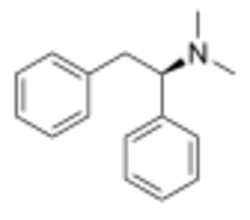
Chemistry:Lefetamine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H19N |
| Molar mass | 225.335 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine.
Discovery
Lefetamine-related 1,2-diphenylethylamines were invented in the 1940s and showed weak analgesic activity.[1]
It was investigated in Japan in the 1950s.[2] The L-isomer showed weak analgesic action comparable to codeine and antitussive action far weaker than codeine. The d-isomer showed no such activity but caused seizures in rats.[3][4]
Society and culture
It was abused in Japan during the 1950s. In a small study in 1989 it showed some effect against opioid withdrawal symptoms without causing withdrawal symptoms itself. It was concluded that it may be an opioid partial agonist.[5]
It has been abused in Europe; in 1989 a small study of 15 abusers and some volunteers found that it had some partial similarity to opioids, that it produced withdrawal symptoms, and had dependence and abuse potential to a certain degree.[6]
In a small study in 1994, it was compared to clonidine and buprenorphine in the detoxification of methadone patients and found to be inferior to both of them.[7]
Regulation may vary; it does not appear as either a narcotic or non-narcotic under the US Controlled Substances Act 1970 [8]
The Canadian Controlled Drugs and Substances Act was amended in 2016 to include the substance as a Schedule III substance. Possession without legal authority can result in maximum 3 years imprisonment. Further, Health Canada amended the Food and Drug Regulations in May, 2016 to classify Lefetamine as a controlled drug.[9]
Research
Some related pyrrylphenylethanones had analgetic activity comparable to morphine.[10] Some pyrrole analogues were reported to have analgesic effects comparable to lefetamine and being devoid of neurotoxic properties.[11]
See also
References
- ↑ "Testing diphenylethylamine compounds for analgesic action". The Journal of Physiology 104 (1): 47–51. June 1945. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1945.sp004105. PMID 16991666.
- ↑ Ogyu K, Fujimura H, Yamakawa Y, Mita I, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von antitussiv wirksamem l-1,2-Diphenyl-1-dimethylaminoaethan und dessen Salzen", DE patent 1159958, issued 1963-12-27, assigned to Institut Seikatsu Kagaku Kenkyusho (Scientific Research Institute for Practical Life, Kyoto)
- ↑ "Pharmacological Studies on Diphenylalkylamine Derivatives. (I)". Bulletin of the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University 39 (1): 67–77. 1961. http://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/2433/75783/1/chd039_1_067.pdf. Retrieved 2011-09-25.
- ↑ "Pharmacological Studies on Diphenylalkylamine Derivatives. (II): On the Actions of l-1,2-Diphenyl-1-dimethylaminoethane Hydrochloride (SPA)". Bulletin of the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University 39 (1): 78–94. 1961. http://repository.kulib.kyoto-u.ac.jp/dspace/bitstream/2433/75782/1/chd039_1_078.pdf. Retrieved 2012-06-30.
- ↑ "Lefetamine: new abuse of an old drug--clinical evaluation of opioid activity". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 24 (2): 95–101. October 1989. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(89)90071-9. PMID 2571492.
- ↑ "Lephetamine abuse and dependence: clinical effects and withdrawal syndrome". British Journal of Addiction 84 (1): 89–95. January 1989. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1989.tb00555.x. PMID 2917208.
- ↑ "Opiate detoxification of methadone maintenance patients using lefetamine, clonidine and buprenorphine". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 36 (2): 139–45. October 1994. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(94)90096-5. PMID 7851281.
- ↑ "DEA Diversion Control Division". http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/quotas/conv_factor/index.html.
- ↑ "Regulations Amending the Food and Drug Regulations (Parts G and J — Lefetamine, AH-7921, MT-45 and W-18)". June 2016. http://www.gazette.gc.ca/rp-pr/p2/2016/2016-06-01/html/sor-dors106-eng.php.
- ↑ "Pyrrylphenylethanones related to cathinone and lefetamine: synthesis and pharmacological activities". Archiv der Pharmazie 325 (7): 403–9. July 1992. doi:10.1002/ardp.19923250707. PMID 1417455.
- ↑ "Synthesis, neuropsychopharmacological effects and analgesic-antiinflammatory activities of pyrrole analogues of lefetamine". Farmaco (Societa Chimica Italiana) 44 (9): 763–77. September 1989. PMID 2604832.
 |
