Astronomy:Utopia Planitia
 Viking 2 lander view of ice in the form of morning frosts in Utopia Planitia (false color) | |
| Location | Northeast of Isidis Planitia, northwest of Aetheria |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 46°42′N 117°30′E / 46.7°N 117.5°E |
Utopia Planitia (Greek and Latin: "Nowhere Land Plain") is a large plain[1] within Utopia, the largest recognized impact basin on Mars[lower-alpha 1] and in the Solar System with an estimated diameter of 3,300 km (2,100 mi).[3] It is the Martian region where the Viking 2 lander touched down and began exploring on September 3, 1976, and the Zhurong rover touched down on May 14, 2021, as a part of the Tianwen-1 mission.[4][5] It is located at the antipode of Argyre Planitia, centered at [ ⚑ ] 46°42′N 117°30′E / 46.7°N 117.5°E.[1] It is also in the Casius quadrangle, Amenthes quadrangle, and the Cebrenia quadrangle of Mars.
Many rocks at Utopia Planitia appear perched, as if wind removed much of the soil at their bases.[6][7] A hard surface crust is formed by solutions of minerals moving up through soil and evaporating at the surface.[8] Some areas of the surface exhibit scalloped topography, a surface that looks like it was carved out by an ice cream scoop. This surface is thought to have formed by the degradation of an ice-rich permafrost.[9] Many features that look like pingos on the Earth are found in Utopia Planitia (~35–50° N; ~80–115° E).[10]
On November 22, 2016, NASA reported finding a large amount of underground ice in the Utopia Planitia region. The volume of water detected has been estimated to be equivalent to the volume of water in Lake Superior.[11][12][13]
Scalloped topography
Scalloped topography is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, between 45° and 60° north and south. It is particularly prominent in the region of Utopia Planitia[14][15] in the northern hemisphere and in the region of Peneus and Amphitrites Patera[16][17] in the southern hemisphere. Such topography consists of shallow, rimless depressions with scalloped edges, commonly referred to as scalloped depressions or simply scallops. Scalloped depressions can be isolated or clustered and sometimes seem to coalesce. A typical scalloped depression displays a gentle equator-facing slope and a steeper pole-facing scarp. This topographic asymmetry is probably due to differences in insolation. Scalloped depressions are believed to form from the removal of subsurface material, possibly interstitial ice, by sublimation. This process may still be happening at present.[18]
Scalloped ground, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. A study published in Icarus, found that the landforms of scalloped topography can be made by the subsurface loss of water ice by sublimation under current Martian climate conditions. Their model predicts similar shapes when the ground has large amounts of pure ice, up to many tens of meters in depth.[19]
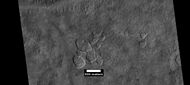
Pedestal craters
Pedestal crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program The ejecta is not symmetrical around crater because the asteroid came at a low angle out of the North East. The ejecta protected the underlying material from erosion; hence the crater looks elevated. The location is Casius quadrangle.
Close-up of East side (right side) of previous image of pedestal crater showing polygons on lobe. Since the margin of the crater has lobes and polygons, it is believed there is ice under the protective top. Picture taken with HiRISE under HiWish program. Note: this is an enlargement of the previous image.
Polygonal patterned ground
Polygonal, patterned ground is quite common in some regions of Mars.[20][21][22][23][24][25] It is commonly believed to be caused by the sublimation of ice from the ground. Sublimation is the direct change of solid ice to a gas. This is similar to what happens to dry ice on the Earth. Places on Mars that display polygonal ground may indicate where future colonists can find water ice. Patterned ground forms in a mantle layer, called latitude dependent mantle, that fell from the sky when the climate was different.[26][27][28][29]
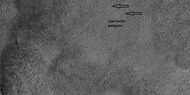
Low center polygons, shown with arrows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Location is Casius quadrangle. Image was enlarged with HiView.
High center polygons, shown with arrows, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Casius quadrangle. Image enlarged with HiView.
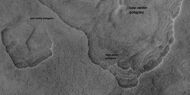
Scalloped terrain labeled with both low center polygons and high center polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Casius quadrangle. Image enlarged with HiView.
Low center polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Casius quadrangle. Image enlarged with HiView.
High and low center polygons, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Casius quadrangle. Image enlarged with HiView.
Other features in Utopia Planitia
Glacier on a crater floor, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. The cracks in the glacier may be crevasses. There is also a gully system on the crater wall.
Layers exposed along Hrad Vallis, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Gallery
In popular culture
In the Star Trek media franchise, Utopia Planitia—both on Mars' surface and a space station in areosynchronous orbit above it—is the site of a major United Federation of Planets shipyard, the Utopia Planitia Fleet Yards. Ships such as the USS Enterprise-D, USS Defiant, USS Voyager and USS Sao Paulo were built there.[30]
Interactive Mars map
Error: Image is invalid or non-existent.
See also
- Glaciers on Mars
- Geography of Mars
- List of plains on Mars
- Scalloped topography
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Utopia Planitia". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Science Center. https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6260.
- ↑ "Utopia". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Science Center. https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6259.
- ↑ McGill, G. E. (1989-03-10). "Buried topography of Utopia, Mars: Persistence of a giant impact depression". Journal of Geophysical Research 94: 2753–2759. doi:10.1029/JB094iB03p02753. Bibcode: 1989JGR....94.2753M.
- ↑ "China succeeds on country's first Mars landing attempt with Tianwen-1". https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2021/05/china-first-mars-landing-attempt-tianwen-1/.
- ↑ "China's first Mars rover Tianwen-1 launches this week. Here's what it will do.". https://www.space.com/china-mars-mission-tianwen-1-details.html.
- ↑ Mutch, T. et al. 1976. "The Surface of Mars: The View from the Viking 2 Lander". Science: 194. 1277–1283.
- ↑ Hartmann, W. 2003. A Traveler's Guide to Mars. Workman Publishing. New York.
- ↑ Arvidson, R. A. Binder, and K. Jones. 1976. "The Surface of Mars". Scientific American: 238. 76–89.
- ↑ Sejourne, A. et al. 2012. Evidence of an eolian ice-rich and stratified permafrost in Utopia Planitia, Mars. Icarus. 60:248–254.
- ↑ Soare, E., et al. 2019. Possible (closed system) pingo and ice-wedge/thermokarst complexes at the mid latitudes of Utopia Planitia, Mars. Icarus. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2019.03.010
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Staff (November 22, 2016). "Scalloped Terrain Led to Finding of Buried Ice on Mars". NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21136.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Lake of frozen water the size of New Mexico found on Mars – NASA". The Register. November 22, 2016. https://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/11/22/nasa_finds_ice_under_martian_surface/.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Mars Ice Deposit Holds as Much Water as Lake Superior". NASA. November 22, 2016. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2016-299.
- ↑ Lefort, A.; Russell, P. S.; Thomas, N.; McEwen, A. S.; Dundas, C. M.; Kirk, R. L. (2009). "Observations of periglacial landforms in Utopia Planitia with the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE)". Journal of Geophysical Research 114 (E4): E04005. doi:10.1029/2008JE003264. Bibcode: 2009JGRE..114.4005L. https://boris.unibe.ch/36929/.
- ↑ Morgenstern, A; Hauber, E; Reiss, D; van Gasselt, S; Grosse, G; Schirrmeister, L (2007). "Deposition and degradation of a volatile-rich layer in Utopia Planitia, and implications for climate history on Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets 112 (E6): E06010. doi:10.1029/2006JE002869. Bibcode: 2007JGRE..112.6010M. https://epic.awi.de/id/eprint/16592/1/Mor2007e.pdf.
- ↑ Lefort, A.; Russell, P.S.; Thomas, N. (2010). "Scalloped terrains in the Peneus and Amphitrites Paterae region of Mars as observed by HiRISE". Icarus 205 (1): 259. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2009.06.005. Bibcode: 2010Icar..205..259L.
- ↑ Zanetti, M.; Hiesinger, H.; Reiss, D.; Hauber, E.; Neukum, G. (2009). "Scalloped Depression Development on Malea Planum and the Southern Wall of the Hellas Basin, Mars". Lunar and Planetary Science 40: p. 2178, abstract 2178. Bibcode: 2009LPI....40.2178Z. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2009/pdf/2178.pdf.
- ↑ "HiRISE | Scallops and Polygons in the Utopia Planitia (PSP_007173_2245)". https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/PSP_007173_2245.
- ↑ Dundas, C., S. Bryrne, A. McEwen. 2015. Modeling the development of martian sublimation thermokarst landforms. Icarus: 262, 154-169.
- ↑ Kostama, V.-P., M. Kreslavsky, Head, J. 2006. Recent high-latitude icy mantle in the northern plains of Mars: Characteristics and ages of emplacement. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 (L11201). doi:10.1029/2006GL025946.
- ↑ Malin, M., Edgett, K. 2001. Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera: Interplanetary cruise through primary mission. J. Geophys. Res. 106 (E10), 23429–23540.
- ↑ Milliken, R., et al. 2003. Viscous flow features on the surface of Mars: Observations from high-resolution Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) images. J. Geophys. Res. 108 (E6). doi:10.1029/2002JE002005.
- ↑ Mangold, N. 2005. High latitude patterned grounds on Mars: Classification, distribution and climatic control. Icarus 174, 336–359.
- ↑ Kreslavsky, M., Head, J. 2000. Kilometer-scale roughness on Mars: Results from MOLA data analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 105 (E11), 26695–26712.
- ↑ Seibert, N., J. Kargel. 2001. Small-scale martian polygonal terrain: Implications for liquid surface water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 (5), 899–902. S
- ↑ Hecht, M. 2002. Metastability of water on Mars. Icarus 156, 373–386
- ↑ Mustard, J., et al. 2001. Evidence for recent climate change on Mars from the identification of youthful near-surface ground ice. Nature 412 (6845), 411–414.
- ↑ Kreslavsky, M.A., Head, J.W., 2002. High-latitude Recent Surface Mantle on Mars: New Results from MOLA and MOC. European Geophysical Society XXVII, Nice.
- ↑ Head, J.W., Mustard, J.F., Kreslavsky, M.A., Milliken, R.E., Marchant, D.R., 2003. Recent ice ages on Mars. Nature 426 (6968), 797–802.
- ↑ Okuda, Michael; Denise Okuda; Debbie Mirek (1999). The Star Trek Encyclopedia. Pocket Books. ISBN 0-671-53609-5.
External links
- Laser altimetry of the north pole of Mars Utopia Planitia located in upper right
- Google Mars scrollable map – centered on Utopia Planitia
- VL2 Site: Utopia Planitia (NASA)
- PIA00576: Martian Sunrise at Utopia Planitia (NASA Photojournal)
- PIA00530: Frost on Utopia Planitia (NASA Photojournal)
- PIA03796: Utopia Planitia (NASA Photojournal)
 |