Chemistry:Kelatorphan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
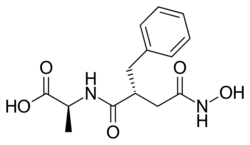
| Formula | C14H18N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 294.307 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Kelatorphan is a drug which acts as a powerful and complete inhibitor of nearly all of the enzymes responsible for catabolism of the endogenous enkephalins, including neutral endopeptidase (NEP), dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPP3), aminopeptidase N (APN), and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).[1][2][3] In mice, with the intracerebroventricular co-administration of a 50 µg dose of kelatorphan (this route is necessary because kelatorphan is incapable of crossing the blood-brain-barrier)[4] hence alongside exogenous [Met]enkephalin (ED50 approximately 10 ng), it potentiated the analgesic effects of the latter by 50,000 times.[1] Kelatorphan also displays potent antinociceptive effects alone,[5] and does not depress respiration, although at high doses it actually increases it.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Analgesic effects of kelatorphan, a new highly potent inhibitor of multiple enkephalin degrading enzymes". European Journal of Pharmacology 102 (3–4): 525–528. July 1984. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(84)90575-2. PMID 6386492.
- ↑ "Spinorphin as an endogenous inhibitor of enkephalin-degrading enzymes: roles in pain and inflammation". Current Protein & Peptide Science 3 (6): 587–599. December 2002. doi:10.2174/1389203023380404. PMID 12470213. http://www.benthamdirect.org/pages/content.php?CPPS/2002/00000003/00000006/0002K.SGM.
- ↑ "Neutral Endopeptidase Inhibitors and Combined Inhibitors Neutral Endopeptidase and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme". Antihypertensive Drugs. CRC Press. 5 September 1997. p. 192. ISBN 978-90-5702-122-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=f8OO3B7eD6wC&pg=PA192. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Effects of the potent analgesic enkephalin-catabolizing enzyme inhibitors RB101 and kelatorphan on respiration". Pain 90 (1–2): 7–13. February 2001. doi:10.1016/S0304-3959(00)00382-1. PMID 11166965.
- ↑ "Potent antinociceptive effects of kelatorphan (a highly efficient inhibitor of multiple enkephalin-degrading enzymes) systemically administered in normal and arthritic rats". Brain Research 497 (1): 94–101. September 1989. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(89)90974-8. PMID 2790459.
 |
