): 1093–1095. March 1966. doi:10.1038/2091093a0. PMID 4958949. Bibcode: 1966Natur.209.1093S. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/18209711.
- ↑ "Pharmacological Action of LSD: LSD Effect on the Neurotransmission and Animal Behavior". Handbook of Substance Misuse and Addictions. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 2022. pp. 2457–2475. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-92392-1_131. ISBN 978-3-030-92391-4. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-030-92392-1_131. Retrieved 7 June 2025.
- ↑ 184.0 184.1 184.2 "Profiles of Psychedelic Drugs: LSD". J Psychedelic Drugs 12 (2): 173–174. 1980. doi:10.1080/02791072.1980.10471571. PMID 7420434.
- ↑ "Neural correlates of the LSD experience revealed by multimodal neuroimaging". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113 (17): 4853–8. April 2016. doi:10.1073/pnas.1518377113. PMID 27071089. PMC 4855588. Bibcode: 2016PNAS..113.4853C. https://www.carhartharrislab.com/s/LSD_PNAS_paper_2016.pdf.
- ↑ 186.0 186.1 Dolder P (2017). The Pharmacology of d-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) (PDF) (Thesis). University of Basel. p. 112. doi:10.5451/UNIBAS-006786123. Retrieved 3 June 2025.
- ↑ "Metabolism of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD): an update". Drug Metab Rev 51 (3): 378–387. August 2019. doi:10.1080/03602532.2019.1638931. PMID 31266388.
- ↑ 188.0 188.1 188.2 "Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion pharmacogenomics of drugs of abuse". Pharmacogenomics 12 (2): 215–233. February 2011. doi:10.2217/pgs.10.171. PMID 21332315. "It is rapidly metabolized to the following five metabolites which have been identified in urine or blood from human users: N-demethyl-LSD (nor-LSD), 2-oxoLSD, 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD, 13-hydroxyLSD and 14-hydroxy-LSD [187–189]. The 13- and 14-hydroxy metabolites are additionally excreted as glucuronides [188]. [...] 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD was shown to be the main human urinary metabolite with concentrations four- to 40-times higher than that of LSD [187,188,191]. As concluded by Yu in his review on indolalkylamines, almost nothing is known regarding the contribution of specific drug-metabolizing enzymes to the production of individual LSD metabolites in humans.".
- ↑ 189.0 189.1 189.2 "Drugs of Abuse (Including Designer Drugs)". Metabolism of Drugs and Other Xenobiotics. Wiley. 18 April 2012. pp. 429–463. doi:10.1002/9783527630905.ch16. ISBN 978-3-527-32903-8. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9783527630905.ch16. Retrieved 7 June 2025. "[LSD] is metabolized to the following five metabolites: N-demethyl-LSD (nor-LSD), 2-oxo-LSD, 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD, 13-hydroxy-LSD, and 14-hydroxy-LSD [72–74]. The 13- and 14-hydroxy metabolites are additionally excreted as glucuronides [74]. 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD was shown to be the main human urinary metabolite with concentrations 4–40 times higher than that of LSD [73–75]. In incubations of LSD with human liver microsomes and hepatocytes, 2,3-dihydroxy-LSD could be identified [71]. So far, the contribution and importance of specific enzymes in the formation of the LSD main metabolites such as 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD still remains unclear."
- ↑ "Cytochrome P450 enzymes contribute to the metabolism of LSD to nor-LSD and 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD: Implications for clinical LSD use". Biochem Pharmacol 164: 129–138. June 2019. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.04.013. PMID 30981875.
- ↑ "Measurement of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in human plasma by gas chromatography/negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry" (PDF). Journal of Analytical Toxicology 14 (3): 189–190. May–June 1990. doi:10.1093/jat/14.3.189. PMID 2374410. http://www.erowid.org/references/refs_view.php?A=ShowDocPartFrame&C=ref&ID=6265&DocPartID=6624.
- ↑ 192.0 192.1 192.2 192.3 192.4 192.5 Alexander T. Shulgin; Ann Shulgin (1997). "#26. LSD-25 Acid; Lysergide; D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide; Meth-LAD; D-Lysergamide, N,N-Diethyl; N,N-Diethyl-D-Lysergamide; 9,10-Didehydro-N,N-Diethyl-6-Methylergoline-8b-Carboxamide". TiHKAL: The Continuation (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. pp. 490–499. ISBN 978-0-9630096-9-2. OCLC 38503252. https://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/tihkal/tihkal26.shtml.
- ↑ "LSD" (in en). Handbook of Medical Hallucinogens. Guilford Publications. 2021. pp. 160. ISBN 978-1-4625-4545-2. https://mcb.berkeley.edu/labs2/presti/sites/mcb.berkeley.edu.labs2.presti/files/u3/2021%20LSD%20Chapter%20Panik%20Presti.pdf. Retrieved March 14, 2024.
- ↑ "Stereoselective LSD-like activity in a series of d-lysergic acid amides of (R)- and (S)-2-aminoalkanes". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 38 (6): 958–66. March 1995. doi:10.1021/jm00006a015. PMID 7699712.
- ↑ "The Total Synthesis of Lysergic Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society 78 (13): 3087–3114. 1956. doi:10.1021/ja01594a039. Bibcode: 1956JAChS..78.3087K.
- ↑ "Total synthesis of (+/-)-lysergic acid, lysergol, and isolysergol by palladium-catalyzed domino cyclization of amino allenes bearing a bromoindolyl group". Organic Letters 10 (22): 5239–42. November 2008. doi:10.1021/ol8022648. PMID 18956869. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/2663242.
- ↑ ((National University of Singapore, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine)) (10 February 2022). "Harvesting baker's yeast for aging-related therapeutics". https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/02/220210154135.htm. Journal Reference: "Reconstituting the complete biosynthesis of D-lysergic acid in yeast". Nature Communications 13 (1). February 2022. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28386-6. PMID 35132076. Bibcode: 2022NatCo..13..712W.
- ↑ "Stability study of LSD under various storage conditions". Journal of Analytical Toxicology 22 (6): 520–5. October 1998. doi:10.1093/jat/22.6.520. PMID 9788528.
- ↑ "Lysergide (LSD) drug profile". https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/drug-profiles/lsd_en.
- ↑ 200.0 200.1 "Motivation and the behavioral effects of LSD" (in en). Psychonomic Science 12 (7): 305–306. July 1968. doi:10.3758/BF03331322. ISSN 0033-3131.
- ↑ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 12th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2020, pp. 1197–1199.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide in Healthy Subjects". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 56 (10): 1219–1230. October 2017. doi:10.1007/s40262-017-0513-9. PMID 28197931.
- ↑ 203.0 203.1 "Concentrations of LSD, 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD, and iso-LSD in hair segments of 18 drug abusers". Forensic Science International 344. March 2023. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2023.111578. PMID 36753839.
- ↑ 204.0 204.1 204.2 "Basic Pharmacology and Effects". Hallucinogens: A Forensic Drug Handbook. Forensic Drug Handbook Series. Elsevier Science. 2003. pp. 67–137. ISBN 978-0-12-433951-4. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=6bb3a7499da8e9852b39cd4db16891147c83f5c6. Retrieved 1 February 2025.
- ↑ 205.0 205.1 "Structure-activity relationships of the classic hallucinogens and their analogs". NIDA Res Monogr 146: 74–91. 1994. PMID 8742795. https://archives.nida.nih.gov/sites/default/files/monograph146.pdf#page=79.
- ↑ 206.0 206.1 "Chemistry of Psychotomimetics". Psychotropic Agents, Part III: Alcohol and Psychotomimetics, Psychotropic Effects of Central Acting Drugs. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 55 / 3. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1982. pp. 3–29. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-67770-0_1. ISBN 978-3-642-67772-4. OCLC 8130916. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1007/978-3-642-67770-0_1.
- ↑ 207.0 207.1 Alexander T. Shulgin (1980). "Hallucinogens". Burger's Medicinal Chemistry. 3 (4 ed.). New York: Wiley. pp. 1109–1137. ISBN 978-0-471-01572-7. OCLC 219960627. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=6ac0c892ee380436f614d3aae0686ef617b2e0c5.
- ↑ Mangner TJ (1978). Potential Psychotomimetic Antagonists. N,n -diethyl-1-methyl-3-aryl-1, 2, 5, 6-tetrahydropyridine-5-carboxamides (Ph.D. thesis). University of Michigan. doi:10.7302/11268. Archived from the original on 30 March 2025.
- ↑ "Chemical Background". Ergot Alkaloids and Related Compounds. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology (HEP). 49. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1978. pp. 29–85. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66775-6_2. ISBN 978-3-642-66777-0.
- ↑ "Some Compounds With Hallucinogenic Activity". Ergot Alkaloids and Related Compounds. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology (HEP). 49. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1978. pp. 567–614. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66775-6_8. ISBN 978-3-642-66777-0. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/8769.
- ↑ "Stimulant and hallucinogenic novel psychoactive substances; an update". Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 16 (11): 1109–1123. 2023. doi:10.1080/17512433.2023.2279192. PMID 37968919.
- ↑ "The use of prodrugs as drugs of abuse". WIREs Forensic Science 6 (3). 2024. doi:10.1002/wfs2.1514. ISSN 2573-9468.
- ↑ 213.0 213.1 "Lysergamides revisited". NIDA Res Monogr 146: 52–73. 1994. PMID 8742794. https://archives.nida.nih.gov/sites/default/files/monograph146.pdf#page=57.
- ↑ 214.0 214.1 "Structure–activity relationships of serotonin 5-HT 2A agonists". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling 1 (5): 559–579. 2012. doi:10.1002/wmts.42. ISSN 2190-460X. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=e28e0e22c3145af5a787c34fbedbaa8f81e1ed6b. Retrieved 22 March 2025.
- ↑ Nichols DE (May 1973). Potential Psychotomimetics: Bromomethoxyamphetamines and Structural Congeners of Lysergic Acid (Thesis). University of Iowa. p. 23. OCLC 1194694085.
- ↑ "Structural analogs of lysergic acid". J Pharm Sci 60 (6): 809–814. June 1971. doi:10.1002/jps.2600600602. PMID 4942861. Bibcode: 1971JPhmS..60..809C.
- ↑ Olsen DE, Dunlap L, Wagner F, Chytil M, Powell NA, "Ergoline-like compounds for promoting neural plasticity", WO patent 2021076572, published 22 April 2021, assigned to Delix Therapeutics, Inc.and The Regents of the University of California
- ↑ "Molecular design of a therapeutic LSD analogue with reduced hallucinogenic potential". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 122 (16). April 2025. doi:10.1073/pnas.2416106122. PMID 40228113. Bibcode: 2025PNAS..12216106T.
- ↑ Dunlap L (2022). "Chapter 5. An Analog of LSD With Antipsychotic Potential". Development of Non-Hallucinogenic Psychoplastogens (PDF) (Ph.D. thesis). University of California, Davis. pp. 105–114.
- ↑ 220.0 220.1 LSD—My Problem Child. McGraw-Hill. 1980. ISBN 0-07-029325-2. http://www.psychedelic-library.org/child.htm. Retrieved April 19, 2010.
- ↑ 221.0 221.1 221.2 221.3 LSD, my problem child: reflections on sacred drugs, mysticism, and science (4th ed.). Santa Cruz, CA: Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies. 2009. ISBN 978-0-9798622-2-9. OCLC 610059315.
- ↑ 222.0 222.1 222.2 222.3 222.4 222.5 Acid dreams: the complete social history of LSD: the CIA, the Sixties, and beyond. New York: Grove Weidenfeld. 1992. ISBN 0-8021-3062-3. OCLC 25281992.
- ↑ (in en) Psychopharmacology. Psychology Press. 2017. p. 226. ISBN 978-1-351-97870-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=XT4lDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA226. Retrieved September 27, 2021.
- ↑ "Flashback: LSD Creator Albert Hofmann Drops Acid for the First Time" (in en-US). Rolling Stone. 2018-04-19. https://www.rollingstone.com/culture/culture-news/flashback-lsd-creator-albert-hofmann-drops-acid-for-the-first-time-629085/. Retrieved 2025-02-10.
- ↑ "Biological Psychiatry in the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries". History of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology. Boston, MA: Springer US. 2008. pp. 381–418. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-34708-0_12. ISBN 978-0-387-34707-3. https://www.timothydavidson.com/Library/Books/Wallace-2008-History%20of%20Psychiatry%20and%20Medical%20Psychology/Wallace%20and%20Gach-2008-History%20of%20Psychiatry%20and%20Medical%20Psychology.pdf#page=413. "In 1938 the Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann produced lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)—the first, and most prominent, of these chemically synthesized agents—in the course of a systematic investigation of partially synthetic amides of lysergic acid in the Sandoz Pharmaceutical Laboratories in Basel (Hofmann 1970). [Taking] LSD by accident in 1943, Hofmann discovered its psychoactivity. He then experimented with it on himself and found that it produced a peculiar restlessness, extreme activity of the imagination, and an uninterrupted stream of images. Hofmann did not publish the results of his experiment, though he became quite famous later. Hofmann and Arthur Stoll, the head of the Sandoz pharmaceutical laboratory in Basle, published the first paper on the synthesis of LSD in 1943, while Stoll went on to publish the first paper on the effects of lysergic diethylamide acid in 1947. [...] Stoll, Arthur and Hofmann, Albert. 1943. Partialsynthese von Alkaloiden vom Typus des Ergobasins. Helv. Chim. Acta 26:944. Stoll, Arthur. 1947. Lysergsäure-diäthylamid, ein Phantastikum aus der Mutterkorngruppe. Schweiz. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 60:279. [The first paper on the hallucinogenic effect of LSD.]"
- ↑ Michael Horowitz (July 1976). "Interview: Albert Hofmann". High Times (11): 24–28, 31, 81. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/13725. "High Times: Why was it four years from your discovery of the psychic effects of LSD [in 1943] until your report was published? [...] Hofmann: [...] After confirmation of the action of this extraordinary compound by volunteers of the Sandoz staff, Professor Arthur Stoll, who was then head of the Sandoz pharmaceutical department, asked me if I would permit his son, Werner A. Stoll—who was starting his career at the psychiatric hospital of the University of Zurich—to submit this new agent to a fundamental psychiatric study on normal volunteers and on psychiatric patients. This investigation took a rather long time, [...] This excellent and comprehensive study was not published until 1947.".
- ↑ "Partialsynthese von Alkaloiden vom Typus des Ergobasins. (6. Mitteilung über Mutterkornalkaloide)". Helvetica Chimica Acta 26 (3): 944–965. 3 May 1943. doi:10.1002/hlca.19430260326. ISSN 0018-019X. Bibcode: 1943HChAc..26..944S.
- ↑ "11. Lysergsäure-diäthylamid, ein Phantastikum aus der Mutterkorngruppe". Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie und Psychiatrie 60: 279–323. 1947. ISSN 0258-7661. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/16963.
- ↑ "Ein neues, in sehr kleinen Mengen wirksames Phantastikum". Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie und Psychiatrie 64: 483–484. 1949. ISSN 0258-7661. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/16676.
- ↑ "Autistic schizophrenic children. An experiment in the use of d-lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25)". Archives of General Psychiatry 6 (3): 203–213. March 1962. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1962.01710210019003. PMID 13894863.
- ↑ "Modification of autistic behavior with LSD-25". The American Journal of Psychiatry 122 (11): 1201–1211. May 1966. doi:10.1176/ajp.122.11.1201. PMID 5325567.
- ↑ "Flashback to the 1960s: LSD in the treatment of autism". Developmental Neurorehabilitation 10 (1): 75–81. 2007. doi:10.1080/13638490601106277. PMID 17608329.
- ↑ "The use of LSD (d-lysergic acid diethylamide) in the therapy of children (a brief review)". The Journal of Asthma Research 5 (2): 139–143. December 1967. doi:10.3109/02770906709104325. PMID 4865578.
- ↑ "Psychiatric Research with Hallucinogens". https://www.druglibrary.org/schaffer/lsd/grob.htm.
- ↑ "French bread spiked with LSD in CIA experiment" (in en). 2010-03-11. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/france/7415082/French-bread-spiked-with-LSD-in-CIA-experiment.html.
- ↑ "Pont-Saint-Esprit poisoning: Did the CIA spread LSD?" (in en-GB). BBC News. 2010-08-23. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-10996838.
- ↑ "Trends in LSD use among US adults: 2015–2018". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 212. July 2020. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.108071. PMID 32450479.
- ↑ "LSD Ganz Persönlich" (in de). MAPS 6 (69). Summer 1969. http://www.maps.org/news-letters/v06n3/06346hof.html.
- ↑ (in en) Medicinal Chemistry: A Molecular and Biochemical Approach. Oxford University Press. 2005. p. 342. ISBN 978-0-19-028296-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=TNXeDAAAQBAJ&pg=PT342. Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ↑ "Hypothesis on Albert Hofmann's Famous 1943 "Bicycle Day"". May 24, 2003. http://www.erowid.org/general/conferences/conference_mindstates4_nichols.shtml.
- ↑ "History Of LSD". http://www.a1b2c3.com/drugs/lsd01.htm.
- ↑ 242.0 242.1 242.2 LSD in the United States (Report). U.S. Department of Justice, Drug Enforcement Administration. Oct 1995.
- ↑ The Search for the Manchurian Candidate: The CIA and Mind Control. U.S.A.: Times Books. 1978. p. 57. ISBN 07139-12790.
- ↑ "The CIA's Secret Quest For Mind Control: Torture, LSD And A 'Poisoner In Chief'" (in en). https://www.npr.org/2019/09/09/758989641/the-cias-secret-quest-for-mind-control-torture-lsd-and-a-poisoner-in-chief.
- ↑ (in English) The Search for The Manchurian Candidate: The CIA and Mind Control. Times Books. 1978. p. 97.
- ↑ "How LSD was popularized". Druglibrary.org. 1972. http://www.druglibrary.org/schaffer/Library/studies/cu/CU50.html.
- ↑ "Did The Death Of Communism Take Koestler And Other Literary Figures With It?". The Huffington Post. 26 January 2010. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2010/01/26/did-the-death-of-communis_n_435939.html.
- ↑ "Out-Of-Sight! SMiLE Timeline". http://pages.cthome.net/tobelman/The_Out-Of-Sight_SMiLE_Site.html.
- ↑ The Communal Experience: Anarchist and Mystical Communities in Twentieth-Century America. Chicago IL: University of Chicago Press. 1978. p. 437. ISBN 0-226-85458-2.
- ↑ United States Congress (October 24, 1968). "Staggers-Dodd Bill, Public Law 90-639". http://www.erowid.org/psychoactives/law/law_fed_staggers-dodd.pdf.
- ↑ "Psycholytic Therapy with MDMA and LSD in Switzerland". 1994. http://www.maps.org/news-letters/v05n3/05303psy.html.
- ↑ "Oregon becomes first state to legalize magic mushrooms as more states ease drug laws in 'psychedelic renaissance'". November 4, 2020. https://www.cnbc.com/2020/11/04/oregon-becomes-first-state-to-legalize-magic-mushrooms-as-more-states-ease-drug-laws.html.
- ↑ Turn On Your Mind: Four Decades of Great Psychedelic Rock. Milwaukie, Michigan: Hal Leonard. 2003. pp. 8–9. ISBN 0-634-05548-8.
- ↑ "Show 41 – The Acid Test: Psychedelics and a sub-culture emerge in San Francisco. [Part 1]: UNT Digital Library" (audio). Digital.library.unt.edu. 1969. https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc19800/m1/.
- ↑ Sixties Rock: Garage, Psychedelic, and Other Satisfactions Music in American Life. Chicago, IL: University of Illinois Press. 2000. p. 60. ISBN 0-252-06915-3.
- ↑ Turn on and Tune in: Psychedelics, Narcotics and Euphoriants. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2009. p. 87. ISBN 978-1-84755-909-8.
- ↑ "OBITUARY — Ron Thelin". 1996-03-22. https://www.sfgate.com/news/article/OBITUARY-Ron-Thelin-2989153.php.
- ↑ "The business of getting high: head shops, countercultural capitalism, and the marijuana legalization movement.". The Sixties 8 (1): 27–49. January 2015. doi:10.1080/17541328.2015.1058480.
- ↑ White Hand Society - The Psychedelic Partnership of Timothy Leary and Allen Ginsberg. City Lights Books. 2010. p. 148. ISBN 978-0-87286-535-8. https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780872865358/page/148.
- ↑ "Acute Effects of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide in Healthy Subjects" (in English). Biological Psychiatry 78 (8): 544–553. 2015-10-15. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.11.015. ISSN 0006-3223. PMID 25575620. http://edoc.unibas.ch/42234/1/20160316150932_56e9691c51f97.pdf.
- ↑ LSD — The Problem-Solving Psychedelic. http://www.psychedelic-library.org/staf3.htm.
- ↑ 262.0 262.1 Heads: A Biography of Psychedelic America. Da Capo Press. 2016. ISBN 978-0-306-82255-1.
- ↑ "Beatles' Acid Test: How LSD Opened the Door to 'Revolver'". Rolling Stone. August 25, 2016. https://www.rollingstone.com/feature/beatles-acid-test-how-lsd-opened-the-door-to-revolver-251417/. Retrieved December 9, 2021.
- ↑ Immigration and American Popular Culture: an Introduction. New York, NY: New York University Press. 2007. pp. 162–4. ISBN 978-0-8147-7552-3.
- ↑ Legends of Rock Guitar: the Essential Reference of Rock's Greatest Guitarists. London: Hal Leonard Corporation, 1997. 1997. p. 48. ISBN 0-7935-4042-9.
- ↑ 266.0 266.1 All We Are Saying: The Last Major Interview with John Lennon and Yoko Ono. New York: St. Martin's Press. 2000. ISBN 978-0-312-25464-3. https://archive.org/details/allwearesayingla00lenn.
- ↑ "The New Far-Out Beatles". Life (Chicago: Time Inc.): 101. 16 June 1967. https://books.google.com/books?id=lVYEAAAAMBAJ&pg=101. Retrieved 8 Dec 2016.
- ↑ Keith Haring: Journey of the Radiant Baby. Bunker Hill Publishing. 2006. p. 25. ISBN 1-59373-052-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=PElY27UXXkYC. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ↑ Daisy Jones (5 June 2017). "Why Certain Drugs Make Specific Genres Sound So Good". Vice. https://www.vice.com/en/article/why-drugs-genres-match-mdma-raves-shrooms-psychedelia-rap-lean/.
- ↑ Kendall Deflin (22 June 2017). "Phishin' With Matisyahu: How LSD "Turned My Entire World Inside Out"". https://liveforlivemusic.com/features/phish-matisyahu-nyc/.
- ↑ "How LSD influenced Western culture". October 17, 2018. https://www.bbc.com/culture/article/20181016-how-lsd-influenced-western-culture.
- ↑ "Final act of the United Nations Conference". UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances. 1971. http://www.unodc.org/pdf/convention_1971_en.pdf.
- ↑ "Poisons Standard". Therapeutic Goods Administration. Australian Government Department of Health. July 2016. https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/F2017L00057.
- ↑ "Misuse of Drugs Act 1981". Government of Western Australia. 18 November 2015. http://www.slp.wa.gov.au/pco/prod/FileStore.nsf/Documents/MRDocument:28280P/$FILE/Misuse%20Of%20Drugs%20Act%201981%20-%20%5B06-e0-00%5D.pdf?OpenElement.
- ↑ Canadian government (1996). "Controlled Drugs and Substances Act". Canadian Department of Justice. http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/C-38.8/page-26.html#h-30.
- ↑ "Drugs and the law: Report of the inquiry into the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971". Runciman Report. London: Police Foundation. 2000. http://www.druglibrary.org/schaffer/Library/studies/runciman/pf3.htm.
- ↑ "After the War on Drugs: Blueprint for Regulation". Transform Drug Policy Foundation. 2009. http://www.tdpf.org.uk/blueprint%20download.htm.
- ↑ Neal v. United States, 516 U.S. 284 (1996). , originating from U.S. v. Neal, 46 F.3d 1405 (7th Cir. 1995)
- ↑ "California Lawmakers Approve Bill To Legalize Psychedelics Possession In Committee" (in en-US). 2021-06-29. https://www.marijuanamoment.net/california-lawmakers-approve-bill-to-legalize-psychedelics-possession-in-committee/.
- ↑ "Ley de Narcomenudeo" (in es). El Pensador. 17 October 2009. http://www.elpensador.com.mx/2009/10/17/Ley-de-Narcomenudeo/.
- ↑ (in cs) Explanatory Report to Act No. 112/1998 Coll., which amends the Act No. 140/1961 Coll., the Criminal Code, and the Act No. 200/1990 Coll., on misdemeanors (Report). Prague: Parliament of the Czech Republic. 1998.
- ↑ Supreme Court of the Czech Republic (25 February 2012), 6 Tdo 156/2010 [NS 7078/2010]
- ↑ 283.0 283.1 DEA (2007). "LSD Manufacture – Illegal LSD Production". U.S. Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration. https://fas.org/irp/agency/doj/dea/product/lsd/lsd-5.htm.
- ↑ "Willy Myco Just Released the First-Ever Video Demonstrating How to Synthesize LSD" (in en-US). 2024-12-18. https://doubleblindmag.com/willy-myco-lsd-synthesis-in-pakistan/.
- ↑ 285.0 285.1 285.2 "Chapter 1 – The LSD Family". Psychedelics Encyclopaedia (3rd ed.). Ronin Publishing. 1992. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-914171-51-5.
- ↑ 286.0 286.1 286.2 "Chapter 2.2 – Forms of the Drug". Hallucinogens: A Forensic Drug Handbook. Academic Press. 2003. pp. 39–41. ISBN 978-0-12-433951-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=l1DrqgobbcwC. Retrieved May 12, 2020.
- ↑ "Street Terms: Drugs and the Drug Trade". Office of National Drug Control Policy. April 5, 2005. http://www.whitehousedrugpolicy.gov/streetterms/ByType.asp?intTypeID=6.
- ↑ DEA (2008). "Photo Library (page 2)". US Drug Enforcement Administration. http://www.usdoj.gov/dea/photo_library2.html#lsd.
- ↑ (in en) Health & Drugs: Disease, Prescription & Medication. Nicolae Sfetcu. 2014. p. 1958. https://books.google.com/books?id=8jF-AwAAQBAJ&dq=acid+blotter+art&pg=PA1958. Retrieved 2023-07-14.
- ↑ "LSD-25 and mescaline as therapeutic adjuvants.". The Use of LSD in Psychotherapy and Alcoholism. New York: Bobbs-Merrill. 1967. pp. 407–426.
- ↑ "Evaluating LSD as a psychotherapeutic agent". A program for the treatment of alcoholism: LSD, malvaria, and nicotinic acid. pp. 353–402.
- ↑ Orange Sunshine: The Brotherhood of Eternal Love and Its Quest to Spread Peace, Love, and Acid to the World. Thomas Dunne Books. 2010. ISBN 978-0-312-55183-4. https://archive.org/details/orangesunshinebr00scho_0.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (October 2005). "LSD Blotter Acid Mimic Containing 4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-amphetamine (DOB) Seized Near Burns, Oregon". Microgram Bulletin 38 (10). http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2005/mg1005.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (November 2006). "Intelligence Alert – Blotter Acid Mimics (Containing 4-Bromo-2,5-Dimethoxy-Amphetamine (DOB)) in Concord, California". Microgram Bulletin 39 (11): 136. http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2006/mg1106.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (March 2008). "Unusual "Rice Krispie Treat"-Like Balls Containing Psilocybe Mushroom Parts in Warren County, Missouri". Microgram Bulletin 41 (3). http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2008/mg0308.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Temporary Class Drug Order Report on 5-6APB and NBOMe compounds". Gov.Uk. May 29, 2013. p. 14. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/204808/J_TCDO_report_on_5-6APB_and_NBOMe_compounds.pdf.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (March 2009). ""Spice" – Plant Material(s) Laced With Synthetic Cannabinoids or Cannabinoid Mimicking Compounds". Microgram Bulletin 42 (3). http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2009/mg0309.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (November 2005). "Bulk Marijuana in Hazardous Packaging in Chicago, Illinois". Microgram Bulletin 38 (11). http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2005/mg1105.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ United States Drug Enforcement Administration (December 2007). "SMALL HEROIN DISKS NEAR GREENSBORO, GEORGIA". Microgram Bulletin 40 (12). http://www.justice.gov/dea/pr/micrograms/2007/mg1207.pdf. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ Erowid. "25I-NBOMe (2C-I-NBOMe) Fatalities / Deaths". Erowid. https://www.erowid.org/chemicals/2ci_nbome/2ci_nbome_death.shtml.
- ↑ "New drug N-bomb hits the street, terrifying parents, troubling cops". New York Daily News. May 6, 2013. http://www.nydailynews.com/news/national/new-synthetic-hallucinogen-n-bomb-killing-users-cops-article-1.1336327.
- ↑ "Powerful N-Bomb drug – responsible for spate of deaths internationally – responsible for hospitalisation of six in Cork". Irish Independent. January 21, 2016. http://www.independent.ie/irish-news/powerful-nbomb-drug-responsible-for-spate-of-deaths-internationally-responsible-for-hospitalisation-of-six-in-cork-34384507.html.
- ↑ "Temporary Class Drug Order Report on 5-6APB and NBOMe compounds". Gov.Uk. May 29, 2013. https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/204808/J_TCDO_report_on_5-6APB_and_NBOMe_compounds.pdf.
- ↑ "Famous LSD users". The Good Drugs Guide. http://www.thegooddrugsguide.com/articles/famous_users/lsd.htm.
- ↑ "People on psychedelics". http://popwiki.net.
- ↑ "Review: Awe for Auden". The Hudson Review (The Hudson Review, Inc.) 68 (3): 492–500. Autumn 2015.
- ↑ "W. H. Auden at Swathmore; An hour of questions and answers with Auden". Exhibition notes from the W.H. Auden Collection. the Swarthmore College Library. 15 November 1971. http://www.swarthmore.edu/library/auden/QandA_pt6.html.
- ↑ "A Master of Memorable speech". The Irish Times. 17 February 2007. https://www.irishtimes.com/news/a-master-of-memorable-speech-1.1195982.
- ↑ "The Impossible Reality of James Cameron" (in en-US). 2010-01-10. https://rollingstoneindia.com/james-cameron/.
- ↑ "Daniel Ellsberg Talks Psychedelics, Consciousness and World Peace" (in en-US). 2022-01-24. https://www.lucid.news/daniel-ellsberg-talks-psychedelics-consciousness-and-world-peace/.
- ↑ Surely You're Joking, Mr. Feynman!: Adventures of a Curious Character. W. W. Norton. 1985. ISBN 978-0-393-01921-6. OCLC 10925248.
- ↑ Genius: The Life and Science of Richard Feynman. Pantheon Books. 1992. ISBN 978-0-679-40836-9. OCLC 243743850.
- ↑ "Q&A with Jerry Garcia: Portrait of an Artist as a Tripper". Relix Magazine. April 20, 2010. http://www.relix.com/features/2010/04/20/q-a-with-jerry-garcia-portrait-of-an-artist-as-a-tripper?3.
- ↑ "The Bill Gates Interview". Playboy. July 1994. http://www.playboy.com/playground/view/50-years-of-the-playboy-interview-bill-gates.
- ↑ "Aldous Huxley's LSD Death Trip". Open Culture. October 2011. http://www.openculture.com/2011/10/aldous_huxleys_lsd_death_trip.html.
- ↑ "The Steve Jobs Reading List: The Books And Artists That Made The Man". Huffington Post. 21 October 2011. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2011/10/21/the-steve-jobs-reading-list-the-books_n_1024021.html.
- ↑ "LSD, My Problem Child · Radiance from Ernst Junger". http://www.psychedelic-library.org/child7.htm.
- ↑ "Is 'Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds' Code for LSD?". 1998-02-15. https://www.snopes.com/fact-check/lucy-in-the-sky-with-diamonds/.
- ↑ "The Truth Behind "LSD"". The Weekly Standard. June 2004. https://www.washingtonexaminer.com/weekly-standard/the-truth-behind-lsd. Retrieved November 3, 2019.
- ↑ "When Michel Foucault Tripped on Acid in Death Valley and Called It "The Greatest Experience of My Life"" (in en-US). September 1975. http://www.openculture.com/2017/09/when-michel-foucault-tripped-on-acid-in-death-valley-and-called-it-the-greatest-experience-of-my-life-1975.html.
- ↑ "Blowing The Philosopher's Fuses: Michel Foucault's LSD Trip in The Valley of Death" (in en-US). June 17, 2019. https://lareviewofbooks.org/article/blowing-the-philosophers-fuses-michel-foucaults-lsd-trip-in-the-valley-of-death/. Wade: "We fell silent to listen to Stockhausen's Songs of Youth. Zabriskie Point was filled with the sound of a kindergarten playground overlaid with electric tonalities. Kontakte followed. Glissandos bounced off the stars, which glowed like incandescent pinballs. Foucault turned to Michael and said this is the first time he really understood what Stockhausen had achieved".
- ↑ Foucault in California: [A True Story-–Wherein the Great French Philosopher Drops Acid in the Valley of Death]. Heyday Books. 2019. ISBN 978-1-59714-463-6. In a letter to Wade, dated 16 September 1978, Foucault authorised the book's publication and added: "How could I not love you?"
- ↑ "LSD: The Geek's Wonder Drug?". Wired. 2006-01-16. https://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/2006/01/70015. Retrieved 2008-03-11. "Like Herbert, many scientists and engineers also report heightened states of creativity while using LSD. During a press conference on Friday, Hofmann revealed that he was told by Nobel-prize-winning chemist Kary Mullis that LSD had helped him develop the polymerase chain reaction that helps amplify specific DNA sequences.".
- ↑ "'There is no such thing as past or future': physicist Carlo Rovelli on changing how we think about time". 2018-04-14. http://www.theguardian.com/books/2018/apr/14/carlo-rovelli-exploding-commonsense-notions-order-of-time-interview.
- ↑ Hallucinations. Vintage Books. 2012. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-307-94743-7. https://www.oliversacks.com/books-by-oliver-sacks/hallucinations/. Retrieved June 30, 2018. "On the West Coast in the early 1960s LSD and morning glory seeds were readily available, so I sampled those, too."
- ↑ "When Trey Parker and Matt Stone went to the Oscars on LSD Swapnil Dhruv Bose". December 27, 2021. https://faroutmagazine.co.uk/when-trey-parker-and-matt-stone-went-to-the-oscars-on-lsd/.
- ↑ "Flashback: Psychiatric Experimentation with LSD in Historical Perspective.". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 50 (7). 1965.
- ↑ Cohen, S. (1959). "The therapeutic potential of LSD-25". A Pharmacologic Approach to the Study of the Mind, p. 251–258.
- ↑ "Use of d-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide in the Treatment of Alcoholism". Q. J. Stud. Alcohol 20 (3): 577–590. 1959. doi:10.15288/qjsa.1959.20.577. PMID 13810249. http://www.erowid.org/references/texts/show/1852docid1733. Retrieved June 20, 2012. Via "Abstract". http://www.hofmann.org/papers/blewett_1.html.
- ↑ "LSD helps to treat alcoholism". Nature News. 2012-03-09. doi:10.1038/nature.2012.10200. http://www.nature.com/news/lsd-helps-to-treat-alcoholism-1.10200. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ↑ 331.0 331.1 331.2 "LSD-Assisted Psychotherapy". http://www.maps.org/research/psilo-lsd.
- ↑ "The Albert Hofmann Foundation". http://www.hofmann.org/.
- ↑ "Studying the effects of classic hallucinogens in the treatment of alcoholism: rationale, methodology, and current research with psilocybin". Current Drug Abuse Reviews 6 (1): 17–29. March 2013. doi:10.2174/15733998113099990002. PMID 23627783.
- ↑ (in en) LSD Therapy for Persons Suffering From Major Depression - Full Text View. February 8, 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03866252. Retrieved 2021-03-09.
- ↑ "Psychedelics are transforming the way we understand depression and its treatment". The Guardian. April 20, 2021. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/apr/20/psychedelics-depression-treatment-psychiatry-psilocybin.
- ↑ "Psychiater Gasser bricht sein Schweigen". Basler Zeitung. July 28, 2009. http://bazonline.ch/wissen/medizin-und-psychologie/Psychiater-Gasser-bricht-sein-Schweigen/story/25732295.
- ↑ "The neurobiology of psychedelic drugs: implications for the treatment of mood disorders". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 11 (9): 642–51. September 2010. doi:10.1038/nrn2884. PMID 20717121.
- ↑ "Classical hallucinogens as antidepressants? A review of pharmacodynamics and putative clinical roles". Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology 4 (4): 156–69. August 2014. doi:10.1177/2045125314527985. PMID 25083275.
- ↑ "Therapeutic Use of LSD in Psychiatry: A Systematic Review of Randomized-Controlled Clinical Trials". Frontiers in Psychiatry 10. January 2020. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00943. PMID 32038315.
- ↑ 340.0 340.1 340.2 340.3 "Single Treatment With MM120 (Lysergide) in Generalized Anxiety Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA 334 (15): 1358–1372. September 2025. doi:10.1001/jama.2025.13481. PMID 40906494.
- ↑ Perrone, Matthew (September 4, 2025). "LSD shows promise for reducing anxiety in drugmaker's midstage study". https://apnews.com/article/lsd-psychedelics-study-anxiety-fda-drugs-trump-8821f7f3683051506d47864db5e5edcf.
- ↑ "Psychedelics promote structural and functional neural plasticity". Cell Reports 23 (11): 3170–3182. 2018. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.022. PMID 29898390.
- ↑ "Towards an understanding of psychedelic-induced neuroplasticity". Neuropsychopharmacology 48 (1): 104–112. January 2023. doi:10.1038/s41386-022-01389-z. PMID 36123427.
- ↑ "Biochemical Mechanisms Underlying Psychedelic-Induced Neuroplasticity". Biochemistry 61 (3): 127–136. February 2022. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00812. PMID 35060714.
- ↑ Moncrieff, Joanna (16 January 2025). "Alternative Approaches: The Good, the Bad and the Worrying: Psychedelics for Depression". Chemically Imbalanced: The Making and Unmaking of the Serotonin Myth. Flint. ISBN 978-1-80399-680-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=e0MkEQAAQBAJ. Retrieved 16 October 2025.
- ↑ "Psychedelics could treat some of the worst chronic pain in the world" (in en-US). 2024-05-15. https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/2024/5/15/24156372/psychedelics-chronic-pain-cluster-headache-medicine-lsd-psilocybin.
- ↑ "RFA-AG-25-004: Safety and Early Efficacy Studies of Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy for Chronic Pain in Older Adults (UG3/UH3 Clinical Trial Required)". https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/rfa-files/RFA-AG-25-004.html.
- ↑ "Lysergic acid diethylamide and psilocybin for the management of patients with persistent pain: a potential role?". Pain Management 8 (3): 217–229. May 2018. doi:10.2217/pmt-2017-0068. PMID 29722608. http://eprints.leedsbeckett.ac.uk/4843/1/LysergicAcidDiethylamide%28LSD%29andPsilocybinAM-JOHNSON.pdf. Retrieved August 22, 2020.
- ↑ "Is it time to revisit the role of psychedelic drugs in enhancing human creativity?". Journal of Psychopharmacology 22 (8): 821–827. November 2008. doi:10.1177/0269881108091597. PMID 18562421.
- ↑ "LSD and creativity". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs 21 (1): 129–134. 1989. doi:10.1080/02791072.1989.10472150. PMID 2723891. http://www.erowid.org/culture/characters/janiger_oscar/janiger_oscar.shtml.
- ↑ LSD, the problem-solving psychedelic. 1967. http://www.psychedelic-library.org/staf3.htm.
- ↑ "Scientific Problem Solving with Psychedelics – James Fadiman" (in en). May 29, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KtL5fafpRKc.
- ↑ The psychedelic explorer's guide: safe, therapeutic, and sacred journeys. Tantor Media. 2018. ISBN 978-1-9773-7476-9. OCLC 1031461623.
Further reading
- Albert Hofmann (1980). LSD: My Problem Child. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-029325-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=e5wQAQAAIAAJ.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to LSD. |
- "Lysergide (LSD)". European Union Drugs Agency (EUDA). https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/drug-profiles/lsd_en.
Documentaries
- Hofmann's Potion a documentary on the origins of LSD, 2002
- Inside LSD National Geographic Channel, 2009
- How to Change Your Mind Netflix docuseries, 2022
Template:Psychedelics Template:Navboxes
 |




