Chemistry:EC586
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
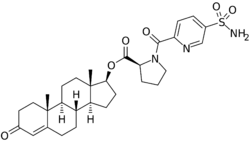
| Other names | EC-586; Testosterone 17β-(1-[[5-(aminosulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]carbonyl]-L-proline); Androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-(1-[[5-(aminosulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]carbonyl]-L-proline); 3-Oxoandrost-4-en-17β-yl 1-[[5-(aminosulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]carbonyl]-L-proline |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H39N3O6S |
| Molar mass | 569.72 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
EC586, also known as testosterone 17β-(1-((5-(aminosulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl)carbonyl)-L-proline), is an androgen and anabolic steroid which is under development by Evestra for use in androgen replacement therapy in men.[1][2] It is an orally active androgen ester – specifically, a C17β sulfonamide–proline ester of the natural and bioidentical androgen testosterone – and acts as a prodrug of testosterone in the body.[2] However, unlike oral testosterone and conventional oral testosterone esters such as testosterone undecanoate, EC586 has high oral potency, may undergo little or no first-pass metabolism, and may not have disproportionate androgenic effects in the liver.[2][3] As such, it may have a variety of desirable advantages over oral testosterone, similarly to parenteral testosterone, but with the convenience of oral administration.[2][3] Evestra intends to seek Investigational New Drug status for EC586 in the fourth quarter of 2018.[needs update][1]
The pharmacokinetics of oral EC586 have been briefly assessed in rats in a small pilot study.[2] Oral EC586 showed area-under-the-curve (AUC) levels that were more than 100-fold greater than those of oral testosterone propionate, the C17β propionate ester of testosterone (AUC0-3h = 330 ng/mL and 2.5 ng/mL, respectively, for doses of 3.0 mg/rat each).[2] As such, EC586 would appear to possess strongly increased oral bioavailability, potency, and systemic exposure relative to testosterone propionate.[2] Additional research and details on the pharmacokinetics and properties of EC586 are to be published "soon".[2]
The mechanism for the absence of first-pass metabolism and lack of disproportionate liver exposure with oral administration has been elucidated for a closely related sulfonamide–proline estradiol ester known as EC508, which shows the same properties as EC586.[2][3]
Clinical trials for EC586 and EC508 are undergoing as of 2023.[4]
See also
- List of androgen esters § Testosterone esters
- List of investigational sex-hormonal agents § Androgenics
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Research Pipeline". Evestra, Inc.. http://www.evestra.com/index-Dateien/Page1242.htm. "EC586: Testosterone prodrug"
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 "A prodrug design for improved oral absorption and reduced hepatic interaction". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 25 (20): 5569–5575. October 2017. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2017.08.027. PMID 28886996.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Estradiol prodrugs (EP) for efficient oral estrogen treatment and abolished effects on estrogen modulated liver functions". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 165 (Pt B): 305–311. January 2017. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.07.008. PMID 27449818.
- ↑ "Current Trends in Steroid Chemistry" (in en). Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal 57 (3): 336–346. 1 June 2023. doi:10.1007/s11094-023-02887-0. ISSN 1573-9031. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11094-023-02887-0.
External links
 |

