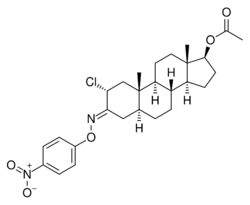
Chemistry:Nisterime acetate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2α-Chloro-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime 17β-acetate; 2α-Chloro-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime 17β-acetate; 2α-Chloro-3-(p-nitrophenoxy)imino-5α-androstan-17β-ol 17β-acetate |
| Routes of administration | Oral[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H35ClN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 503.04 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Nisterime acetate (USAN) (developmental code name ORF-9326), also known as 2α-chloro-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime 17β-acetate or as 2α-chloro-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime 17β-acetate, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) that was developed as a postcoital contraceptive but was never marketed.[2][3][1] It is an androgen ester – specifically, the C17α acetate ester of nisterime.[2] Unlike antiprogestogens like mifepristone, nisterime acetate does not prevent implantation and instead induces embryo resorption as well as interrupts the post-implantation stage of pregnancy.[4]
Nisterime acetate is described as an androgen by some sources.[2][5] However, it has also been reported that the drug lacks hormonal activity in bioassays, including androgenic, estrogenic, or progestogenic activity (as well as antagonistic activity).[1][6] This finding has been described as puzzling in light of the potent abortifacient activity of the drug in animals and it has been said that its mechanism of action remains unknown.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "The Post-Implantive Contragestational Activity of 17β-acetoxy-2α-chloro-3-(p-nitrophenoxy) imino-5α androstane (ORF 9326) in the Rat". Federation Proceedings 36 (3): 342. 1977.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 876–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA876.
- ↑ "Disposition of ORF 9326, a novel contragestational steroid, in animals". Steroids 32 (2): 147–156. September 1978. doi:10.1016/0039-128x(78)90001-6. PMID 102053.
- ↑ "The Use of Pharmacological Agents to Study Implantation". Cellular and Molecular Aspects of Implantation. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 479–. ISBN 978-1-4613-3180-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=iknTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA479.
- ↑ "Nisterime acetate". KEGG DRUG. http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?dr:D05174.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Research frontiers in fertility regulation. Harper & Row. 1980. pp. 368. ISBN 978-0-06-142902-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=YatsAAAAMAAJ. "ORF 9326 (17β-acetoxy-2α-chloro-3(p-nitrophenoxy) imino-5-androstane) is a derivative of dihydrotestosterone (Fig. 33-1). This compound was found to interrupt pregnancy in a number of species, but the fact that it has no hormonal activity is puzzling and its mechanism of action is still unknown."
 |

