Chemistry:2C-T-13
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
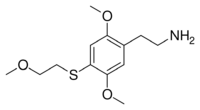
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-{2,5-Dimethoxy-4-[(2-methoxyethyl)sulfanyl]phenyl}ethan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H21NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 271.38 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2C-T-13 (2,5-dimethoxy-4-(β-methoxyethylthio)phenethylamine) is a psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was presumably first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book PiHKAL.[1]
Chemistry
The drug has structural properties similar to mescaline and other drugs in the 2C-T series, with the most closely related compounds being 2C-T-7 and 2C-T-21.
General information
The dosage range of 2C-T-13 is typically 25 - 40 mg and its duration is approximately 6–8 hours according to Shulgin.[1] 2C-T-13 produces many closed-eye visuals and geometric patterns. It also produces slight visual distortion.[1]
Pharmacology
The mechanism that produces 2C-T-13's hallucinogenic and entheogenic effects has not been specifically established; however, it is most likely to result from action as a 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist in the brain, a mechanism of action shared by all of the hallucinogenic tryptamines and phenethylamines for which the mechanism of action is known.
Dangers
The toxicity of 2C-T-13 is not well documented. 2C-T-13 is slightly less potent than 2C-T-7, but it may be expected that at higher doses it would display similar toxicity to that of other phenethylamines of the 2C-T family.
Legality
2C-T-13 is not scheduled in the United States, but possession and sales of 2C-T-13 could be prosecuted under the Federal Analog Act because of its structural similarities to 2C-T-7.
As of October 31, 2016, 2C-T-13 is a controlled substance (Schedule III) in Canada.[2]
References
 |

