Chemistry:Akuammine
From HandWiki
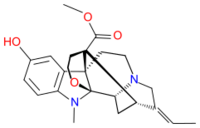
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Vincamajoridine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H26N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 382.460 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Akuammine (vincamajoridine[2]) is an indole alkaloid. It is the most abundant alkaloid found in the seeds from the tree Picralima nitida,[3] commonly known as akuamma, comprising 0.56% of the dried powder. It has also been isolated from Vinca major.[2] Akuammine is structurally related to yohimbine, mitragynine and more distantly Voacangine, all of which are alkaloid plant products with pharmacological properties.
Pharmacology
Akuammine has antimalarial activity,[3] and may be the primary constituent of P. nitida seeds responsible for this activity.[4]
Akuammine is an opioid agonist with low affinity, selective for the mu-opioid receptor, when tested in vitro.[5][6]
References
- ↑ Merck Index (12th ed.). 200.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "The identity of vincamajoridine and akuammine". Experientia 11 (9): 343. September 1955. doi:10.1007/BF02159911. PMID 13262018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Akuammine: an antimalarial indolemonoterpene alkaloid of Picralima nitida seeds". Planta Medica 59 (6): 565–6. December 1993. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959764. PMID 8302957.
- ↑ African Ethnobotany: Poisons and Drugs : Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology. CRC Press. 1996. p. 123. ISBN 9783826100772.
- ↑ "Opioid activity of alkaloids extracted from Picralima nitida (fam. Apocynaceae)". European Journal of Pharmacology 350 (1): 101–8. May 1998. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00232-5. PMID 9683021.
- ↑ "Akuammine and dihydroakuammine, two indolomonoterpene alkaloids displaying affinity for opioid receptors". Journal of Natural Products 55 (3): 380–4. March 1992. doi:10.1021/np50081a017. PMID 1317407.
 |

