Chemistry:Cericlamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral[1] |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 8 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
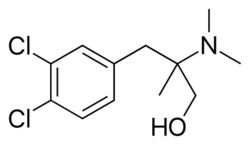
| Formula | C12H17Cl2NO |
| Molar mass | 262.17 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cericlamine (INN; developmental code JO-1017) is a potent and moderately selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) of the amphetamine family (specifically, a derivative of phentermine, and closely related to chlorphentermine, a highly selective serotonin releasing agent) that was investigated as an antidepressant for the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and anorexia nervosa by Jouveinal but did not complete development and was never marketed.[1][2][3][4] It reached phase III clinical trials in 1996 before development was discontinued in 1999.[5]
According to Czech scientists, cericlamine is claimed to be part of a highly advanced “fifth generation” of antidepressants as was venlafaxine.[6]
The daily dosage was reported to be 300mg.[1]
See also
- 3,4-Dichloroamphetamine
- Alaproclate
- Bupropion
- Chlorphentermine
- Clortermine
- Cloforex
- Etolorex
- Femoxetine
- Ifoxetine
- Indalpine
- Methylenedioxyphentermine
- Omiloxetine
- Panuramine
- para-Chloroamphetamine
- para-Chloromethamphetamine
- Phentermine
- Pirandamine
- Seproxetine
- Viqualine
- Zimelidine
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "A Multicentre Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Dose-Finding Study with Cericlamine in Major Depression". Clinical Neuropharmacology 15: 176B. 1992. doi:10.1097/00002826-199202001-00339. ISSN 0362-5664.
- ↑ "Investigational drugs for eating disorders". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 12 (3): 491–9. March 2003. doi:10.1517/13543784.12.3.491. PMID 12605570.
- ↑ Stereoselective Biocatalysis. CRC Press. 3 January 2000. pp. 48–. ISBN 978-0-8247-8282-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=QwgCzKDfNAoC&pg=PA48.
- ↑ Neurochemistry in Clinical Application. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 81–. ISBN 978-1-4615-1857-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=d2DlBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA81.
- ↑ "Cericlamine". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800001340.
- ↑ Svestka, J. (1994). "Antidepressives of the 3rd, 4th and 5th generation". Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 90 (1): 3–19. PMID 8174184.
 |
