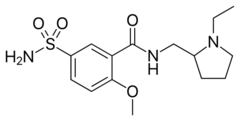
Chemistry:Sulpiride
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dogmatil, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets, capsules, solution), intramuscular injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–40%[1][2] |
| Protein binding | <40%[1] |
| Metabolism | Not metabolized;[4][5][6][7][8] 95% is exerted as the unchanged drug[1][4] |
| Elimination half-life | 6–8 hours[1][3] |
| Excretion | Urine (70–90%),[3][2] Feces.[4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H23N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 341.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Sulpiride, sold under the brand name Dogmatil among others, is an atypical antipsychotic (although some texts have referred to it as a typical antipsychotic)[9] medication of the benzamide class which is used mainly in the treatment of psychosis associated with schizophrenia and major depressive disorder, and sometimes used in low dosage to treat anxiety and mild depression. Sulpiride is commonly used in Asia, Central America, Europe, South Africa and South America. Levosulpiride is its purified levo-isomer and is sold in India for similar purpose. It is not approved in the United States , Canada , or Australia . The drug is chemically and clinically similar to amisulpride.
Medical uses
Sulpiride's primary use in medicine is in the management of the symptoms of schizophrenia.[1] It has been used as both a monotherapy and adjunctive therapy (in case of treatment-resistance) in schizophrenia.[1][10][11][12][13][14] It has also been used in the treatment of dysthymia.[15] There is evidence, although low quality, that Sulpiride could accelerate antidepressant response in patients with major depressive disorder.[16] There is also evidence of its efficacy in treating panic disorder.[17][18] Sulpiride is indicated for the treatment of vertigo in some countries.[19] In Japan, Sulpiride is both approved as a treatment for schizophrenia and for major depressive disorder (low dose).[20][21]
Contraindications
Contraindications[1]
- Hypersensitivity to sulpiride
- Pre-existing breast cancer or other prolactin-dependent tumors
- Phaeochromocytoma
- Intoxication with other centrally-active drugs
- Concomitant use of levodopa
- Acute porphyria
- Comatose state or CNS depression
- Bone-marrow suppression
Cautions[1]
- Pre-existing Parkinson's disease
- Patients under 18 years of age (insufficient clinical data)
- Pre-existing severe heart disease/bradycardia, or hypokalemia (predisposing to long QT syndrome and severe arrhythmias)
- Patients with pre-existing epilepsy. Anticonvulsant therapy should be maintained
- Lithium use — increased risk of neurological side effects of both drugs
Pregnancy and lactation
- Pregnancy: Animal studies did not reveal any embryotoxicity or fetotoxicity, nor did limited human experience. Due to insufficient human data, pregnant women should be treated with sulpiride only if strictly indicated. Additionally, the newborns of treated women should be monitored, because isolated cases of extrapyramidal side effects have been reported.[1]
- Lactation: Sulpiride is found in the milk of lactating women. Since the consequences are unclear, women should not breastfeed during treatment.[1]
Side effects
Sulpiride is usually well tolerated, producing few adverse effects. Their incidences[spelling?] are as follows:[1][10][22][23][24][25][26][27][28]
- Common (>1%) adverse effects
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Extrapyramidal side effects
- - Tremor
- - Dystonia
- - Akathisia — a sense of inner restlessness that presents itself with the inability to stay still
- - Parkinsonism
- Somnolence (not a very prominent adverse effect considering its lack of α1 adrenergic, histamine and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor affinity)
- Insomnia
- Weight gain or loss
- Hyperprolactinemia (elevated plasma levels of the hormone, prolactin which can, in turn lead to sexual dysfunction, galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, etc.)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Nasal congestion
- Anticholinergic adverse effects such as:
- - Dry mouth
- - Constipation
- - Blurred vision
- Impaired concentration
- Rare (<1% incidence) adverse effects
- Tardive dyskinesia — a rare, often permanent[citation needed] movement disorder that, more often than not, results from prolonged treatment with antidopaminergic agents such as antipsychotics. It presents with slow (hence tardive), involuntary, repetitive and purposeless movements that most often affect the facial muscles.
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome — a rare, life-threatening complication that results from the use of antidopaminergic agents. Its incidence increases with concomitant use of lithium (medication) salts
- Blood dyscrasias — rare, sometimes life-threatening complications of the use of a number of different antipsychotics (most notably clozapine) which involves abnormalities in the composition of a person's blood (e.g. having too few white blood cells per unit volume of blood). Examples include:
- - Agranulocytosis — a significant drop in white blood cell count, leaving individuals wide open to life-threatening opportunistic infections
- - Neutropenia
- - Leucopenia
- - Leukocytosis[29]
- Seizures
- Torsades de pointes
- Unknown incidence adverse effects include
- QTc interval prolongation which can lead to potentially fatal arrhythmias.
- Cholestatic jaundice[30]
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Primary biliary cirrhosis[31]
- Allergic reactions
- Photosensitivity — sensitivity to light
- Skin rashes
- Depression
- Catatonia
- Palpitations
- Agitation
- Diaphoresis — sweating without a precipitating factor (e.g. increased ambient temperature)
- Hypotension — low blood pressure
- Hypertension — high blood pressure
- Venous thromboembolism (probably rare)
Overdose
Sulpiride has a relatively low order of acute toxicity. Substantial amounts may cause severe but reversible dystonic crises with torticollis, protrusion of the tongue, and/or trismus. In some cases all the classical symptoms typical of severe Parkinson's disease may be noted; in others, over-sedation/coma may occur. The treatment is largely symptomatic. Some or all extrapyramidal reactions may respond to the application of anticholinergic drugs such as biperiden or benzatropine. All patients should be closely monitored for signs of long QT syndrome and severe arrhythmias.
Interactions
Sulpiride neither inhibits nor stimulates cytochrome P450 family (CYP) of oxidizing enzymes in human, thus would not cause clinically significant interactions with other drugs,[5] which are metabolized by CYPs. However, the risk or severity of adverse effects can be increased when sulpiride is combined with other drugs, but this is not related to substrates, inducers and inhibitors of CYPs.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Receptor | Affinity (Ki, nM) |
|---|---|
| DAT | >10,000 |
| 5-HT1A | >10,000 |
| 5-HT2A | 4,786 |
| 5-HT3 | >10,000 |
| 5-HT6 | |
| 5-HT7 | |
| α1 | >10,000 |
| α2 | >10,000 |
| D1 | >10,000 |
| D2 | 9.8 |
| D3 | 8.05 |
| D4 | 54 |
| H1 | >10,000 |
| V3 | >10,000 |
| Affinity values are toward cloned human receptors. | |
Sulpiride is a selective antagonist at dopamine D2, D3 and 5-HT1A receptors. Antagonism at 5-HT1A dominates in doses exceeding 600 mg daily. In doses of 600 to 1,600 mg sulpiride shows mild sedating and antipsychotic activity. Its antipsychotic potency compared to chlorpromazine is only 0.2 (1/5). In low doses (in particular 50 to 200 mg daily) its prominent feature is antagonism of presynaptic inhibitory dopamine and serotonin receptors, accounting for some antidepressant activity and a stimulating effect. Additionally, it alleviates vertigo.
The benzamide neuroleptics (including sulpiride, amisulpride, and sultopride) have been shown to activate the endogenous gamma-hydroxybutyrate receptor in vivo at therapeutic concentrations.[32] Sulpiride was found in one study in rats to upregulate GHB receptors.[33] GHB has neuroleptic properties and it is believed binding to this receptor may contribute to the effects of these neuroleptics.
Sulpiride, along with clozapine, and valproate has been found to activate DNA demethylation in the brain.[34]
History
Sulpiride was discovered in 1966 as a result of a research program by Justin-Besançon and C. Laville at Laboratoires Delagrange who were working to improve the anti-dysrhythmic properties of procainamide; the program led first to metoclopramide and later to sulpiride.[35][36] Laboratoires Delagrange was acquired by Synthelabo in 1991[37][38] which eventually became part of Sanofi.[39]
Society and culture
Brand names
Sulpiride is marketed under the brand names Dogmatil (Germany , HK, SG, Philippines ), Dolmatil (IE, United Kingdom ), Eglonyl (Russia , South Africa , HR, SI), Espiride (South Africa ), Modal (IL), Prometar (UY), Equilid (Brazil ) and Sulpor (United Kingdom ), among many others.[40]
Medicinal forms
These include tablet and oral solution[41]
Patient Aversions
Some individuals from the Caribbean region may have an aversion to taking the medication due to the association with the brand name of Dogmatil. Dogmatil has been associated with dog medication.
Research
Sulpiride has been studied for use as a hormonal contraceptive in women in whom conventional oral contraceptives are contraindicated and to potentiate progestogen-only contraceptives.[42][43] The contraceptive effects of sulpiride are due to its prolactin-releasing and antigonadotropic effects and the hyperprolactinemia–amenorrhea state that it induces.[42][43]
Since the use of psychotropic drugs is efficient in treating irritable bowel syndrome (IBS),[44] sulpiride is studied as potential sole maintenance therapy in the treatment of IBS.[45][46][44]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 "Sulpiride Tablets 200mg, 400mg (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC). Sanofi. 21 January 2010. http://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/18936/SPC/Sulpiride+Tablets+200mg%2c+400mg/#PHARMACODYNAMIC_PROPS.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Absolute bioavailability, rate of absorption, and dose proportionality of sulpiride in humans". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 81 (1): 26–32. January 1992. doi:10.1002/jps.2600810106. PMID 1619566.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Pharmacokinetics of sulpiride in humans after intravenous and intramuscular administrations". J Pharm Sci 80 (12): 1119–24. December 1991. doi:10.1002/jps.2600801206. PMID 1815069.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Metabolism of sulpiride in man and rhesus monkeys". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie 232 (1): 79–91. March 1978. PMID 96745.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "No inhibition of cytochrome P450 activities in human liver microsomes by sulpiride, an antipsychotic drug". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 28 (1): 188–191. January 2005. doi:10.1248/bpb.28.188. PMID 15635191.
- ↑ "Psychotropic drugs and liver disease: A critical review of pharmacokinetics and liver toxicity". World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pharmacology and Therapeutics 8 (1): 26–38. February 2017. doi:10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i1.26. PMID 28217372.
- ↑ "Antipsychotic Drugs and Liver Injury". Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry 30 (1): 47–51. February 2018. PMID 29719358.
- ↑ "Biotransformation of sultopride in man and several animal species". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems 15 (6): 469–476. June 1985. doi:10.3109/00498258509045020. PMID 4036171.
- ↑ Joint Formulary Committee (2013). British National Formulary (BNF) (65 ed.). London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85711-084-8. https://archive.org/details/bnf65britishnati0000unse.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 The Maudsley prescribing guidelines in psychiatry. West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell. 2012. ISBN 978-0-470-97948-8.
- ↑ "Sulpiride augmentation for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD008125. January 2010. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008125.pub2. PMID 20091661.
- ↑ "Effectiveness of sulpiride in adult patients with schizophrenia". Schizophrenia Bulletin 39 (3): 673–83. May 2013. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbs002. PMID 22315480.
- ↑ "Sulpiride for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD001162. 2000. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001162. PMID 10796605.
- ↑ "Sulpiride versus other antipsychotics for schizophrenia (Protocol)". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD008126. October 2009. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008126.
- ↑ "The substituted benzamides and their clinical potential on dysthymia and on the negative symptoms of schizophrenia". Molecular Psychiatry 7 (3): 247–53. 2002. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001040. PMID 11920152.
- ↑ "Combined treatment with sulpiride and paroxetine for accelerated response in patients with major depressive disorder". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 25 (6): 545–51. December 2005. doi:10.1097/01.jcp.0000185425.00644.41. PMID 16282835.
- ↑ "The response to sulpiride in social anxiety disorder: D2 receptor function". Journal of Psychopharmacology 27 (2): 146–51. February 2013. doi:10.1177/0269881112450778. PMID 22745189.
- ↑ "Sulpiride and refractory panic disorder". Psychopharmacology 223 (2): 247–9. September 2012. doi:10.1007/s00213-012-2818-6. PMID 22864966.
- ↑ "Medicinanet - Equilid 50". http://www.medicinanet.com.br/bula/2239/equilid_50.htm.
- ↑ "Search results detail| Kusurino-Shiori(Drug information Sheet)". http://www.rad-ar.or.jp/siori/english/kekka.cgi?n=35833.
- ↑ "Brain Networks Reveal the Effects of Antipsychotic Drugs on Schizophrenia Patients and Controls". Frontiers in Psychiatry 10: 611. 2019-09-12. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00611. PMID 31572229.
- ↑ "Sulpiride and perphenazine in schizophrenia. A double-blind clinical trial". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 80 (1): 92–6. July 1989. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1989.tb01305.x. PMID 2669445.
- ↑ "Sulpiride versus haloperidol, a clinical trial in schizophrenia. A preliminary report". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. Supplementum 311: 31–41. 1984. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1984.tb06857.x. PMID 6367362.
- ↑ "Sulpiride and haloperidol in schizophrenia: a double-blind cross-over study of therapeutic effect, side effects and plasma concentrations". The British Journal of Psychiatry 147 (3): 283–8. September 1985. doi:10.1192/bjp.147.3.283. PMID 3904885.
- ↑ "A randomized double blind group comparative study of sulpiride and amitriptyline in affective disorder". Psychopharmacology 81 (3): 258–60. 1983. doi:10.1007/bf00427274. PMID 6417717.
- ↑ "A double blind trial of sulpiride in Huntington's disease and tardive dyskinesia". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 47 (8): 844–7. August 1984. doi:10.1136/jnnp.47.8.844. PMID 6236286.
- ↑ "Clinical trials of benzamides in psychiatry". Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology 35: 163–94. 1982. PMID 6756060.
- ↑ "Controlled trial of sulpiride in chronic schizophrenic patients". The British Journal of Psychiatry 137 (6): 522–9. December 1980. doi:10.1192/bjp.137.6.522. PMID 7011469.
- ↑ "Leukocytosis related to the therapeutic dosage of sulpiride". Biological Psychiatry 35 (12): 963. June 1994. doi:10.1016/0006-3223(94)91244-0. PMID 8080896.
- ↑ "Severe cholestatic jaundice due to sulpiride". Israel Journal of Medical Sciences 23 (12): 1259–60. December 1987. PMID 3326861.
- ↑ "Symptomatic primary biliary cirrhosis triggered by administration of sulpiride". The American Journal of Gastroenterology 94 (12): 3660–1. December 1999. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.01634.x. PMID 10606349.
- ↑ "Displacement of [3H] gamma-hydroxybutyrate binding by benzamide neuroleptics and prochlorperazine but not by other antipsychotics". European Journal of Pharmacology 256 (2): 211–4. April 1994. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(94)90248-8. PMID 7914168.
- ↑ "Sulpiride, but not haloperidol, up-regulates gamma-hydroxybutyrate receptors in vivo and in cultured cells". European Journal of Pharmacology 346 (2–3): 331–7. April 1998. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(98)00068-5. PMID 9652377.
- ↑ "Clozapine and sulpiride but not haloperidol or olanzapine activate brain DNA demethylation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105 (36): 13614–9. September 2008. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805493105. PMID 18757738. Bibcode: 2008PNAS..10513614D.
- ↑ Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. 31 October 2005. pp. 205–. ISBN 978-0-470-01552-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Cb6BOkj9fK4C&pg=PA130.
- ↑ "Translating 5-HT receptor pharmacology". Neurogastroenterology and Motility 21 (12): 1235–8. December 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01425.x. PMID 19906028.
- ↑ "Synthélabo rachète les laboratoires Delagrange". Les Echos. October 17, 1991. http://www.lesechos.fr/17/10/1991/LesEchos/15996-035-ECH_synthelabo-rachete-les-laboratoires-delagrange.htm.
- ↑ "Laboratoires Delagrange". Bibliothèque nationale de France. http://data.bnf.fr/12198004/laboratoires_delagrange/.
- ↑ "A look back at Sanofi's merger with Synthélabo". PMLiVE. May 24, 2013. http://www.pmlive.com/pharma_news/a_look_back_at_sanofis_merger_with_synthelabo_477146.
- ↑ "Sulpiride". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/international/sulpiride.html.
- ↑ "Sulpiride 200mg/5ml Oral Solution". EMC. Datapharm. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/13116/smpc#gref.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "[One thousand months of contraception with sulpiride"] (in fr). Revue Française de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique 71 (1): 53–61. January 1976. PMID 959705. https://www.popline.org/node/429364. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "Sulpiride and the potentiation of progestogen only contraception". British Medical Journal 291 (6495): 559–61. August 1985. doi:10.1136/bmj.291.6495.559. PMID 2994800.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 "[Treatment for irritable bowel syndrome--psychotropic drugs, antidepressants and so on]" (in Japanese). Nihon Rinsho 64 (8): 1495–500. August 2006. PMID 16898620.
- ↑ "New regimen for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with emphasis on Sulpride as the sole maintenance therapy". Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 9 (5): 154–157. 2019. doi:10.22270/jddt.v9i5.3424.
- ↑ "[Sulpiride treatment of irritable colon syndrome]" (in Russian). Klin Med (Mosk) 78 (7): 22–6. 2000. PMID 10979637.
External links
 |

