Chemistry:Azidomorphine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Azidomorphine |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H20N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 312.373 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
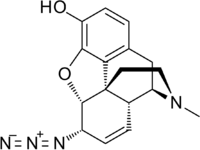
Azidomorphine[1] is an opiate analogue that is a derivative of morphine, where the 7,8 double bond has been saturated and the 6-hydroxy group has been replaced by an azide group.[2]
Azidomorphine binds with high affinity to the mu opioid receptor,[3] and is around 40× more potent than morphine in vivo. It has similar effects to morphine, including analgesia, sedation, and respiratory depression. However, its addiction liability has been found to be slightly lower than that of morphine in animal studies.[4][5]
References
- ↑ "Analgesic Compositions" GB patent 1396663
- ↑ "The pharmacology of azidomorphine and azidocodeine". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 25 (12): 929–39. December 1973. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09982.x. PMID 4150295.
- ↑ "Azidomorphine is an agonist of high-affinity opioid receptor binding sites". Neurochemical Research 11 (11): 1565–9. November 1986. doi:10.1007/bf00965775. PMID 2825053.
- ↑ "Azidomorphines: a new family of potent analgesics with low dependence capacity". Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology 3 (1–3): 95–108. 1979. doi:10.1016/0364-7722(79)90074-2. PMID 45567.
- ↑ "Investigations of the analgesic and morphine-like properties of azidomorphine". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 201 (3): 580–6. June 1977. PMID 405472.
 |
