Biology:KCNA4
 Generic protein structure example |
| Potassium channel Kv1.4 tandem inactivation domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
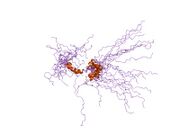
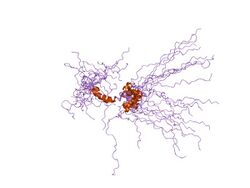 solution structure of the tandem inactivation domain (residues 1-75) of potassium channel rck4 (kv1.4) | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | K_channel_TID | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF07941 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR012897 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1kn7 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 4 also known as Kv1.4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNA4 gene.[1][2][3] It contributes to the cardiac transient outward potassium current (Ito1), the main contributing current to the repolarizing phase 1 of the cardiac action potential.[4]
Description
Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. Four sequence-related potassium channel genes - shaker, shaw, shab, and shal - have been identified in Drosophila, and each has been shown to have human homolog(s). This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, shaker-related subfamily. This member contains six membrane-spanning domains with a shaker-type repeat in the fourth segment. It belongs to the A-type potassium current class, the members of which may be important in the regulation of the fast repolarizing phase of action potentials in heart and thus may influence the duration of cardiac action potential. The coding region of this gene is intronless, and the gene is clustered with genes KCNA3 and KCNA10 on chromosome 1 in humans.[3]
KCNA4 (Kv1.4) contains a tandem inactivation domain at the N terminus. It is composed of two subdomains. Inactivation domain 1 (ID1, residues 1-38) consists of a flexible N terminus anchored at a 5-turn helix, and is thought to work by occluding the ion pathway, as is the case with a classical ball domain. Inactivation domain 2 (ID2, residues 40-50) is a 2.5 turn helix with a high proportion of hydrophobic residues that probably serves to attach ID1 to the cytoplasmic face of the channel. In this way, it can promote rapid access of ID1 to the receptor site in the open channel. ID1 and ID2 function together to bring about fast inactivation of the Kv1.4 channel, which is important for the role of the channel in short-term plasticity.[5]
Interactions
KCNA4 has been shown to interact with DLG4,[6][7][8][9] KCNA2[10] and DLG1.[6][8][11]
See also
- Voltage-gated potassium channel
- Voltage-gated potassium-channel Kv1.4 IRES
References
- ↑ "Sequence of a human fetal skeletal muscle potassium channel cDNA related to RCK4". Nucleic Acids Research 18 (23): 7160. December 1990. doi:10.1093/nar/18.23.7160. PMID 2263489.
- ↑ "International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels". Pharmacological Reviews 57 (4): 473–508. December 2005. doi:10.1124/pr.57.4.10. PMID 16382104.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Entrez Gene: KCNA4 potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 4". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3739.
- ↑ "The molecular physiology of the cardiac transient outward potassium current (I(to)) in normal and diseased myocardium". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 33 (5): 851–72. May 2001. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2001.1376. PMID 11343410.
- ↑ "Solution structure and function of the "tandem inactivation domain" of the neuronal A-type potassium channel Kv1.4". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278 (18): 16142–50. May 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210191200. PMID 12590144.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Inward rectifier K+ channel Kir2.3 is localized at the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses". American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 282 (6): C1396-403. June 2002. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00615.2001. PMID 11997254.
- ↑ "CRIPT, a novel postsynaptic protein that binds to the third PDZ domain of PSD-95/SAP90". Neuron 20 (4): 693–707. April 1998. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81009-0. PMID 9581762.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Differential K+ channel clustering activity of PSD-95 and SAP97, two related membrane-associated putative guanylate kinases". Neuropharmacology 35 (7): 993–1000. 1996. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(96)00093-7. PMID 8938729.
- ↑ "N-terminal PDZ-binding domain in Kv1 potassium channels". FEBS Letters 531 (3): 529–37. November 2002. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03572-X. PMID 12435606.
- ↑ "Subunit composition of Kv1 channels in human CNS". Journal of Neurochemistry 73 (2): 849–58. August 1999. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730849.x. PMID 10428084.
- ↑ "SAP97 increases Kv1.5 currents through an indirect N-terminal mechanism". FEBS Letters 547 (1–3): 205–11. July 2003. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00668-9. PMID 12860415.
Further reading
- "PCR detection of two RFLPs in exon I of the alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA) gene". Human Genetics 90 (3): 327. November 1992. doi:10.1007/bf00220095. PMID 1362562.
- "The potassium channel gene HK1 maps to human chromosome 11p14.1, close to the FSHB gene". Human Genetics 90 (3): 319–21. November 1992. doi:10.1007/bf00220091. PMID 1487251. https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bvb:20-opus-59184.
- "Sequence and functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of a human insulinoma and islet potassium channel". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88 (1): 53–7. January 1991. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.1.53. PMID 1986382. Bibcode: 1991PNAS...88...53P.
- "Molecular cloning and characterization of two voltage-gated K+ channel cDNAs from human ventricle". FASEB Journal 5 (3): 331–7. March 1991. doi:10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001794. PMID 2001794.
- "Clustering of Shaker-type K+ channels by interaction with a family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases". Nature 378 (6552): 85–8. November 1995. doi:10.1038/378085a0. PMID 7477295. Bibcode: 1995Natur.378...85K.
- "Chromosomal mapping in the mouse of eight K(+)-channel genes representing the four Shaker-like subfamilies Shaker, Shab, Shaw, and Shal". Genomics 18 (3): 568–74. December 1993. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80358-1. PMID 7905852.
- "Assignment of human potassium channel gene KCNA4 (Kv1.4, PCN2) to chromosome 11q13.4-->q14.1". Genomics 15 (2): 463–4. February 1993. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1094. PMID 8449523.
- "Interaction between the C terminus of NMDA receptor subunits and multiple members of the PSD-95 family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases". The Journal of Neuroscience 16 (7): 2157–63. April 1996. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-07-02157.1996. PMID 8601796.
- "Differential K+ channel clustering activity of PSD-95 and SAP97, two related membrane-associated putative guanylate kinases". Neuropharmacology 35 (7): 993–1000. 1997. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(96)00093-7. PMID 8938729.
- "GKAP, a novel synaptic protein that interacts with the guanylate kinase-like domain of the PSD-95/SAP90 family of channel clustering molecules". The Journal of Cell Biology 136 (3): 669–78. February 1997. doi:10.1083/jcb.136.3.669. PMID 9024696.
- "CRIPT, a novel postsynaptic protein that binds to the third PDZ domain of PSD-95/SAP90". Neuron 20 (4): 693–707. April 1998. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81009-0. PMID 9581762.
- "Localization of postsynaptic density-93 to dendritic microtubules and interaction with microtubule-associated protein 1A". The Journal of Neuroscience 18 (21): 8805–13. November 1998. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-21-08805.1998. PMID 9786987.
- "Subunit composition of Kv1 channels in human CNS". Journal of Neurochemistry 73 (2): 849–58. August 1999. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730849.x. PMID 10428084.
- "Mutations in the KCNA1 gene associated with episodic ataxia type-1 syndrome impair heteromeric voltage-gated K(+) channel function". FASEB Journal 13 (11): 1335–45. August 1999. doi:10.1096/fasebj.13.11.1335. PMID 10428758.
- "Interaction of gamma 1-syntrophin with diacylglycerol kinase-zeta. Regulation of nuclear localization by PDZ interactions". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (28): 26526–33. July 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104156200. PMID 11352924.
- "A discrete amino terminal domain of Kv1.5 and Kv1.4 potassium channels interacts with the spectrin repeats of alpha-actinin-2". FEBS Letters 498 (1): 87–92. June 2001. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02505-4. PMID 11389904.
- "Ligand binding of the second PDZ domain regulates clustering of PSD-95 with the Kv1.4 potassium channel". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (5): 3640–6. February 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106940200. PMID 11723117.
- "The PDZ1 domain of SAP90. Characterization of structure and binding". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (9): 6967–73. March 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109453200. PMID 11744724.
External links
- Kv1.4+Potassium+Channel at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- KCNA4+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P15385 (Rat Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 4) at the PDBe-KB.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
 |