Chemistry:MK-0773
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
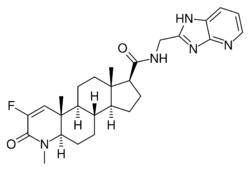
| Other names | PF-05314882; N-(3H-Imidazo(4,5-b)pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-2-fluoro-4-methyl-3-oxo-4-aza-5α-androst-1-ene-17β-carboxamide |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H34FN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 479.600 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
MK-0773, also known as PF-05314882, is a steroidal, orally active selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) that was under development by Merck and GTx for the treatment of sarcopenia (loss of muscle mass) in women and men.[1][2][3] Clinical trials for sarcopenia began in late 2007 but the collaboration between Merck and GTx ended in early 2010 and GTx terminated development of MK-0773 shortly thereafter.[2] MK-0773 was developed as a more advanced version of the related compound TFM-4AS-1.[4]
MK-0773 is a 4-azasteroid[5] and a potent and selective agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).[1] It binds to the AR with an EC50 of 6.6 nM and is a partial agonist in transactivation modulation of the AR with an IP of 25 nM and Emax of 78% and has a TRAF2 Emax of 29% and an N/C interaction (virilization-related) counterscreen assay Emax of 2%.[1] That is, it produces promoter activation but induces the N/C interaction almost negligibly.[1] MK-0773 is reportedly four times as potent as testosterone as an agonist of the AR.[2] The drug is selective and does not bind to other steroid hormone receptors such as the progesterone receptor or glucocorticoid receptor and shows no significant inhibition of 5α-reductase (IC50 > 10 μM).[1] In addition, it is non-aromatizable and hence has no potential for estrogenic effects or side effects, like gynecomastia.[6] MK-0773 had similar effects on lipid metabolism relative to DHT, including a decrease in total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) of a similar magnitude.[1]
MK-0773 shows tissue-selective androgenic effects in vivo in animals.[1] It increases lean body mass with maximal anabolic effects that are approximately 80% of those of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[1] However, it had less than 5% of the effect of DHT on uterine weight, about 30 to 50% of the increase of sebaceous gland area induced by DHT, and increased the weight of the seminal vesicles by 12% of that of DHT at the highest dosage assessed.[4][1] It had similarly reduced effects on the prostate gland.[1] No significant increase in gene expression of six candidate genes related to virilization was observed.[7] As such, MK-0773 shows a profile of an anabolic SARM with limited effects on sebaceous glands and reproductive tissues in animals and a reduced propensity for virilization.[1]
In human clinical studies, MK-0773 produced anabolism in women and men while producing no or very low effects on sebaceous glands, the endometrium, or the prostate gland after 12 weeks of treatment.[1][7][8][9] A decrease in total cholesterol and HDL was also observed in the clinical studies.[1] MK-0773 produced a significant increase in lean body mass in elderly (≥65 years of age) women with sarcopenia and moderate physical dysfunction.[10][11][12] It also increased muscle strength relative to placebo but this failed to reach statistical significance.[10][12] MK-0773 has been associated with elevated liver enzymes in clinical studies.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 "Discovery of the selective androgen receptor modulator MK-0773 using a rational development strategy based on differential transcriptional requirements for androgenic anabolism versus reproductive physiology". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 285 (22): 17054–17064. May 2010. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.099002. PMID 20356837.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Problems, Controversies, and Solutions". Steroids and Doping in Sports: A Reference Handbook: A Reference Handbook. ABC-CLIO. 26 November 2013. pp. 85–. ISBN 978-1-61069-314-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tAtIAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA85.
- ↑ "MK 0773". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800024550.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Deciphering the selective androgen receptor modulators paradigm". Expert Opin Drug Discov 8 (2): 191–218. February 2013. doi:10.1517/17460441.2013.741582. PMID 23231475.
- ↑ "Identification of selected in vitro generated phase-I metabolites of the steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator MK-0773 for doping control purposes". European Journal of Mass Spectrometry 22 (2): 49–59. 2016. doi:10.1255/ejms.1415. PMID 27419898.
- ↑ "Biomarkers of Bone Metabolism and Serum Free Estradiol (E2) Levels in Medically Castrated Older Men Treated with MK-0773 (MK), Testosterone (T), or Placebo (PBO) for 12 Weeks.". Endocrine Reviews 31 (3): S48. June 2010.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Bone Disorders: Translational Medicine Case Studies". Translational Medicine and Drug Discovery. Cambridge University Press. 31 January 2011. pp. 136–. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511976087.007. ISBN 978-1-139-49872-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=cJif7ofwbcEC&pg=PA136.
- ↑ Stoch SA, Friedman EJ, Zhu H, Xu Y, Wong P, Chappell DL, et al. (2008). A 12-week pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PD) study of MK-0773 in healthy postmenopausal (PMP) subjects. The Endocrine Society 90th Annual Meeting, June 12–15, San Francisco, CA. Abst. OR35–33.
- ↑ Stoch SA, et al. (2009) 91st Annual Meeting of the Endocrine Society, Washington, D.C. Abst. S21–24.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "A phase IIA randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial to study the efficacy and safety of the selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), MK-0773 in female participants with sarcopenia". The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging 17 (6): 533–543. 2013. doi:10.1007/s12603-013-0335-x. PMID 23732550.
- ↑ "Sarcopenia and Androgens: A Link between Pathology and Treatment". Frontiers in Endocrinology 5: 217. 2014. doi:10.3389/fendo.2014.00217. ISBN 9781771883719. PMID 25566189. PMC 4270249. https://books.google.com/books?id=U3amCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA258.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Weight and Appetite Loss in Cancer". Psycho-Oncology. Oxford University Press. 23 April 2015. pp. 242–. ISBN 978-0-19-936331-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=oy9mBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA242.
 |
