Chemistry:Oliceridine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | OH li SER i deen |
| Trade names | Olinvyk |
| Other names | TRV-130, TRV130 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
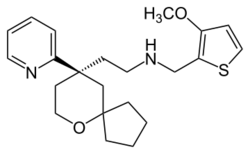
| Formula | C22H30N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 386.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Oliceridine, sold under the brand name Olinvyk, is an opioid medication that is used for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults.[2] It is given by intravenous (IV) injection.[2]
The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, constipation, itchy skin and low oxygen levels in blood.[3]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2020.[3]
Medical uses
Oliceridine is indicated for short-term intravenous use in hospitals or other controlled clinical settings, such as during inpatient and outpatient procedures.[2] It is not indicated for at-home use.[2]
Adverse effects
The safety profile of oliceridine is similar to other opioids.[2] As with other opioids, the most common side effects of oliceridine are nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache and constipation.[2] Prolonged use of opioid analgesics during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome.[2]
Olinvyk carries a boxed warning about addiction, abuse and misuse; life-threatening respiratory depression; neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome; and risks from concomitant use with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system depressants.[2] Unlike other opioids for intravenous administration, Olinvyk has a maximum recommended daily dose limit of 27 milligrams.[2]
Contraindications
Oliceridine should not be given to people with significant respiratory depression; acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment; known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction; or known hypersensitivity to the medication.[2]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Oliceridine is a μ-opioid receptor biased agonist developed by Trevena. In cell-based (in vitro) research, oliceridine elicits robust G protein signaling, with potency and efficacy similar to that of morphine, but with less β-arrestin 2 recruitment and receptor internalization.[4] It has been suggested that this might be due to its low intrinsic efficacy,[5] rather than functional selectivity or 'G protein bias', although the validity of that conclusion has also been questioned.[6] In vivo, it may have fewer adverse effects (including respiratory depression and constipation) compared with morphine.[7][8][9] In general, in vitro potency does not guarantee any clinical relevance in humans.[10]
History
A total of 1,535 participants with moderate to severe acute pain were treated with oliceridine in controlled and open-label trials.[2] Its safety and efficacy were established by comparing oliceridine to placebo in randomized, controlled studies of participants who had undergone bunion surgery or abdominal surgery.[2] Participants administered oliceridine reported decreased pain compared to placebo at the approved doses.[2]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved oliceridine based on evidence from three clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02815709, Trial 2/NCT02820324 and Trial 3) of 1558 participants 18 to 89 years old who were in need of pain medication.[3] The trials were conducted at 53 sites in the United States.[3]
Trial 1 enrolled participants who underwent bunion surgery.[3] Participants with moderate to severe post-surgical pain were randomly assigned to receive oliceridine, placebo or an approved drug to treat pain (morphine) for 48 hours intravenously.[3] Neither the participants nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed.[3] All participants were allowed to use a rescue pain medication, if the pain was not well controlled using the trial medications.[3]
Trial 2 enrolled participants who underwent surgical removal of abdominal wall fat (abdominoplasty) and had moderate to severe pain.[3] Participants were randomly assigned to receive oliceridine, placebo or an approved drug to treat pain (morphine) for 24 hours intravenously.[3] Neither the participants nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed.[3] All participants were allowed to use a rescue pain medication, if the pain was not well controlled using the trial medications.[3]
To assess the benefits of oliceridine, participants used a numerical scale to score how severe the pain was after the surgery.[3] The scores for the participants receiving oliceridine were compared to the scores for the participants who received placebo and those who received morphine.[3]
In the third trial, participants who had pain following various type of surgeries or due to a medical condition received at least one dose of oliceridine.[3] Data from this trial were used only to assess the side effects of oliceridine.[3]
Oliceridine was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2020.[2] The FDA granted approval of Olinvyk to Trevena Inc.[2]
Society and culture
Legal status
An advisory committee of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) voted against the approval of oliceridine in 2018, due to concerns that the benefit of the drug did not exceed the risk. The risks of oliceridine include prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG, and depression of the respiratory drive (which could cause a person to stop breathing).[11] As a result of the committee's vote, the FDA declined to approve oliceridine, citing safety concerns.[12][13]
Oliceridine was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2020.[2] The FDA granted approval of Olinvyk to Trevena Inc.[2]
The DEA issued an interim final rule on October 30, 2020, designating oliceridine as CSA Schedule II (DEA Code 9245).[full citation needed]
See also
References
- ↑ "Olinvyk- oliceridine injection, solution". 18 August 2020. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=ce167984-8b9d-40b7-84ce-d0f33fff1eaa#LINK_5124ccc6-4102-466b-ad71-15d663677a4a.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 "FDA Approves New Opioid for Intravenous Use in Hospitals, Other Controlled Clinical Settings". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 7 August 2020. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 "Drug Trials Snapshots: Olinvyk". 7 August 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/drug-trials-snapshots-olinvyk.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "A G protein-biased ligand at the μ-opioid receptor is potently analgesic with reduced gastrointestinal and respiratory dysfunction compared with morphine". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 344 (3): 708–717. March 2013. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.201616. PMID 23300227.
- ↑ "Low intrinsic efficacy for G protein activation can explain the improved side effect profiles of new opioid agonists". Science Signaling 13 (625): eaaz3140. March 2020. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aaz3140. PMID 32234959. https://nottingham-repository.worktribe.com/output/4193457.
- ↑ "Low Intrinsic Efficacy Alone Cannot Explain the Improved Side Effect Profiles of New Opioid Agonists". Biochemistry 61 (18): 1923–1935. September 2022. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00466. PMID 34468132.
- ↑ "Structure-activity relationships and discovery of a G protein biased μ opioid receptor ligand, [(3-methoxythiophen-2-yl)methyl]({2-[(9R)-9-(pyridin-2-yl)-6-oxaspiro-[4.5]decan-9-yl]ethyl})amine (TRV130), for the treatment of acute severe pain". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 56 (20): 8019–8031. October 2013. doi:10.1021/jm4010829. PMID 24063433.
- ↑ "First clinical experience with TRV130: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 54 (3): 351–357. March 2014. doi:10.1002/jcph.207. PMID 24122908.
- ↑ Staff (1 October 2015). "Acute Postoperative Pain". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News 35 (17): 40.
- ↑ "Does potency predict clinical efficacy? Illustration through an antihistamine model". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology 89 (1): 7–11; quiz 11–2, 77. July 2002. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61904-7. PMID 12141724.
- ↑ "FDA Panel Votes Against Analgesic Oliceridine" (in en). MedPage Today, LLC. 11 October 2018. https://www.medpagetoday.com/painmanagement/opioids/75668.
- ↑ "FDA rejects Trevena's painkiller oliceridine | FierceBiotech". Questex LLC. 5 November 2018. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/fda-rejects-trevena-s-painkiller-oliceridine.
- ↑ "Hot topics in opioid pharmacology: mixed and biased opioids". British Journal of Anaesthesia 122 (6): e136–e145. June 2019. doi:10.1016/j.bja.2019.03.006. PMID 31010646.
External links
- "Oliceridine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/oliceridine.
- Clinical trial number NCT02815709 for "Study of Oliceridine (TRV130) for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Acute Pain After Bunionectomy (APOLLO-1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT02820324 for "Study of Oliceridine (TRV130) for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Acute Pain After Abdominoplasty" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |
