Chemistry:Homoquinolinic acid
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
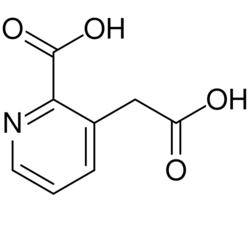 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Homoquinolinate |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H7NO4 |
| Molar mass | 181.147 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Homoquinolinic acid (HQA) is a potent excitotoxin[1] which is a conformationally-restricted analogue of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and a partial agonist of the main/glutamate site of the NMDA receptor, with some selectivity for NR2B subunit-containing receptors.[2][3][4] It is approximately equipotent to NMDA and about five times more potent than quinolinic acid as an agonist of the NMDA receptor.[5] HQA has also been found to label a novel, yet uncharacterized binding site, which can be distinguished from the NMDA receptor with the use of 2-carboxy-3-carboxymethylquinoline (CCMQ), a selective ligand of the uncharacterized site.[6]
See also
- Aspartate
- Ibotenic acid
- Tetrazolylglycine
References
- ↑ Quinolinic acid and the kynurenines. CRC Press. 1989. ISBN 978-0-8493-6592-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=BwtrAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Psychopharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. 31 July 2010. pp. 511–. ISBN 978-3-540-68698-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=qoyYobgX0uwC&pg=PA511.
- ↑ "The endogenous agonist quinolinic acid and the non endogenous homoquinolinic acid discriminate between NMDAR2 receptor subunits". Neurochemistry International 28 (4): 445–52. April 1996. doi:10.1016/0197-0186(95)00091-7. PMID 8740453.
- ↑ Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 24 January 2012. pp. 404–. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Sd6ot9ul-bUC&pg=PA404.
- ↑ C.S.A. Neurosciences Abstracts. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts. 1984. https://books.google.com/books?id=AV4mAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ Glutamate and GABA Receptors and Transporters: Structure, Function and Pharmacology. CRC Press. 4 October 2001. pp. 73–. ISBN 978-0-203-29938-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=7f0eC_olTJMC&pg=PA73.
 |

