Chemistry:E-4031
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
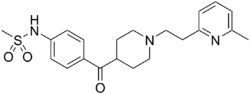
| Other names | (1-[2-(6-methyl-2-pyridyl)ethyl]-4-(4-methylsulfonyl-aminobenzoyl)piperidine) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H27N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 401.53 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
E-4031 is an experimental class III antiarrhythmic drug that blocks potassium channels of the hERG-type.[1]
Chemistry
E-4031 is a synthesized toxin that is a methanesulfonanilide class III antiarrhythmic drug.[2]
Target
E-4031 acts on a specific class of voltage-gated potassium channels mainly found in the heart, the hERG channels. hERG channels (Kv11.1) mediate the IKr current, which repolarizes the myocardial cells.[3][4] The hERG channel is encoded by ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG).[5]
Mode of action
E-4031 blocks hERG-type potassium channels [5][6] by binding to the open channels.[7] Its structural target within the hERG-channel is unclear, but some other methanesulfonanilide class III antiarrhythmic drugs are known to bind to the S6 domain or C-terminal of the hERG-channel.[8][9][10][11][12][13]
Reducing IKr in myocardial cells prolongs the cardiac action potential and thus prolongs the QT-interval.[7][14] In non-cardiac cells, blocking Ikr has a different effect: it increases the frequency of action potentials.[5]
Toxicity
As E-4031 can prolong the QT-interval, it can cause lethal arrhythmias.[13]
Therapeutic use
E-4031 is solely used for research purposes. So far, one clinical trial has been conducted to test the effect of E-4031 on prolongation of the QT-interval.[15]
References
- ↑ "Postnatal development of E-4031-sensitive potassium current in rat carotid chemoreceptor cells". Journal of Applied Physiology 98 (4): 1469–77. April 2005. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01254.2003. PMID 15591286.
- ↑ "4'-[(4-Piperidyl)carbonyl]methanesulfonanilides as potent, selective, bioavailable class III antiarrhythmic agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 33 (3): 903–5. March 1990. doi:10.1021/jm00165a003. PMID 2308138.
- ↑ "Pharmacological removal of human ether-à-go-go-related gene potassium channel inactivation by 3-nitro-N-(4-phenoxyphenyl) benzamide (ICA-105574)". Molecular Pharmacology 77 (1): 58–68. January 2010. doi:10.1124/mol.109.059543. PMID 19805508.
- ↑ "Human ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG) K+ channels: function and dysfunction". Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology 98 (2–3): 137–48. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2008.10.006. PMID 19027781.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "The class III antiarrhythmic agent E-4031 selectively blocks the inactivating inward-rectifying potassium current in rat anterior pituitary tumour cells (GH3/B6 cells).". Pflügers Archiv 434 (1): 1–10. 1997. doi:10.1007/s004240050356. PMID 9094250.
- ↑ "Two components of cardiac delayed rectifier K+ current. Differential sensitivity to block by class III antiarrhythmic agents". The Journal of General Physiology 96 (1): 195–215. July 1990. doi:10.1085/jgp.96.1.195. PMID 2170562.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Class III antiarrhythmic drugs block HERG, a human cardiac delayed rectifier K+ channel. Open-channel block by methanesulfonanilides". Circulation Research 78 (3): 499–503. March 1996. doi:10.1161/01.res.78.3.499. PMID 8593709.
- ↑ "Molecular determinant of high-affinity dofetilide binding to HERG1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes: involvement of S6 sites". Molecular Pharmacology 57 (2): 367–74. February 2000. PMID 10648647.
- ↑ "A structural basis for drug-induced long QT syndrome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97 (22): 12329–33. October 2000. doi:10.1073/pnas.210244497. PMID 11005845. Bibcode: 2000PNAS...9712329M.
- ↑ "Open channel block of HERG K(+) channels by vesnarinone". Molecular Pharmacology 60 (2): 244–53. August 2001. doi:10.1124/mol.60.2.244. PMID 11455010.
- ↑ "Molecular determinants of voltage-dependent human ether-a-go-go related gene (HERG) K+ channel block". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277 (26): 23587–95. June 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200448200. PMID 11960982.
- ↑ "Voltage-dependent profile of human ether-a-go-go-related gene channel block is influenced by a single residue in the S6 transmembrane domain". Molecular Pharmacology 63 (5): 1051–8. May 2003. doi:10.1124/mol.63.5.1051. PMID 12695533.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Structural determinants of HERG channel block by clofilium and ibutilide". Molecular Pharmacology 66 (2): 240–9. August 2004. doi:10.1124/mol.104.000117. PMID 15266014.
- ↑ "Differential effects of the new class III antiarrhythmic agents almokalant, E-4031 and D-sotalol, and of quinidine, on delayed rectifier currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes". Cardiovascular Research 26 (11): 1145–52. November 1992. doi:10.1093/cvr/26.11.1145. PMID 1291093.
- ↑ "Assessment of reverse use-dependent blocking actions of class III antiarrhythmic drugs by 24-hour Holter electrocardiography". Journal of the American College of Cardiology 27 (1): 84–9. January 1996. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(95)00424-6. PMID 8522715.
 |

