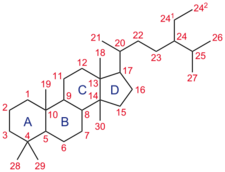
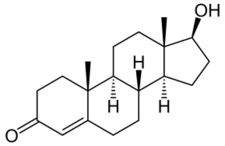
Short description: None
This is a list of androgens/anabolic steroids (AAS) or testosterone derivatives. Androgen esters are mostly not included in this list. The major classes of testosterone derivatives include the following (as well as combinations thereof):
- Testosterone derivatives: direct derivatives of testosterone not falling into the groups below
- 4,5α-Reduced/dihydrogenated testosterone derivatives: dihydrotestosterone (DHT) derivatives
- 19-Demethylated testosterone derivatives: 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) derivatives
- 17α-Alkylated testosterone derivatives: methyltestosterone and ethyltestosterone derivatives
- 17α-Ethynylated/vinylated testosterone derivatives: ethynyltestosterone (ethisterone) and vinyltestosterone derivatives
The last group consists of progestins with mostly only very weak androgenic/anabolic activity.
This article pertains to steroidal androgens; nonsteroidal androgens like the selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) andarine and enobosarm (ostarine) are not included here.
Testosterone derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Cloxotestosterone
|
Testosterone 17-chloral hemiacetal ether
|
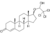
|
✓
|
| Quinbolone
|
Δ1-Testosterone 17β-cyclopentenyl enol ether
|

|
✓
|
| Silandrone
|
Testosterone 17β-trimethylsilyl ether
|
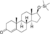
|
–
|
Dihydrotestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
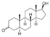
| Dihydrotestosterone (DHT); androstanolone, stanolone)
|
4,5α-Dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
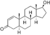
| 1-Testosterone (dihydro-1-testosterone, dihydroboldenone)
|
4,5α-Dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
–
|
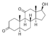
| 11-Ketodihydrotestosterone (11-KDHT)
|
11-Keto-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
–
|
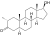
| Drostanolone
|
2α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
| Epitiostanol (epithioandrostanol)
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
✓
|
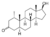
| Mesterolone
|
1α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
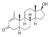
| Metenolone (methenolone, methylandrostenolone)
|
1-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
✓
|
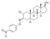
| Nisterime
|
2α-Chloro-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 3-O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime
|
|
–
|
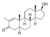
| Stenbolone
|
2-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
✓
|
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Mepitiostane
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 17β-(1-methoxycyclopentane) ether
|
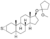
|
✓
|
| Mesabolone
|
4,5α-Dihydro-δ1-testosterone 17β-(1-methoxycyclohexane) ether
|
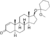
|
–
|
| Prostanozol
|
2'H-5α-Androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol 17β-tetrahydropyran ether
|
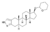
|
–
|
Azine dimers
19-Nortestosterone (nandrolone) derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Esters
17α-Alkylated testosterone derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
17α-Alkylated dihydrotestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Androisoxazole
|
17α-Methyl-5α-androstano[3,2-c]isoxazol-17β-ol
|
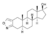
|
✓
|
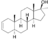
| Desoxymethyltestosterone
|
3-Deketo-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ2-testosterone
|
|
–
|
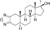
| Furazabol
|
17α-Methyl-5α-androstano[2,3-c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-17β-ol
|
|
✓
|
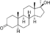
| Mestanolone (methyl-DHT)
|
17α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
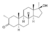
| Methasterone (methyldrostanolone)
|
2α,17α-Dimethyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
–
|
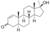
| Methyl-1-testosterone (methyldihydro-1-testosterone)
|
17α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
–
|
| Methyldiazinol
|
3-Azi-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
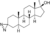
|
–
|
| Methylepitiostanol
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
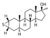
|
–
|
| Methylstenbolone
|
2,17α-Dimethyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
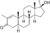
|
–
|
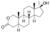
| Oxandrolone
|
2-Oxa-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
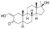
| Oxymetholone
|
2-Hydroxymethylene-4,5α-dihydro-17α-methyltestosterone
|
|
✓
|
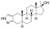
| Stanozolol
|
17α-Methyl-2'H-5α-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol
|
|
✓
|
Prodrugs
Azine dimers
17α-Alkylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
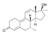
| Dimethyltrienolone (7α,17α-dimethyltrenbolone)
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|
|
–
|
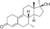
| Dimethyldienolone (7α,17α-dimethyldienolone)
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
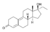
| Ethyldienolone
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
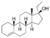
| Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol)
|
17α-Ethyl-3-deketo-19-nortestosterone
|
|
✓
|
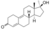
| Methyldienolone
|
17α-Methyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
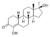
| Methylhydroxynandrolone (MOHN, MHN)
|
4-Hydroxy-17α-methyl-19-nortestosterone
|
|
–
|
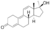
| Metribolone (methyltrienolone, R-1881)
|
17α-Methyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|
|
–
|
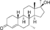
| Mibolerone
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nortestosterone
|
|
✓
|
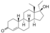
| Norboletone
|
17α-Ethyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone
|
|
–
|
| Norethandrolone (ethylnandrolone, ethylestrenolone)
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
✓
|
| Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethisterone)
|
17α-Methyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
✓
|
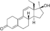
| RU-2309 (18-methymetribolone, 17α-methyl-THG)
|
17α,18-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|
|
–
|
| Tetrahydrogestrinone (THG)
|
17α-Ethyl-18-methyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|
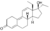
|
–
|
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Esters
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Propetandrol
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone 3-propionate
|

|
✓
|
17α-Vinylated testosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Vinyltestosterone
|
17α-Ethenyltestosterone
|
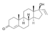
|
–
|
17α-Vinylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
The 17α-ethenylated (vinylated) testosterone derivative norvinisterone (vinylnortestosterone) is much more potent as an AAS than the 17α-ethynylated testosterone derivatives and is intermediate in potency between the 17α-ethynylated progestins and conventional AAS, with approximately one-third and one-fifth of the respective androgenic and anabolic activity of nandrolone in animal bioassays.[1]
Vinyltestosterone has been described as a weak AAS, though stronger than its 17α-ethynylated analogue ethisterone.[2]
17α-Ethynylated testosterone derivatives
17α-Ethynylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
| Quingestanol
|
4-Hydro-19-nor-δ3,5-testosterone 3-cyclopentyl ether?
|
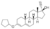
|
–
|
Esters
Ethers and esters
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
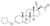
| Quingestanol acetate
|
4-Hydro-17α-ethynyl-19-nor-δ3,5-testosterone 3-cyclopentyl ether 17β-acetate?
|
|
✓
|
17α-Ethynylated testosterone derivatives are potent progestins with only very weak androgenic/anabolic activity and are used as oral contraceptives or for the treatment of gynecological conditions in women. They are invariably classified as progestins rather than as AAS. However, these progestins are testosterone derivatives and do have significant androgenic/anabolic activity, sometimes producing acne and other mild androgenic effects in women. Conversely, in men, these drugs may actually have functional antiandrogen effects due to their potent progestogenic and hence antigonadotropic activity and capacity to suppress gonadal testosterone production.[3]
See also
Notes
? = Chemical names that are unverified.
References
- ↑ Saunders, Francis J.; Drill, Victor A. (1956). "The Myotrophic and Androgenic Effects of 17-Ethyl-19-Nortestosterone and Related Compounds". Endocrinology 58 (5): 567–572. doi:10.1210/endo-58-5-567. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 13317831.
- ↑ "The effects of 17-vinyl testosterone upon the rat adrenal". Endocrinology 45 (6): 564–70. 1949. doi:10.1210/endo-45-6-564. PMID 15402199.
- ↑ Paulsen, C. Alvin; Leach, Robert B.; Lanman, John; Goldston, Norman; Maddock, W. O.; Heller, Carl G. (1962). "Inherent Estrogenicity of Norethindrone and Norethynodrel: Comparison with Other Synthetic Progestins and Progesterone1". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 22 (10): 1033–1039. doi:10.1210/jcem-22-10-1033. ISSN 0021-972X. PMID 13942007. "Androgenic effects were absent for each of the compounds in the doses administered as judged by: (a) marked decrease in libido and sexual potentia in each of 21 normal male subjects receiving norethynodrel, norethindrone and norethandrolone; (b) failure to increase libido and sexual potentia in each of four hypogonadotrophic eunuchoidal men receiving norethandrolone (each had previously responded to testosterone administration); (c) no virilization of 14 of 15 postmenopausal women receiving the three progestins (one who was taking norethandrolone at the dose level of 30 mg daily noted lowering in the pitch of her voice during the second month of therapy).".
Further reading
{{Navbox
| name = Androgens and antiandrogens
| title = Androgens and antiandrogens
| state = collapsed
| listclass = hlist
| groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Androgens
(incl. AAS)
| list1 =
| group3 = Antigonadotropins
| list3 =
- D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
- Estrogens (e.g., bifluranol, [[diethylstilbestrol, estradiol, estradiol esters, ethinylestradiol, ethinylestradiol sulfonate, paroxypropione)
- GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin)
- GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix)
- Progestogens (incl., chlormadinone acetate, [[cyproterone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, gestonorone caproate, [[Chemistry:Medroxyprogesterone medroxyprogesterone acetate, Chemistry:Megestrol acetate|megestrol acetate]])
| group4 = Others
| list4 =
}}
| liststyle = background:#DDDDFF;
| list3 =
- See also
- Androgen receptor modulators
- Estrogens and antiestrogens
- Progestogens and antiprogestogens
- List of androgens/anabolic steroids
}}
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List of androgens and anabolic steroids. Read more |