Chemistry:Embutramide
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
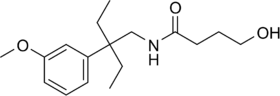
| Formula | C17H27NO3 |
| Molar mass | 293.407 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Embutramide (INN, USAN, BAN) (brand name Embutane) is a potent analgesic and sedative drug that is structurally related to GHB.[1][2][3] It was developed by Hoechst A.G. in 1958[4] and was investigated as a general anesthetic agent, but was found to have a very narrow therapeutic window, with a 50 mg/kg dose producing effective sedation and a 75 mg/kg dose being fatal. Along with strong sedative effects, embutramide also produces respiratory depression and ventricular arrhythmia. Because of these properties, it was never adopted for medical use as an anesthetic as it was considered too dangerous for this purpose. Instead it is used for euthanasia in veterinary medicine, mainly for the euthanization of dogs.[citation needed]
Embutramide is formulated as a combination product under the brand name Tributame, which also contains chloroquine and lidocaine.[5]
Embutramide is used for euthanasia of a range of different animals, mainly small animals kept as pets rather than large farm animals. It may cause significant pain to the animal being euthanized,[6] and so may be less humane than older drugs used for this purpose such as pentobarbital; however, it may have less abuse potential than barbiturates especially in the Tributame combination formulation, and so is less likely to be diverted for recreational abuse.[7] Embutramide has however been reported to be used for suicide by people with access to the drug,[8][9] and was added to the list of Schedule III drugs in the US in 2006, as a Non-Narcotic with ACSCN 2020, which classifies it with depressants such as benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and other sedative-hypnotics.[10]
Chemistry
Embutramide is considered an analog of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) due to its structural similarity to this naturally occurring neurotransmitter. GHB is known for its medical applications, such as treating narcolepsy and alcohol withdrawal symptoms. However, its recreational use has led to its classification as a controlled substance in many countries. The analog status of embutramide is significant in terms of its regulation and controlled use to prevent any potential misuse or abuse.
Synthesis

Alkylation of (3-Methoxyphenyl)acetonitrile [19924-43-7] (1) with bromoethane gives 2-Ethyl-2-(3-methoxyphenyl)-butanenitrile [40692-21-5] (2). Sodium borohydride is used to reduce the nitrile group to give 2-ethyl-2-(3-methoxyphenyl)butan-1-amine [93309-48-9] (3'). Amide formation via reaction with gamma-butyrolactone completed the synthesis of embutramide (4).
References
- ↑ The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 482–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA482.
- ↑ Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 31 October 1999. pp. 108–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=mqaOMOtk61IC&pg=PA108.
- ↑ Small Animal Toxicology. Elsevier Health Sciences. 7 August 2013. pp. 315–. ISBN 978-0-323-24198-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=BLkPFlB15v0C&pg=PA315.
- ↑ Schmitt K, Henning I, Lindner E, Ott H, "New gamma-hydroxy-carboxylic acid amides and process for their manufacture", US patent 3045043, issued 17 July 1962, assigned to Hoechst AG
- ↑ "TRIBUTAME Euthanasia Solution". Freedom of Information Summary NADA 141-245. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/animalveterinary/products/approvedanimaldrugproducts/foiadrugsummaries/ucm051493.pdf.
- ↑ "[The use of T61 for the humane killing of pets and laboratory animals]" (in nl, nl-be). Tijdschrift voor Diergeneeskunde 115 (13): 625–32. July 1990. PMID 2371711.
- ↑ "DEA lists embutramide as schedule III controlled substance". http://www.avma.org/onlnews/javma/nov06/061101b.asp.
- ↑ "Suicide by ingestion of T-61". Veterinary and Human Toxicology 31 (4): 319–20. August 1989. PMID 2815545.
- ↑ "Blood investigation in a fatality involving the veterinary drug T-61". Journal of Analytical Toxicology 26 (7): 529–31. October 2002. doi:10.1093/jat/26.7.529. PMID 12423012.
- ↑ "DEA lists embutramide as schedule III controlled substance". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 229 (9): 1358. November 2006. PMID 17139797. https://www.avma.org/javma-news/2006-11-01/dea-lists-embutramide-schedule-iii-controlled-substance. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
- ↑ Schmitt Karl, et al. U.S. Patent 3,045,043 (1962 to Hoechst Ag).
- ↑ Karl Schmitt, et al. GB1002436 (1965 to Hoechst AG).
- ↑ "science24.com - Synthesis of embutramide in mild conditions". https://science24.com/paper/23038. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
 |
