Chemistry:Drostanolone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Drolban, Masteril, Masteron, others (all as drostanolone propionate) |
| Other names | Dromostanolone; 2α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone; 2α-Methyl-DHT; 2α-Methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection (as drostanolone propionate) |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H32O2 |
| Molar mass | 304.474 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Drostanolone, or dromostanolone, is an anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was never marketed.[1][2][3] An androgen ester prodrug of drostanolone, drostanolone propionate, was formerly used in the treatment of breast cancer in women under brand names such as Drolban, Masteril, and Masteron.[1][2][3][4] This has also been used non-medically for physique- or performance-enhancing purposes.[3]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Medication | Ratioa |
|---|---|
| Testosterone | ~1:1 |
| Androstanolone (DHT) | ~1:1 |
| Methyltestosterone | ~1:1 |
| Methandriol | ~1:1 |
| Fluoxymesterone | 1:1–1:15 |
| Metandienone | 1:1–1:8 |
| Drostanolone | 1:3–1:4 |
| Metenolone | 1:2–1:30 |
| Oxymetholone | 1:2–1:9 |
| Oxandrolone | 1:3–1:13 |
| Stanozolol | 1:1–1:30 |
| Nandrolone | 1:3–1:16 |
| Ethylestrenol | 1:2–1:19 |
| Norethandrolone | 1:1–1:20 |
| Notes: In rodents. Footnotes: a = Ratio of androgenic to anabolic activity. Sources: See template. | |
Like other AAS, drostanolone is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).[3] It is not a substrate for 5α-reductase and is a poor substrate for 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD), and therefore shows a high ratio of anabolic to androgenic activity.[3] As a DHT derivative, drostanolone is not a substrate for aromatase and hence cannot be aromatized into estrogenic metabolites.[3] While no data are available on the progestogenic activity of drostanolone, it is thought to have low or no such activity similarly to other DHT derivatives.[3] Since the drug is not 17α-alkylated, it is not known to cause hepatotoxicity.[3]
Chemistry
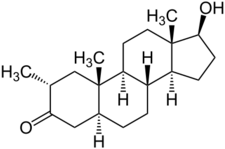
Drostanolone, also known as 2α-methyl-5α-dihydrotestosterone (2α-methyl-DHT) or as 2α-methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of DHT.[1][2][3] It is specifically DHT with a methyl group at the C2α position.[1][2][3]
History
Drostanolone and its ester drostanolone propionate were first described in 1959.[3][5] Drostanolone propionate was first introduced for medical use in 1961.[6]
Society and culture
Generic names
Drostanolone is the generic name of the drug and its INN, BAN, and DCF.[1][2] It has also been referred to as dromostanolone.[1][2]
Legal status
Drostanolone, along with other AAS, is a schedule III controlled substance in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act.[7]
Synthesis
Bolazine is when react 2 eq. with hydrazine to give dimer

Treatment of DHT (androstan-17β-ol-3-one, stanolone) [521-18-6] (1) with methyl formate and the strong base sodium methoxide gives [4033-95-8] (2). The newly added formyl function in the product is shown in the enol form. Catalytic hydrogenation reduces that function to a methyl group (3). The addition of hydrogen from the bottom face of the molecule leads to the formation of β-methyl isomer where the methyl group occupies the higher-energy axial position. Strong base-induced equilibration of the methyl group leads to the formation of the sterically favoured equatorial α-methyl isomer, affording dromostanolone (4).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 652–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA652.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 377–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA377.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 Llewellyn, William (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 517–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=afKLA-6wW0oC&pg=PT517.
- ↑ "Hormonal therapy of breast cancer with special reference to Masteril therapy". South African Medical Journal = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Geneeskunde 49 (49): 2036–40. November 1975. PMID 1242823.
- ↑ "Steroids. CV.12-Methyl and 2-Hydroxymethylene-androstane Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society 81 (2): 427–432. 1959. doi:10.1021/ja01511a040. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1402–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=_J2ti4EkYpkC&pg=PA1402.
- ↑ Karch, Steven B. (21 December 2006). Drug Abuse Handbook, Second Edition. CRC Press. pp. 30–. ISBN 978-1-4200-0346-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZjrMBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA30.
- ↑ "Steroids. CV. 1 2-Methyl and 2-hydroxymethylene-androstane derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society 81 (2): 427–432. January 1959. doi:10.1021/ja01511a040.
- ↑ Volovel'skii, L.N. et al, Zh. Obschch. Khim., 1966, 46, 1772.
- ↑ Ringold HJ, Rosenkranz G, US patent 2908693, issued 1959, assigned to Syntex SA
- ↑ Ringold HJ, Rosenkranz G, US patent 3118915, issued 1964, assigned to Roche Palo Alto LLC
- ↑ GB patent 1005896 US patent 3249627, issued 1966, assigned to Ormonoterapia Richter Spa
External links
{{Navbox
| name = Androgens and antiandrogens | title = Androgens and antiandrogens | state = collapsed | listclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Androgens
(incl. AAS)
| list1 =
| group2 = Antiandrogens | list2 = {{Navbox|child | groupstyle = text-align:center; | groupwidth = 9em;
| group1 = AR antagonists | list1 =
- Steroidal: Abiraterone acetate
- Canrenone
- Chlormadinone acetate
- Cyproterone acetate
- Delmadinone acetate
- Dienogest
- Drospirenone
- Medrogestone
- Megestrol acetate
- Nomegestrol acetate
- Osaterone acetate
- Oxendolone
- Potassium canrenoate
- Spironolactone
- Nonsteroidal: Apalutamide
- Bicalutamide
- Cimetidine
- Darolutamide
- Enzalutamide
- Flutamide
- Ketoconazole
- Nilutamide
- Seviteronel†
- Topilutamide (fluridil)
| group2 = Steroidogenesis| list2 =
inhibitors
| 5α-Reductase | |
|---|---|
| Others |
| group3 = Antigonadotropins | list3 =
- D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
- Estrogens (e.g., bifluranol, [[diethylstilbestrol, estradiol, estradiol esters, ethinylestradiol, ethinylestradiol sulfonate, paroxypropione)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin)
- GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix)
- Progestogens (incl., chlormadinone acetate, [[cyproterone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, gestonorone caproate, [[Chemistry:Medroxyprogesterone medroxyprogesterone acetate, Chemistry:Megestrol acetate|megestrol acetate]])
| group4 = Others | list4 =
- Androstenedione immunogens: Androvax (androstenedione albumin)
- Ovandrotone albumin (Fecundin)
}}
| liststyle = background:#DDDDFF;| list3 =
- #WHO-EM
- ‡Withdrawn from market
- Clinical trials:
- †Phase III
- §Never to phase III
- See also
- Androgen receptor modulators
- Estrogens and antiestrogens
- Progestogens and antiprogestogens
- List of androgens/anabolic steroids
}}
 |
