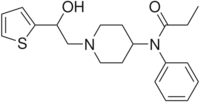
Chemistry:Betahydroxythiofentanyl
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | β-hydroxythiofentanyl |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H26N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 358.50 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Betahydroxythiofentanyl (β-hydroxythiofentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl.
Betahydroxythiofentanyl was sold briefly on the black market from around 1985,[1] before the introduction of the Federal Analog Act in 1986 which for the first time attempted to control entire families of drugs based on their structural similarity rather than scheduling each drug individually as they appeared.[2] β-hydroxythiofentanyl was anecdotally said to be one of the more favored fentanyl analogs by opiate addicts[citation needed]; however, its brief career as a street drug was short-lived and was eventually terminated with the introduction of the Federal Analogue Act.
Betahydroxythiofentanyl has similar effects to fentanyl. Side effects of fentanyl analogs are similar to those of fentanyl itself, which include itching, nausea and potentially serious respiratory depression, which can be life-threatening. Fentanyl analogs have killed hundreds of people throughout Europe and the former Soviet republics since the most recent resurgence in use began in Estonia in the early 2000s, and novel derivatives continue to appear.[3]
Legal status
As of October 2015, betahydroxythiofentanyl is a controlled substance in China.[4]
As of May 2016, betahydroxythiofentanyl is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Valter K, Arrizabalaga P. Designer Drugs Directory (1998), p150. ISBN:0-444-20525-X
- ↑ "Designer Drugs: Past History and Future Prospects". Journal of Forensic Sciences 33 (2): 569–575. 1988. doi:10.1520/JFS11976J. PMID 3286815.
- ↑ "Fentanyls: Are we missing the signs? Highly potent and on the rise in Europe". The International Journal on Drug Policy 26 (7): 626–31. July 2015. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2015.04.003. PMID 25976511. http://www.ijdp.org/article/S0955-3959%2815%2900097-3/abstract.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in zh). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
- ↑ "Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Butyryl Fentanyl and Beta-Hydroxythiofentanyl into Schedule I". Drug Enforcement Administration. 12 May 2016. https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2016-05-12/pdf/2016-11219.pdf.
 |

