Chemistry:Metofoline
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
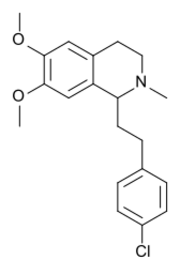
| Formula | C20H24ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 345.87 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Metofoline (INN), also known as methofoline (USAN), is an opioid analgesic drug discovered in the 1950s by a team of Swiss researchers at Hoffmann-La Roche.[1]
Methopholine is an isoquinoline derivative which is not structurally related to most other opioids.[2] However, its structural similarity to the non-opioid alkaloid papaverine is notable.
Metofoline has around the same efficacy as an analgesic as codeine, and was evaluated for the treatment of postoperative pain.[3][4][5] Metofoline tablets were marketed in the United States under the brand name of Versidyne,[6] but the drug was withdrawn from the market in 1965 due to the occurrence of ophthalmic side-effects alongside the discovery that the drug could produce cataracts in dogs.[7]
Metofoline has two enantiomers, with the levo (R) enantiomer being the active form, around 3x the potency of codeine, and the (S) enantiomer being inactive.
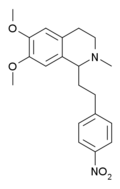
Analogs where the 4'-chloro group has been replaced by other electron withdrawing groups have also been tested, the fluoro derivative being slightly more potent than chloro, and the nitro derivative being most potent of all, with the racemic 4'-nitromethopholine being around 20x the potency of codeine.[8][9]
Later research was carried out by Bristol-Myer in the 1960s[10] and animal studies suggested derivatives with significantly increased analgesic activity of over x50 codeine.[11]
See also
References
- ↑ "Tetrahydroisoquinoline Derivatives" US patent 3067203, issued 1962-12-04, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche
- ↑ "The opiate receptor: a model explaining structure-activity relationships of opiate agonists and antagonists". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 73 (11): 4215–9. November 1976. doi:10.1073/pnas.73.11.4215. PMID 186791. Bibcode: 1976PNAS...73.4215F.
- ↑ "An evaluation of the efficacy of methopholine for the relief of postoperative pain". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences 244 (3): 337–43. September 1962. doi:10.1097/00000441-196209000-00010. PMID 14475666.
- ↑ "Methopholine, A New Analgesic Agent". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences 246 (5): 550–7. November 1963. doi:10.1097/00000441-196311000-00005. PMID 14082642.
- ↑ "Plasma levels and renal excretion of unchanged methopholine in man". Experientia 23 (11): 934–6. November 1967. doi:10.1007/bf02136231. PMID 6057015.
- ↑ "Versidyne. Its use in vascular headache". Headache 2 (4): 203–8. January 1963. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.1963.hed0204203.x. PMID 13975764.
- ↑ 30 FR 4083 March 27, 1965
- ↑ Opioid Analgesics, Chemistry and Receptors. New York: Plenum Press. 1986. p. 390. ISBN 0-306-42130-5.
- ↑ "Synthesen in der Isochinolinreihe. Substituierte 1-[ω-(Nitrophenyl)alkyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isochinoline". Helvetica Chimica Acta 46 (4): 1127–1132. 1963. doi:10.1002/hlca.19630460405.
- ↑ US Patent 3378561A 1-beta-arylthioethyltetrahydro-isoquinolines
- ↑ 'Tetrahydroisoquinolines. I. The Preparation and Analgesic Activity of Some 1-Thiophenoxyethyltetrahydroisoquinolines and 1-Phenoxyethyltetrahydroisoquinolines'J. Med. Chem. 1969 Jul;12(4):575-80. doi: 10.1021/jm00304a003.
 |
