Chemistry:Lysergamides
Lysergamides, also known as ergoamides[1][2][3] or as lysergic acid amides, are amides of lysergic acid (LA). They are ergolines, with some lysergamides being found naturally in ergot as well as other fungi. Lysergamides are notable in containing embedded phenethylamine and tryptamine moieties within their ergoline ring system.[4]
The simplest lysergamides are ergine (lysergic acid amide; LSA) and isoergine (iso-lysergic acid amide; iso-LSA). In terms of pharmacology, the lysergamides include numerous serotonin and dopamine receptor agonists, most notably the psychedelic drug lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) but also a number of pharmaceutical drugs like ergometrine, methylergometrine, methysergide, and cabergoline.[5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17] Various analogues of LSD, such as the psychedelics ALD-52 (1A-LSD), ETH-LAD, LSZ, and 1P-LSD and the non-hallucinogenic 2-bromo-LSD (BOL-148), have also been developed. Ergopeptines like ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, and bromocriptine are also lysergamides, but with addition of a small peptide moiety at the amide. Close analogues of lysergamides that are not technically lysergamides themselves include lisuride, terguride, bromerguride, and JRT.
Lysergamides were first discovered and described in the 1930s.[18][19][20]
Simplified or partial ergolines and lysergamides, such as NDTDI (8,10-seco-LSD), DEMPDHPCA, and N-DEAOP-NMT, are also known.[21][22][23]
Use and effects
The doses, potencies, durations, and effects of lysergamides have been reviewed by Alexander Shulgin.[24][25][26][27][28] They have also been reviewed by Albert Hofmann,[29] David E. Nichols,[30] and other researchers.[31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39]
| Common name | Code | Dose | Potency (×LSD) | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lysergic acid amide (LSA; ergine) | LA-111 | 500–6,000 μg | ≤10% | ~4–10 hours |
| Isolysergic acid amide (iso-LSA; isoergine) | Iso-LA-819 | 2,000–5,000 μg | <10% | ~4–10 hours |
| Lysergic acid methylamide | LAM | ~500 μg | ≤20% | ? |
| Lysergic acid dimethylamide | DAM-57 | 500–1,200 μg | 10% | ? |
| Lysergic acid ethylamide (LAE) | LAE-32 | 500–1,600 μg | ≤10% | ? |
| 1-Acetyl-LAE | ALA-10, 1A-LAE | ~1,200 μg | ≤10% | ? |
| 1-Methyl-LAE | MLA-74 | ~2,000 μg | 5% | ? |
| Lysergic acid methylethylamide | LME-54 | ? | ~33% | ? |
| Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) | LSD-25, METH-LAD | 50–200 μg | 100% | 8–12 hours |
| Isolysergic acid diethylamide | Iso-LSD | >4,000 μg | <2% | ? |
| l-Lysergic acid diethylamide | l-LSD | >10,000 μg | <1% | ? |
| l-Isolysergic acid diethylamide | l-Iso-LSD | >500 μg | <5% | ? |
| 2,3-Dihydro-LSD | 2,3-DH-LSD | ~150–400 μg | ~15% | ~8–12 hours |
| 9,10-Dihydro-LSD | 9,10-DH-LSD | >2,500 μg | <2% | ? |
| 10-Hydroxy-9,10-dihydro-LSD | Lumi-LSD | ? | <1% | ? |
| 2-Bromo-LSD | BOL-148 | >1,000 μg (≥6,000 μg) | <10% (≤2%) | ? |
| 2-Iodo-LSD | IOL | ? | ? | ? |
| 2-Oxo-LSD (2-oxy-LSD) | – | >300 μg | ? | ? |
| 1-Acetyl-LSD | ALD-52, 1A-LSD | 100–200 μg | 100% | ~8–12 hours[40] |
| 1-Methyl-LSD | MLD-41 | 200–300 μg | 30% | ? |
| 1-Hydroxymethyl-LSD | OML-632 | ? | ~70% | ? |
| 1-Propionyl-LSD | 1P-LSD | 100–200 μg | 100% | ~8–12 hours[41][40] |
| 1-Methyl-2-bromo-LSD | MBL-61, MOB-61 | >10,000 μg | <1% | ? |
| 1-Methyl-2-iodo-LSD | MIL | ? | ? | ? |
| Lysergic acid propylamide | LAP | >500 μg | <20% | ? |
| Lysergic acid methylpropylamide | LMP-55; LAMPA; MPLA | >100 μg | <100% | ? |
| Lysergic acid ethylpropylamide | LEP-57; EPLA | ? | ~33% | ? |
| Lysergic acid methylisopropylamide | MiPLA | 180–300 μg | ~33–50% | ? |
| Lysergic acid dipropylamide | DPL | >1,000 μg | <10% | ? |
| Lysergic acid dibutylamide | LBB-66 | ? | 0% | ? |
| Lysergic acid diallylamide | DAL | >1,000 μg | <10% | ? |
| Ergonovine (ergometrine)a | – | 5,000–10,000 μg | ≤1% | ? |
| Methylergonovine (methylergometrine)b | – | 2,000 μg | 5% | ? |
| Propisergidec | PML-946 | >3,000 μg | ? | ? |
| Methysergided | UML-491 | 4,000–8,000 μg | 2% | ? |
| Lysergic acid piperidide | LA-Pip | ? | ? | ? |
| Lysergic acid pyrrolidide (LPD) | LPD-824 | ~800 μg | 5–10% | ? |
| Lysergic acid pyrrolinide | LPN | ? | ? | ? |
| 1-Methyl-LPD | MPD-75 | >1,600 μg | ≤10% | ? |
| Lysergic acid morpholide | LSM-775, SLM | 300–600 μg | 10–30% | ? |
| Lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide | LA-SS-Az, LSZ | 100–300 μg | 50% | ~4–10 hours[41] |
| Nor-LSD (6-nor-LSD) | H-LAD | >500 μg | <20% | ? |
| 6-Ethyl-nor-LSD | ETH-LAD | 40–150 μg | 200% | 8–12 hours |
| 6-Propyl-nor-LSD | PRO-LAD | 80–200 μg | 100% | 6–8 hours |
| 6-Allyl-nor-LSD | AL-LAD, ALLY-LAD | 50–160 μg | 100% | 6–8 hours |
| 6-n-Butyl-nor-LSD | BU-LAD | ≥400–500 μg | <30% | ? |
| 6-Propynyl-nor-LSD | PARGY-LAD | 160–500 μg | 20–60% | ? |
| 6-(β-Phenethyl)-nor-LSD | PHENETH-LAD | >350–500 μg | <30% | ? |
| Footnotes: a = Ergonovine is lysergic acid hydroxyisopropylamide. b = Methylergonovine is lysergic acid hydroxy-sec-butylamide. c = Propisergide is 1-methylergonovine. d = Methysergide is 1-methylmethylergonovine. Refs: Main: [24][25][26][27][28][42][43][44][38][39][18][32][33][36][35][45][41] Additional: [17][40][46][47][48][49] | ||||
The properties of various additional lysergamides, for instance in terms of serotonin antagonism, have also been described.[50]
Interactions
History

Lysergamides, such as ergine, isoergine, and ergometrine, were discovered by the early 1930s,[18][19][20] and LSD was discovered by 1938 and its hallucinogenic effects in 1943 by Albert Hofmann.[51][52] Many synthetic lysergamide analogues of LSD, modified at the amide and/or 1 or 2 positions, were first described by Hofmann and colleagues in the mid-to-late 1950s.[29][34][42][53] N(6)-Substituted lysergamides were first reported in 1970 and thereafter in the 1970s and 1980s by multiple groups, including Hofmann and colleagues, Yuji Nakahara and Tetsukichi Niwaguchi and colleagues, and David E. Nichols and colleagues.[54][55][56][6] The psychedelic effects of N(6)-substituted lysergamides were reported by Alexander Shulgin in 1986 and thereafter.[57][37][25][28] Additional novel lysergamides modified at the amide, like LA-3Cl-SB and LA-Aziridine, were described by Nichols and Robert Oberlender and colleagues in the late 1980s,[58][37][54] while LSZ (LA-Azetidine) was described by the same group in 2002.[9] Numerous 1-substituted LSD prodrugs such as 1P-LSD and 1V-LSD and other psychedelic lysergamides were developed by Lizard Labs in the 2010s and 2020s.[59][60][61]
List of lysergamides
| Structure | Name (synonyms) | CAS # | R1 | R6 | R2 | R3 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
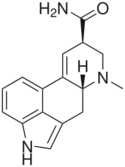 |
Ergine (lysergic acid amide, lysergamide) | 478-94-4 | H | CH3 | H | H | - |
 |
Isoergine (isolysergic acid amide, isolysergamide) | 2889-26-1 | H | CH3 | H | H | 8-epi |
 |
LAM (lysergic acid methylamide) | 50485-06-8 | H | CH3 | CH3 | H | - |
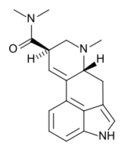 |
DAM-57 (lysergic acid dimethylamide) | 4238-84-0 | H | CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | - |
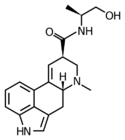 |
Ergometrine (ergonovine; lysergic acid propanolamide) | 60-79-7 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
 |
Propisergide (1-methylergonovine; PML-946) | 5793-04-4 | CH3 | CH3 | CH(CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
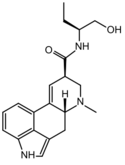 |
Methylergometrine (methylergonovine; lysergic acid butanolamide) | 113-42-8 | H | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
 |
Methysergide (1-methyl-lysergic acid butanolamide; UML-491) | 361-37-5 | CH3 | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | H | - |
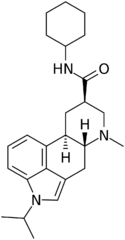 |
Amesergide (LY-237733; 9,10-dihydro-11-isopropyllysergic acid cyclohexylamide) | 121588-75-8 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | C6H11 | H | - |
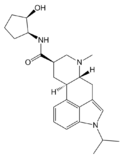 |
LY-215840 (1-isopropyl-9,10-dihydro-N-(2-hydroxycyclopent-anyl)lysergamide) | 137328-52-0 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | C5H8OH | H | - |
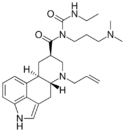 |
Cabergoline (N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-6-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-9,10-dihydrolysergamide) | 81409-90-7 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | CONHCH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH2N(CH3)2 | - |
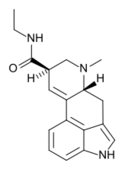 |
LAE-32 (lysergic acid ethylamide) | 478-99-9 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | H | - |
 |
LAP (lysergic acid propylamide) | ? | H | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | H | - |
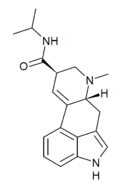 |
iPLA (lysergic acid isopropylamide; LAiP) | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | H | - | |
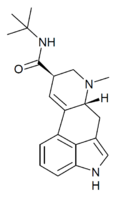 |
LAtB (lysergic acid tert-butylamide) | H | CH3 | C(CH3)3 | H | - | |
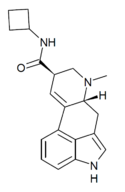 |
LAcB (lysergic acid cyclobutylamide) | H | CH3 | (CH2)4 | H | - | |
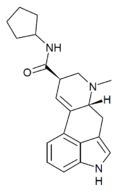 |
Cepentil (lysergic acid cyclopentylamide) | H | CH3 | (CH2)5 | H | - | |
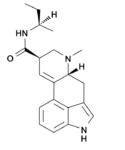 |
LSB (lysergic acid 2-butylamide) | 137765-82-3 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)CH2CH3 | H | - |
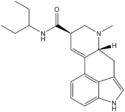 |
LSP (lysergic acid 3-pentylamide) | H | CH3 | CH(CH2CH3)CH2CH3 | H | - | |
 |
DPL (lysergic acid dipropylamide) | H | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
DiPLA (lysergic acid diisopropylamide) | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | - | |
 |
LBB-66 (lysergic acid dibutylamide) | H | CH3 | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | - | |
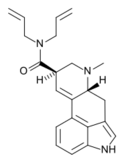 |
DAL (lysergic acid diallylamide) | H | CH3 | H2C=CH-CH2 | H2C=CH-CH2 | - | |
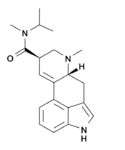 |
MiPLA (lysergic acid methylisopropylamide) | 100768-08-9 | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | - |
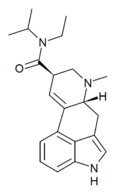 |
EiPLA (lysergic acid ethylisopropylamide) | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH2CH3 | - | |
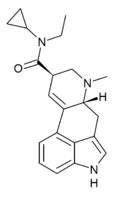 |
EcPLA (lysergic acid ethylcyclopropylamide) | H | CH3 | C3H5 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
LEO (lysergic acid ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamide) | 65527-58-4 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2OH | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
LA-MeO (lysergic acid ethyl-2-methoxyethylamide) | H | CH3 | CH2CH2OCH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
ETFELA (lysergic acid N-ethyl-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)amide) | H | CH3 | CH2CF3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
WO 2022/008627 Compound 4; TRALA-04[62] | H | CH3 | CH2CH2F | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
WO 2022/226408 Example 29;[63] TRALA-08 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2F | CH2CH2F | - | |
 |
LA-3Cl-SB (lysergic acid N-(3-chloro-sec-butyl)amide) | H | CH3 | CH(CH3)CClHCH3 | H | - | |
 |
LME-54 (lysergic acid methylethylamide) | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH3 | - | |
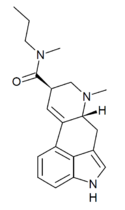 |
LAMPA (LMP-55; lysergic acid methylpropylamide) | 40158-98-3 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | - |
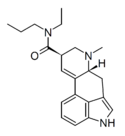 |
EPLA (lysergic acid ethylpropylamide; LEP-57) | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | - | |
 |
LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide; LAD) | 50-37-3 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
Iso-LSD | 2126-78-5 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 8-epi |
 |
l-LSD | 3184-49-4 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 5,8-epi |
 |
l-Iso-LSD | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 5-epi | |
 |
Nor-LSD (6-nor-LSD) | 35779-43-2 | H | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
ETH-LAD (6-ethyl-6-nor-LSD) | 65527-62-0 | H | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
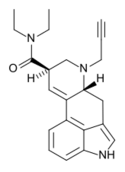 |
PARGY-LAD (6-propynyl-6-nor-LSD) | 2767597-51-1 | H | HC≡C−CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
AL-LAD (6-allyl-6-nor-LSD) | 65527-61-9 | H | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
PRO-LAD (6-propyl-6-nor-LSD) | 65527-63-1 | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
IP-LAD (6-isopropyl-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH(CH3)2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
MAL-LAD (METAL-LAD; 6-methallyl-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2=C(CH3)CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
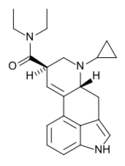 |
CYP-LAD (TRALA-22; 6-cyclopropyl-6-nor-LSD) | H | C3H5 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
CPM-LAD (6-cyclopropylmethyl-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2C3H5 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
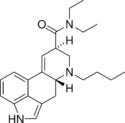 |
BU-LAD (6-butyl-6-nor-LSD) | 96930-87-9 | H | CH2CH2CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
PHENETH-LAD (6-(phenethyl)-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2CH2C6H5 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
NBOMe-LAD (6-(2-methoxybenzyl)-LAD) | H | CH2C6H4-o-OCH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
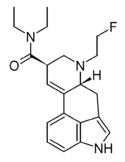 |
FLUORETH-LAD (FE-LAD; TRALA-15; 6-(2-fluoroethyl)-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2CH2F | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
FP-LAD (WO 2022/226408 Example 2; TRALA-16; 6-(3-fluoropropyl)-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2CH2CH2F | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
CE-LAD (CHLORETH-LAD; 6-(2-chloroethyl)-6-nor-LSD) | H | CH2CH2Cl | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1-Formyl-LSD (1F-LSD) | CH=O | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
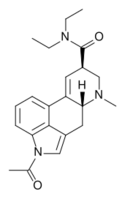 |
ALD-52 (1-acetyl-LSD; 1A-LSD) | 3270-02-8 | COCH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
ALA-10 (1-acetyl-LAE; 1A-LAE) | 50485-03-5 | COCH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | H | - |
 |
1P-LSD (1-propionyl-LSD) | 2349358-81-0 | COCH2CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
 |
1B-LSD (1-butanoyl-LSD) | 2349376-12-9 | COCH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
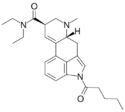 |
1V-LSD (1-valeryl-LSD) | CO(CH2)3CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1H-LSD (1-hexanoyl-LSD) | CO(CH2)4CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1DD-LSD (1-dodecanoyl-LSD) | CO(CH2)10CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1cP-LSD (1-cyclopropylmethanoyl-LSD) | COC3H5 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
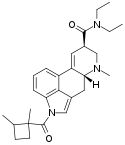 |
1D-LSD (1-(1,2-dimethylcyclobutane-1-carbonyl)-LSD) | COC4H5(CH3)2 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1F-LSD (1-(furan-2-carbonyl)-LSD; 1-(2-furoyl)-LSD; SYN-L-005) | COC4H3O | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1T-LSD (1-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-LSD) | COC4H3S | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
 |
1S-LSD (1-(3-(trimethylsilyl)propionyl)-LSD) | CO(CH2)2Si(CH3)3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
| File:1P-AL-LAD structure.png | 1P-AL-LAD (1-propionyl-6-allyl-6-nor-LSD) | COCH2CH3 | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
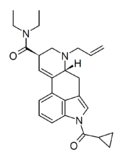 |
1cP-AL-LAD (1-cyclopropylmethanoyl-6-allyl-6-nor-LSD) | COC3H5 | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
| File:1T-AL-LAD structure.png | 1T-AL-LAD (1-(2-thienoyl)-6-allyl-6-nor-LSD)[64] | COC4H3S | H2C=CH-CH2 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
| File:1P-ETH-LAD.svg | 1P-ETH-LAD (1-propionyl-6-ethyl-6-nor-LSD) | COCH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - | |
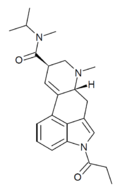 |
1P-MiPLA (1-propionyl-lysergic acid methylisopropylamide) | COCH2CH3 | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | - | |
| File:1cP-MIPLA.svg | 1cP-MiPLA (1-cyclopropionyl-lysergic acid methylisopropylamide) | 3028950-74-2 | COC3H5 | CH3 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | - |
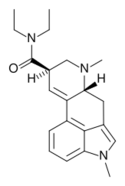 |
MLD-41 (1-methyl-LSD) | 4238-85-1 | CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
| File:MLA-74.svg | MLA-74 (1-methyl-LAE) | 7240-57-5 | CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | H | - |
| File:1-Hydroxymethyl-LSD.svg | OML-632 (1-hydroxymethyl-LSD) | 114004-70-5 | CH2OH | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
| File:1-Dimethylaminomethyl-LSD.svg | 1-Dimethylaminomethyl-LSD | ? | CH2NCH2CH2 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | - |
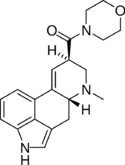 |
LSM-775 (lysergic acid morpholide) | 4314-63-0 | H | CH3 | CH2CH2-O-CH2CH2 | - | |
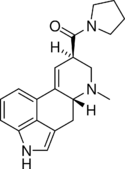 |
LPD-824 (lysergic acid pyrrolidide) | 2385-87-7 | H | CH3 | (CH2)4 | - | |
| File:MPD-75 structure.png | MPD-75 (1-methyllysergic acid pyrrolidide) | 7221-79-6 | CH3 | CH3 | (CH2)4 | - | |
 |
Lysergic acid pyrrolinide | ? | H | CH3 | CH2-CH=CH-CH2 | - | |
| File:LA-Cispyr structure.png | LA-Cispyr | ? | H | CH3 | cis-CH(CH3)-CH2CH2-CH(CH3) | - | |
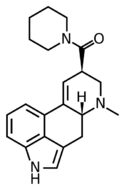 |
LA-Pip (lysergic acid piperidide) | 50485-23-9 | H | CH3 | (CH2)5 | - | |
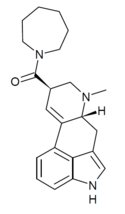 |
LA-Azepane (lysergic acid azepane)[65] | H | CH3 | (CH2)6 | - | ||
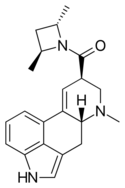 |
Lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide (LA-SS-Az, LSZ, LA-Azetidine) | 470666-31-0 | H | CH3 | CH2(CHCH3)2CH2 | - | |
| File:WO22-008627-1 structure.png | WO 2022/008627 Compound 1 [66] | H | CH3 | (CH2)2C(CH2)2O | - | ||
| File:LA-Aziridine structure.png | Lysergic acid-(2,3-dimethylaziridinyl)amide (LA-Aziridine) | ? | H | CH3 | ? | - | |
 |
2-Bromo-LSD (BOL-148; bromolysergide) | 478-84-2 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Br |
| File:2-iodo-LSD structure.png | 2-Iodo-LSD (IOL) | 3712-25-2 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-I |
| File:2-oxo-LSD structure.png | 2-Oxo-LSD (2-oxy-LSD) | ? | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Oxo |
| File:3-OH-2-oxo-LSD structure.png | 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD | ? | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Oxo, 3-OH |
| File:1-Methyl-2-bromo-LSD.svg | MBL-61 (MOB-61; 1-methyl-2-bromo-LSD) | 50484-98-5 | CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Br |
| File:1-Methyl-2-iodo-LSD.svg | MIL (1-methyl-2-iodo-LSD) | 97165-34-9 | CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-I |
| File:1P-BOL-148 structure.png | 1P-BOL-148 (1-propionyl-2-bromo-LSD) | COCH2CH3 | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 2-Br | |
| File:12-Hydroxy-LSD.svg | 12-Hydroxy-LSD (12-OH-LSD) | 60573-89-9 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 12-OH |
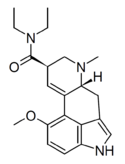 |
12-Methoxy-LSD (12-MeO-LSD) | 50484-99-6 | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 12-OMe |
| File:13-F-LSD structure.png | 13-Fluoro-LSD[67] | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 13-F | |
| File:13-Hydroxy-LSD.svg | 13-Hydroxy-LSD | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 13-OH | |
| File:13-MeO-LSD structure.png | 13-Methoxy-LSD | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 13-OMe | |
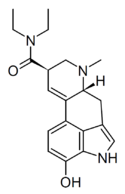 |
14-Hydroxy-LSD | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 14-OH | |
| File:14-MeO-LSD structure.png | 14-Methoxy-LSD | H | CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH2CH3 | 14-OMe | |
Related compounds
| Structure | Name | Chemical name | CAS # |
|---|---|---|---|
| File:2,3-Dihydro-LSD structure.png | 2,3-Dihydro-LSD (2,3-DH-LSD) | N,N-diethyl-6-methyl-9,10-didehydro-2,3-dihydroergoline-8β-carboxamide | ? |
| File:9,10-Dihydro-LSD structure.png | 9,10-Dihydro-LSD (9,10-DH-LSD) | (10ξ)-N,N-diethyl-6-methylergoline-8β-carboxamide | 3031-47-8 |
 |
AWD 52-39 | N,N-diacetoxyethyl-9,10-dihydrolysergamide | 109002-91-7 |
 |
Bromerguride (2-bromolisuride) | 1,1-diethyl-3-(2-bromo-9,10-didehydro-6-methyl-8α-ergolinyl)urea | 83455-48-5 |
 |
Bromocriptine | (5′α)-2-bromo-12′-hydroxy-5′-(2-methylpropyl)-3′,6′,18-trioxo-2′-(propan-2-yl)ergotaman | 25614-03-3 |
| File:Descarboxylysergic acid.svg | Descarboxylysergic acid | 6-methyl-9,10-didehydroergoline | 51867-17-5 |
 |
Dihydroergotamine (DHE-45) | (5'α)-9,10-dihydro-12'-hydroxy-2'-methyl-5'-(phenylmethyl)-ergotaman-3',6',18-trione | 511-12-6 |
| File:Disulergine structure.png | Disulergine | N,N-dimethyl-N'-(6-methylergoline-8α-yl)sulfamide | 59032-40-5 |
| File:Dosergoside structure.png | Dosergoside | N-((1S,2R,3E)-2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-3-heptadecenyl)-6-methylergoline-8β-carboxamide | 87178-42-5 |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | Ergoline | (6aR)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline | 478-88-6 |
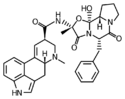 |
Ergotamine | 5′α-benzyl-12′-hydroxy-2′-methyl-3′,6′,18-trioxoergotaman | 113-15-5 |
| File:Etisulergine structure.png | Etisulergine | N,N-diethyl-N'-(6-methylergolin-8α-yl)sulfamide | 64795-23-9 |
| File:GYKI-32887 structure.png | GYKI-32887 | 8-((N-2-azidoethyl-N-methylsulfonylamino)methyl)-6-methylergol-8-ene | 78463-86-2 |
| File:JRT.svg | JRT | (7S)-N,N-diethyl-6-methyl-6,9-diazatetracyclo[7.6.1.02,7.012,16]hexadeca-1(15),2,10,12(16),13-pentaene-4-carboxamide | ? |
| File:Lumi-LSD structure.png | Lumi-LSD (10-hydroxy-9,10-dihydro-LSD) | N,N-diethyl-10-hydroxy-6-methylergoline-8β-carboxamide | |
| File:Lysergine.svg | Lysergine | 9,10-didehydro-6,8β-dimethylergoline | 519-10-8 |
 |
Lysergol | (6-methyl-9,10-didehydroergolin-8β-yl)methanol | 1413-67-8 |
 |
Lysergic acid | 6-methyl-9,10-didehydroergoline-8β-carboxylic acid | 82-58-6 |
 |
Lergotrile | 2-chloro-6-methylergoline-8β-acetonitrile | 36945-03-6 |
 |
Lisuride | 1,1-diethyl-3-(6-methyl-9,10-didehydroergolin-8α-yl)urea | 18016-80-3 |
| File:Proteguride structure.png | Proterguride (6-propyl-9,10-dihydrolisuride) | 1,1-diethyl-3-(6-n-propyl-8α-ergolinyl)urea | 77650-95-4 |
 |
Terguride (9,10-dihydrolisuride) | N,N-diethyl-N'-[(8α)-6-methylergolin-8-yl]urea | 37686-84-3 |
See also
- Ergoline
- Partial lysergamide
- Substituted tryptamine
- Substituted phenethylamine
- Lizard Labs
References
- ↑ Jamieson, Cooper S.; Misa, Joshua; Tang, Yi; Billingsley, John M. (2021-04-29). "Biosynthesis and synthetic biology of psychoactive natural products" (in en). Chemical Society Reviews 50 (12): 6950–7008. doi:10.1039/D1CS00065A. ISSN 0306-0012. PMID 33908526. PMC 8217322. https://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D1CS00065A. "There are three main ergot alkaloid classes, clavines, ergoamides (lysergamides), and ergopeptides, with 3 belonging to the ergoamide class." 2.5 Lysergic acid and LSD, p. 6970".
- ↑ Wong, Garrett; Lim, Li Rong; Tan, Yong Quan; Go, Maybelle Kho; Bell, David J.; Freemont, Paul S.; Yew, Wen Shan (2022-02-07). "Reconstituting the complete biosynthesis of D-lysergic acid in yeast" (in en). Nature Communications 13 (1): 712. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28386-6. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 35132076. Bibcode: 2022NatCo..13..712W. "The ergot alkaloids are broadly classified into three groups—the clavines, ergoamides, and the ergopeptines, all of which are distinguished by the different modifications appended to the core ergoline structure. [...] Results and discussion / Biosynthetic resolution of the ergot alkaloid pathway".
- ↑ St. Germaine, Danielle (2023-12-14). "Psychedelic Therapies Webinar Highlights". https://www.caymanchem.com/news/psychedelic-therapies-webinar-highlights.
"More recently, ergot alkaloids, in particular ergoamides, also known as lysergic acid amides, have gained notoriety through their use as synthetic precursors for lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)." - ↑ Lee, K.; Poudel, Y. B.; Glinkerman, C. M.; Boger, D. L. (2015). "Total synthesis of dihydrolysergic acid and dihydrolysergol: development of a divergent synthetic strategy applicable to rapid assembly of D-ring analogs". Tetrahedron 71 (35): 5897–5905. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2015.05.093. PMID 26273113. "Embedded in the structures of the ergot alkaloids are conformationally-restricted variants of the phenethylamine pharmacophores of both dopamine and related biogenic amines as well as that of serotonin.".
- ↑ Pioch RP, "Lysergic Acid Amides", US patent 2997470, published 1956-03-05, issued 1961-08-22
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 28 (9): 1252–1255. September 1985. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
- ↑ "Drug discrimination and receptor binding studies of N-isopropyl lysergamide derivatives". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 47 (3): 667–673. March 1994. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(94)90172-4. PMID 8208787.
- ↑ "LSD and structural analogs: pharmacological evaluation at D1 dopamine receptors". Psychopharmacology 118 (4): 401–409. April 1995. doi:10.1007/BF02245940. PMID 7568626.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Lysergamides of isomeric 2,4-dimethylazetidines map the binding orientation of the diethylamide moiety in the potent hallucinogenic agent N,N-diethyllysergamide (LSD)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 45 (19): 4344–4349. September 2002. doi:10.1021/jm020153s. PMID 12213075.
- ↑ "Ergot and its alkaloids". American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 70 (5): 98. October 2006. doi:10.5688/aj700598. PMID 17149427.
- ↑ "The pharmacology of lysergic acid diethylamide: a review". CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 14 (4): 295–314. 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00059.x. PMID 19040555.
- ↑ "Return of the lysergamides. Part I: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-propionyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1P-LSD)". Drug Testing and Analysis 8 (9): 891–902. September 2016. doi:10.1002/dta.1884. PMID 26456305.
- ↑ "Return of the lysergamides. Part II: Analytical and behavioural characterization of N6 -allyl-6-norlysergic acid diethylamide (AL-LAD) and (2'S,4'S)-lysergic acid 2,4-dimethylazetidide (LSZ)". Drug Testing and Analysis 9 (1): 38–50. January 2017. doi:10.1002/dta.1985. PMID 27265891.
- ↑ "Return of the lysergamides. Part III: Analytical characterization of N6 -ethyl-6-norlysergic acid diethylamide (ETH-LAD) and 1-propionyl ETH-LAD (1P-ETH-LAD)". Drug Testing and Analysis 9 (10): 1641–1649. October 2017. doi:10.1002/dta.2196. PMID 28342178.
- ↑ "Return of the lysergamides. Part IV: Analytical and pharmacological characterization of lysergic acid morpholide (LSM-775)". Drug Testing and Analysis 10 (2): 310–322. February 2018. doi:10.1002/dta.2222. PMID 28585392.
- ↑ "Return of the lysergamides. Part V: Analytical and behavioural characterization of 1-butanoyl-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1B-LSD)". Drug Testing and Analysis 11 (8): 1122–1133. August 2019. doi:10.1002/dta.2613. PMID 31083768.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Pharmacological characterization of the LSD analog N-ethyl-N-cyclopropyl lysergamide (ECPLA)". Psychopharmacology 236 (2): 799–808. February 2019. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-5055-9. PMID 30298278. "Importantly, MIPLA has been reported to have about one-third the potency of LSD as a psychedelic in man (Shulgin 2016); recent online postings indicate that MIPLA is available as an NPS (Anonymous 2018). By contrast, little is known about the pharmacology of LAMPA. In a study conducted in six hallucinogen-experienced subjects, administration of LAMPA (100 μg p.o.) had no effect in four subjects and produced effects consistent with a threshold dose of LSD in two subjects (Abramson and Rolo 1967). [...] According to Shulgin, human subjects administered MIPLA at doses of 180–300 μg experienced LSD-like psychedelic effects, making it about two- to threefold less potent than LSD (Shulgin 2016). [...] Shulgin AT (2016) Pharmacology Notebook 9. Available online: https://www.erowid.org/library/ books_online/shulgin_labbooks/shulgin_pharmacology_notebook9_searchable.pdf [Accessed: January 20, 2018]".
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 "Indolealkylamines and Related Compounds". Hallucinogenic Agents. Bristol: Wright-Scientechnica. 1975. pp. 98–144. ISBN 978-0-85608-011-1. OCLC 2176880. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Books/978-0-85608-011-1#page=55. "Table 4.3.—Comparative Hallucinogenic Potencies in Man of Derivatives of D-Lysergic Acid. [...]"
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 The evolution of drug discovery : from traditional medicines to modern drugs (1st ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2011. p. 245. ISBN 9783527326693. https://books.google.com/books?id=iDNy0XxGqT8C&pg=PA245.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "98. The alkaloids of ergot. Part III. Ergine, a new base obtained by the degradation of ergotoxine and ergotinine" (in en). Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 763–766. 1932. doi:10.1039/jr9320000763. ISSN 0368-1769. https://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=jr9320000763.
- ↑ Shulgin, Alexander T. (1976). "Psychotomimetic Agents". Psychopharmacological Agents: Use, Misuse and Abuse. Medicinal Chemistry: A Series of Monographs. 4. Academic Press. pp. 59–146. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-290559-9.50011-9. ISBN 978-0-12-290559-9. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1016/B978-0-12-290559-9.50011-9. "The largest number of structural analogs of LSD that have been prepared involve the opening of one or more of the rings of the parent lysergic acid system. The compounds with the piperidine ring (ring D) opened [see (I)] are encountered as natural products in the several Convolvulaceae discussed in Section II,B on ololiuqui. The opening of ring C (by cleavage of the 10-11 bond to the indole "4 position") results in a series of N-α-disubstituted tryptamines. Additionally, analogs are known with the indolic nitrogen replaced with sulfur (benzothiophenes) and with an aliphatic chain (tetralins). A recent review covers this chemistry (Campaigne and Knapp, 1971), but there is apparently no human psychopharmacology as yet known."
- ↑ Nichols DE (May 1973). Potential Psychotomimetics: Bromomethoxyamphetamines and Structural Congeners of Lysergic Acid (Thesis). University of Iowa. p. 23. OCLC 1194694085.
- ↑ "Structural analogs of lysergic acid". J Pharm Sci 60 (6): 809–814. June 1971. doi:10.1002/jps.2600600602. PMID 4942861.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Basic Pharmacology and Effects". Hallucinogens: A Forensic Drug Handbook. Forensic Drug Handbook Series. Elsevier Science. 2003. pp. 67–137. ISBN 978-0-12-433951-4. https://web.archive.org/web/20250223164514/https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=6bb3a7499da8e9852b39cd4db16891147c83f5c6.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 "Structure-activity relationships of the classic hallucinogens and their analogs". NIDA Res Monogr 146: 74–91. 1994. PMID 8742795. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Books/NIDA146.74.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Chemistry of Psychotomimetics". Psychotropic Agents, Part III: Alcohol and Psychotomimetics, Psychotropic Effects of Central Acting Drugs. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 55 / 3. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1982. pp. 3–29. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-67770-0_1. ISBN 978-3-642-67772-4. OCLC 8130916. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1007/978-3-642-67770-0_1.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Alexander T. Shulgin (1980). "Hallucinogens". Burger's Medicinal Chemistry. 3 (4 ed.). New York: Wiley. pp. 1109–1137. ISBN 978-0-471-01572-7. OCLC 219960627. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=6ac0c892ee380436f614d3aae0686ef617b2e0c5.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Alexander T. Shulgin; Ann Shulgin (1997). "#26. LSD-25 Acid; Lysergide; D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide; Meth-LAD; D-Lysergamide, N,N-Diethyl; N,N-Diethyl-D-Lysergamide; 9,10-Didehydro-N,N-Diethyl-6-Methylergoline-8b-Carboxamide". TiHKAL: The Continuation (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. pp. 490–499. ISBN 978-0-9630096-9-2. OCLC 38503252. https://www.erowid.org/library/books_online/tihkal/tihkal26.shtml. "The second major location of variations in the structure of LSD has been in the nature of the alkyl groups on the amide nitrogen atom. Some of these are Sandoz syntheses, some are from other research groups, and a few of them are found in nature. Some of these have been studied in man, and some have not. A few of the original clutch of Sandoz compounds have both 1-substituents and amide alkyl (R) group variations: [...]"
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Psychotomimetic Drugs: Chemical and Pharmacological Aspects". Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl 8: 240–258. June 1959. PMID 13852489. https://www.samorini.it/doc1/alt_aut/ek/hofmann-psychotomimetic-drugs.pdf.
- ↑ Chemistry and Structure-Activity Relationships of Psychedelics. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36. 2018. pp. 1–43. doi:10.1007/7854_2017_475. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1007/7854_2017_475.
- ↑ "Chemical Background". Ergot Alkaloids and Related Compounds. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology (HEP). 49. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1978. pp. 29–85. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66775-6_2. ISBN 978-3-642-66777-0.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Mangner TJ (1978). Potential Psychotomimetic Antagonists. N,N-Diethyl-1-methyl-3-aryl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-5-carboxamides (Ph.D. thesis). University of Michigan. doi:10.7302/11268. Archived from the original on 30 March 2025.
Table 1. Human psychotomimetic potencies of LSD analogs. [...]
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Some Compounds With Hallucinogenic Activity". Ergot Alkaloids and Related Compounds. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology (HEP). 49. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 1978. pp. 567–614. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66775-6_8. ISBN 978-3-642-66777-0. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/8769#page=30. "Table 2. Psychotomimetic activity and some pharmacodynamic effects of structural analogues of LSD [...]"
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 "Lysergic acid diethylamide and related substances". Ann N Y Acad Sci 66 (3): 668–676. March 1957. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb40756.x. PMID 13425249. Bibcode: 1957NYASA..66..668R. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/3876.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 "D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD): A Review of its Present Status". Clin Pharmacol Ther 6 (2): 183–255. 1965. doi:10.1002/cpt196562183. PMID 14288188. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/2117.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Relationships of psychotomimetic to anti-serotonin potencies of congeners of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD-25)". Psychopharmacologia 1: 20–28. 1959. doi:10.1007/BF00408108. PMID 14405872. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/13773#page=4.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 "Stereoselective aspects of hallucinogenic drug action and drug discrimination studies of entactogens". Purdue University. May 1989. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Theses/Oberlender1989#page=49. "Table 2. Relative potency values for lysergic acid amides. [...]"
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "Quantum chemical studies on drug actions. 3. Correlation of hallucinogenic and anti-serotonin activity of lysergic acid derivatives with quantum chemical data". Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 6 (1): 65–100. July 1973. PMID 4734018. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/14168. "Table I – Structure and Several Biological Activities of Lysergates [...]".
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Quantum chemical studies on drug actions. IV. Correlation of substituent structures and anti-serotonin activity in lysergamide series". Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 7 (2): 259–274. February 1974. PMID 4818373. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/20652#page=7. "Table I – Quantum Chemical Data on Lysergamide Derivatives".
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 "Pharmacokinetics and subjective effects of 1P-LSD in humans after oral and intravenous administration". Drug Test Anal 12 (8): 1144–1153. August 2020. doi:10.1002/dta.2821. PMID 32415750.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 "The use patterns of novel psychedelics: experiential fingerprints of substituted phenethylamines, tryptamines and lysergamides". Psychopharmacology (Berl) 239 (6): 1783–1796. June 2022. doi:10.1007/s00213-022-06142-4. PMID 35487983.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Abramson, H. A. (1959). "Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD-25): XXIX. The Response Index as a Measure of Threshold Activity of Psychotropic Drugs in Man". The Journal of Psychology 48 (1): 65–78. doi:10.1080/00223980.1959.9916341. ISSN 0022-3980. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/20361.
- ↑ "Correlation between the potency of hallucinogens in the mouse head-twitch response assay and their behavioral and subjective effects in other species". Neuropharmacology 167. May 2020. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107933. PMID 31917152. PMC 9191653. http://usdbiology.com/cliff/Courses/Advanced%20Seminars%20in%20Neuroendocrinology/Serotonergic%20Psychedelics%2020/Halberstadt%2020%20Neuropharm%20potency%20of%20hallucinogens%20%20head-twitch.pdf. "Table 4 Human potency data for selected hallucinogens. [...]".
- ↑ "Recreational use, analysis and toxicity of tryptamines". Curr Neuropharmacol 13 (1): 26–46. January 2015. doi:10.2174/1570159X13666141210222409. PMID 26074742. PMC 4462041. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=90639cbd4ed3fc89df491868f3276f2288f9b1d2. "Ergine, or lysergic acid amide (LSA), is an alkaloid of the ergoline family closely related to LSD, found in the seeds of Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian baby woodrose) and Ipomoea violacea (Morning Glories). Hallucinogenic activity of LSA occurs with 4-10 seeds of Argyreia nervosa or with 150–200 seeds (3–6 g) of Ipomoea violacea: seeds could be crushed or eaten whole, or also drunk as an extract, after soaking in water [42]. The onset of the hallucinatory effects, after ingestion of Hawaiian Baby Woodrose, is from 20 to 40 minutes and their total duration is from 5 to 8 hours: the plateau is reached after 4-6 hours and the return to normality is after 1-2 hours from the plateau. [...] However, as regards to the assumption of the Morning Glory seeds, the onset of the hallucinatory effects is from 30 to 180 minutes and they last for 4 to 10 hours. The users reported that they return to normality after about 24 hours [67].".
- ↑ Gupta, Satya P.; Singh, Prithvi; Bindal, Mahesh C. (1 December 1983). "QSAR studies on hallucinogens". Chemical Reviews 83 (6): 633–649. doi:10.1021/cr00058a003. ISSN 0009-2665. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/cr00058a003. "TABLE XII. Antiserotonin and Hallucinogenic Activities and Hückel's Total MO Energy of LSD and its Analogues [...] Data collected by Kumbar and Siva Sankar,91,92 from ref 70a, 87, 88, and 90; all activities are relative to that of LSD taken as 100.".
- ↑ Chen, W.; De Wit-Bos, L. (2020). Risk assessment of Argyreia nervosa (Report). doi:10.21945/rivm-2019-0210. https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/2019-0210.pdf.
- ↑ "Entheogenic effects of ergonovine". J Psychedelic Drugs 11 (1–2): 147–149. 1979. doi:10.1080/02791072.1979.10472099. PMID 522166. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/12845. "In 1977 and 1978 Hofmann reported that ergonovine maleate was entheogenic,1 a surprising finding in view of its widespread use in obstetrics (Wasson, Hofmann & Ruck 1978; Hofmann 1977). This report was based on a self-experiment conducted by Hofmann on 1 April 1976, with 2.0 mg of ergonovine maleate taken orally. Hofmann reported that this dose manifested a "slightly hallucinogenic activity" lasting more than five hours.2 [...] Our experiments corroborate Hofmann's report that ergonovine possesses entheogenic properties. We found the active dose to lie between 5.0 and 10.0 mg, peroral. It is interesting to note that Hofmann experienced distinct entheogenic effects at 2.0 mg, while Wasson and Ruck did not. Similarly, J.B. experienced distinct entheogenic effects at 3.0 mg, whereas J.O. and P.N. did not. This underscores the importance of metabolic individuality in the uptake and metabolism of mind-altering drugs. With respect to entheogenic effects 10 mg of ergonovine maleate is roughly equivalent to 50 μg is, ergonovine possesses about that LSD-tartrate, 1/200th the entheogenic potency of LSD.".
- ↑ "A comparison of 2,3-dihydro-lysergic acid diethylamide with LSD-25". Psychopharmacologia 6 (3): 229–233. September 1964. doi:10.1007/BF00404013. PMID 5319153.
- ↑ "Prophylactic Treatment of Migraine by Means of Lysergic Acid Derivatives". Triangle 6: 116–125. October 1963. PMID 14087164.
- ↑ "Comparative study on the serotonin antagonism of amide derivatives of lysergic acid and of ergot alkaloids". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 122 (1): 124–136. January 1958. doi:10.1016/S0022-3565(25)11933-2. PMID 13502837. https://bibliography.maps.org/resources/download/19096.
- ↑ Walker, Scott R.; Pullella, Glenn A.; Piggott, Matthew J.; Duggan, Peter J. (5 July 2023). "Introduction to the chemistry and pharmacology of psychedelic drugs". Australian Journal of Chemistry 76 (5): 236–257. doi:10.1071/CH23050. ISSN 0004-9425. https://www.publish.csiro.au/ch/pdf/CH23050. Retrieved 4 April 2025.
- ↑ McKenna, Terence (1999). "[Chapter 14: A Brief History of Psychedelics"]. Food of the Gods: The Search for the Original Tree of Knowledge : a Radical History of Plants, Drugs and Human Evolution. Rider. pp. 223–245. ISBN 978-0-7126-7038-8. https://alquimiahealingarts.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Food-Of-The-Gods-Terence-Mckenna.pdf#page=117.
- ↑ Stoll, A.; Hofmann, A. (1955). "Amide der stereoisomeren Lysergsäuren und Dihydro-lysergsäuren. 38. Mitteilung über Mutterkornalkaloide". Helvetica Chimica Acta 38 (2): 421–433. doi:10.1002/hlca.19550380207. ISSN 0018-019X. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hlca.19550380207. Retrieved 5 June 2025.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 "Stereochemical Aspects of Hallucinogenesis". Biochemistry and Physiology of Substance Abuse. 3. Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press. 1991. pp. 1–39. ISBN 978-0-8493-4463-3. OCLC 26748320. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Books/BiochemistryPhysiologySubstanceAbuse3.1. "Chemical transformations at N(6) were not accomplished until after clinical studies had been terminated. Initial work in this area was reported in 1970 by Fehr et al.184 who synthesized d-lysergic acid with various N(6) alkyl groups from 6-nor-d-lysergic acid methyl ester.151 Similar chemistry was first applied to LSD by Nakahara and Niwaguchi,185 then by Niwaguchi et al.,186 and most recently by Hoffman and Nichols.162 Initial pharmacological studies identified high activity in the isolated rat uterus preparation for the ethyl, propyl, and allyl analogues, from which high potency in the CNS was predicted.161"
- ↑ Fehr, T.; Stadler, P. A.; Hofmann, A. (1970). "Demethylierung des Lysergsäuregerüstes. 73. Mitteilung über Mutterkornalkaloide [1"]. Helvetica Chimica Acta 53 (8): 2197–2201. doi:10.1002/hlca.19700530832. ISSN 0018-019X. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hlca.19700530832. Retrieved 29 June 2025.
- ↑ "Lysergic Acid Diethylamideおよび関連化合物に関する研究(第4報)Norlysergic Acidの各種Amide誘導体ならびに関連化合物の合成". Yakugaku Zasshi 96 (5): 673–678. 1976. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.96.5_673. ISSN 0031-6903. PMID 987200. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/yakushi1947/96/5/96_5_673/_pdf. Retrieved 27 March 2025.
- ↑ "Studies of the Relationship Between Molecular Structure and Hallucinogenic Activity". Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24 (2): 335–340. February 1986. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(86)90362-x. PMID 3952123. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/10.1016/0091-3057(86)90362-X. "The ergolines can be viewed as rigid tetracyclic tryptamines. Within this class of compound is found the semisynthetic d-lysergic acid diethylamide (Fig 8) (d-LSD), the most potent of the hallucinogenic drugs. [...] Of the many structural modifications which have been made to the LSD structure, none had yielded a compound more potent than LSD itself. This report will briefly describe some derivatives of LSD which do appear to have somewhat higher potency than LSD. [...] The observations of potency comparable to, or greater than LSD [with N(6)-alkyl-substituted lysergamides] was of great interest. It seemed likely, based on the generalization in the drug discrimination assay and the high potencies of several of the derivatives, that these might well be more potent hallucinogens in man than LSD. Very recently, preliminary studies were carried out (A T Shulgin, personal communication) which indicated that indeed, the N(6)-ethyl and the N(6)-allyl-nor-LSD derivatives are somewhat more potent than LSD, by perhaps a factor of 2–3. Early results also indicated that N(6)-propyl-nor-LSD retains activity comparable to LSD, but with perhaps less visual distortion. These preliminary results were obtained after only a few experiments with each compound and further evaluation to define the potency and character of these lysergamides is underway.".
- ↑ "Lysergamides revisited". NIDA Research Monograph 146: 52–73. 1994. PMID 8742794. https://bitnest.netfirms.com/external/Books/NIDA146.52.
- ↑ Niesporek, Tom (17 August 2022). Der Hype um legales LSD in Deutschland: Wie das Verbot umgangen wird [The hype surrounding legal LSD in Germany: How the ban is circumvented]. YouTube (in German). VICE auf Deutsch. Event occurs at 2:10–8:12, 20:05–20:41. Retrieved 29 September 2025.
{{cite AV media}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Încrosnatu, Dănuț (17 July 2023). "From 1V-LSD to 1D-LSD: The Evolution of Legal Lysergamides". https://www.sociedelic.com/from-1v-lsd-to-1d-lsd-the-evolution-of-legal-lysergamides/.
- ↑ Chiara, Jean-Baptiste (27 July 2022). "LSD light : Gobe, c'est du légal !" (in fr). https://www.technikart.com/lsd-light-gobe-cest-du-legal/.
- ↑ Trachsel D, et al. Lysergic acid derivatives with modified LSD-like action. US 2023/0414583
- ↑ Kruegel AC. Novel Ergolines and Methods of Treating Mood Disorders. Patent WO 2022/226408
- ↑ "Synthesis and analytical characterization of 1-(2-thienoyl)-6-allyl-nor-d-lysergic acid diethylamide (1T-AL-LAD)". Drug Testing and Analysis 17 (4): 494–501. June 2024. doi:10.1002/dta.3747. PMID 38922764.
- ↑ "Lysergic acid amides". 5 March 1956. https://patents.google.com/patent/US2997470A/en. "EXAMPLE 38 Preparation of d-lysergic acid hexamethylene imide: [...]"
- ↑ Grill M, "Improved Method for the Production of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) and Novel Derivatives thereof.", WO patent 2022/008627
- ↑ ; Lee Dunlap & Florence Wagner et al."Ergoline-like compounds for promoting neural plasticity" WO patent 2021076572, published 22 April 2021, assigned to Delix Therapeutics, Inc.and The Regents of the University of California
External links
Template:Chemical classes of psychoactive drugs
 |
