Chemistry:3-Iodothyronamine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
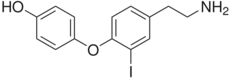
4-[4-(2-Aminoethyl)-2-iodophenoxy]phenol | |
| Other names
T1AM
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14INO2 | |
| Molar mass | 355.17 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Iodothyronamine (T1AM) is an endogenous thyronamine. T1AM is a high-affinity ligand for the trace amine-associated receptor TAAR1 (TAR1, TA1), a recently discovered G protein-coupled receptor.[1][2] T1AM is the most potent endogenous TAAR1 agonist yet discovered.[3] Activation of TAAR1 by T1AM results in the production of large amounts of cAMP. This effect is coupled with decreased body temperature and cardiac output.[4] Wu et al. have pointed out that this relationship is not typical of the endocrine system, indicating that TAAR1 activity may not be coupled to G-proteins in some tissues, or that T1AM may interact with other receptor subtypes.[3]
T1AM may be part of a signaling pathway to modulate cardiac function, as the compound can induce negative inotropic effects and decrease cardiac output.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ "3-Iodothyronamine is an endogenous and rapid-acting derivative of thyroid hormone". Nat. Med. 10 (6): 638–42. 2004. doi:10.1038/nm1051. PMID 15146179.
- ↑ "Trace amine-associated receptor agonists: synthesis and evaluation of thyronamines and related analogues". J. Med. Chem. 49 (3): 1101–12. 2006. doi:10.1021/jm0505718. PMID 16451074.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Alternate Pathways of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism". Thyroid 15 (8): 943–958. 2005. doi:10.1089/thy.2005.15.943. PMID 16131336.
- ↑ "New compound may act to keep thyroid activity in check". http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2004-05/ohs-ncm051404.php.
- ↑ "Cardiac effects of 3-iodothyronamine: a new aminergic system modulating cardiac function". The FASEB Journal 21 (7): 1597–608. 2007. doi:10.1096/fj.06-7474com. PMID 17284482.
External links
- 3-iodothyronamine at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |

