Chemistry:Pyrovalerone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
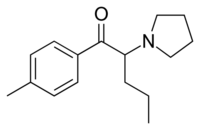
| Formula | C16H23NO |
| Molar mass | 245.366 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| | |
Pyrovalerone (Centroton, 4-Methyl-β-keto-prolintane, Thymergix, O-2371)[1] is a psychoactive drug with stimulant effects via acting as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). It was developed in the 1980s and had briefly been approved in Spain and France for chronic fatigue or lethargy[2] and as an anorectic or appetite suppressant, but was withdrawn from both markets around 2001 due to safety concerns including problems with abuse and dependence.[3] It is closely related on a structural level to a number of other cathinone stimulants, such as α-PVP, MDPV and prolintane (Promotil, Katovit).
Side effects of pyrovalerone include anorexia or loss of appetite, anxiety, fragmented sleep or insomnia, and trembling, shaking, or muscle tremors. Withdrawal following abuse upon discontinuation often results in depression.
The R-enantiomer of pyrovalerone is devoid of pharmacologic activity.[4]
See also
- 4-Et-PVP
- α-Pyrrolidinohexiophenone (α-PHP)
- α-Pyrrolidinopentiothiophenone (α-PVT)
- Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV)
- Naphyrone (O-2482)
- Prolintane (Promotil, Katovit)
- 4'-Methyl-α-pyrrolidinohexiophenone (MPHP, 4-MPHP)
References
- ↑ US Patent 3314970
- ↑ "Evaluation of pyrovalerone in chronically fatigued volunteers". Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 13 (10): 631–5. October 1971. PMID 4402508.
- ↑ "[Abuse of pyrovalerone by drug addicts]". Annales médico-psychologiques 2 (4): 745–8. November 1975. PMID 9895.
- ↑ "1-(4-Methylphenyl)-2-pyrrolidin-1-yl-pentan-1-one (Pyrovalerone) analogues: a promising class of monoamine uptake inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49 (4): 1420–32. February 2006. doi:10.1021/jm050797a. PMID 16480278.
 |
