Chemistry:Deltorphin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
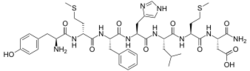
(3S)-3-[(2S)-2-[(2S)-2-[(2S)-2-[(2S)-2-[(2R)-2-[(2S)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanamido]-4-(methylsulfanyl)butanamido]-3-phenylpropanamido]-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido]-4-methylpentanamido]-4-(methylsulfanyl)butanamido]-3-carbamoylpropanoic acid
or L-tyrosyl-D-methionyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-histidyl-L-leucyl-L-methionyl-L-α-asparagine | |
| Other names
Deltorphin A; Dermenkephalin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C44H62N10O10S2 | |
| Molar mass | 955.154 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Deltorphin, also known as deltorphin A and dermenkephalin, is a naturally occurring, exogenous opioid heptapeptide and thus, exorphin, with the amino acid sequence Tyr-D-Met-Phe-His-Leu-Met-Asp-NH2.[1][2][3] Along with the other deltorphins (such as deltorphin I and deltorphin II) and the dermorphins, deltorphin is endogenous to frogs of the genus Phyllomedusa such as P. bicolor and P. sauvagei where it is produced in their skin, and is not known to occur naturally in any other species.[1][2][4] Deltorphin is one of the highest affinity and most selective naturally occurring opioid peptides known, acting as a very potent and highly specific agonist of the δ-opioid receptor.[1][2][3]
Deltorphins have an unusually high blood–brain barrier penetration rate. The nonselective opiate antagonist naloxone inhibits deltorphin uptake by brain microvessels, but neither the selective δ-opioid antagonist naltrindole nor a number of opioid peptides with different affinities for δ- or μ-opioid receptors compete with deltorphins for the transport.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Deltorphin, a novel amphibian skin peptide with high selectivity and affinity for delta opioid receptors". European Journal of Pharmacology 162 (1): 123–8. March 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(89)90611-0. PMID 2542051.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Isolation of dermenkephalin from amphibian skin, a high-affinity delta-selective opioid heptapeptide containing a D-amino acid residue". FEBS Letters 255 (2): 269–74. September 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(89)81104-4. PMID 2551734.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86 (13): 5188–92. July 1989. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.13.5188. PMID 2544892. Bibcode: 1989PNAS...86.5188E.
- ↑ "Conformational properties of deltorphin: new features of the delta-opioid receptor". FEBS Letters 247 (2): 283–8. April 1989. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(89)81353-5. PMID 2541018.
- ↑ Fiori, Anna; Cardelli, Patrizia; Negri, Lucia; Savi, Maria Rosaria; Strom, Roberto; Erspamer, Vittorio (1997-08-19). "Deltorphin transport across the blood–brain barrier". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94 (17): 9469–9474. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.17.9469. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9256506. Bibcode: 1997PNAS...94.9469F.
 |
