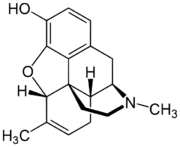
Chemistry:Methyldesorphine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 3-Hydroxy-6,N-dimethyl- 4,5-epoxymorphin-6-en |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 283.371 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Methyldesorphine is an opioid analgesic. First synthesized in Germany in 1940 and patented in the US in 1952,[1] it has a high potential for abuse as with any potent opioid agonist, and is sometimes found along with desomorphine as a component of the home-made opioid mixture known as "Krokodil" used in Russia and the neighboring former Soviet republics.[2] It is approximately 15 times more potent than morphine as an analgesic[3][4] but if the 6-7 bond is saturated, the β isomer is some 50 times more potent than morphine.
Methyldesorphine is listed as a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act 1970 in the United States with a DEA ACSCN of 9302 and zero annual aggregate manufacturing quota. The free base conversion ratio of the hydrochloride is 0.89.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Payne GB, Pfister III K, "Δ6-Desoxymorphine Compounds and Process of Producing the Same", US patent 2694068, published 1952-08-05, issued 1954-09-11, assigned to Merck & Co., Inc.
- ↑ "Chromatographic Study of Expert and Biological Samples Containing Desomorphine". Journal of Analytical Chemistry 63 (4): 361–370. 2008. doi:10.1007/s10809-008-4009-5.
- ↑ Opioid Analgesics, Chemistry and Receptors. New York: Plenum Press. 1986. pp. 37–38. ISBN 0-306-42130-5.
- ↑ Opiates. Academic Press. 1986. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-12-443830-9.
- ↑ "Conversion Factors for Controlled Substances". Diversion Control Division. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. Department of Justice. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/quotas/conv_factor/index.html.
 |

