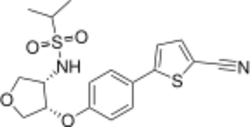
Chemistry:BIIB-104
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | PF-04958242 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H20N2O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 392.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
BIIB-104, also known as PF-04958242 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia.[1][2][3] It was also under development for the treatment of age-related sensorineural hearing loss, but development for this indication was terminated due to insufficient effectiveness.[3][4] As of July 2018, BIIB-104 is in phase II clinical trials for cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia.[3]
BIIB-104 belongs to the biarylpropylsulfonamide group of AMPAR PAMs, which also includes LY-404187, LY-503430, and mibampator (LY-451395) among others.[5] It is described as a "high-impact" AMPAR PAM, unlike so-called "low-impact" AMPAR PAMs like CX-516 and its cogener farampator (CX-691, ORG-24448).[2] In animals, low doses of BIIB-104 have been found to enhance cognition and memory, whereas higher doses produce motor coordination disruptions and convulsions.[2] The same effects, as well as neurotoxicity at higher doses, have been observed with orthosteric and other high-impact allosteric AMPAR activators.[2]
In healthy volunteers, BIIB-104 has been found to significantly reduce ketamine-induced deficits in verbal learning and working memory without attenuating ketamine-induced psychotomimetic effects.[2] It was able to complete reverse ketamine-induced impairments in spatial working memory in the participants.[2]
In addition to its actions on the AMPAR, BIIB-104 has been reported to act as a GlyT1 glycine transporter blocker.[6][7] As such, it is also a glycine reuptake inhibitor, and may act indirectly to activate the glycine receptor and the glycine co-agonist site of the NMDA receptor by increasing extracellular levels of glycine.[6][7]
See also
References
- ↑ "The discovery and characterization of the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor potentiator N-{(3S,4S)-4-[4-(5-cyano-2-thienyl)phenoxy]tetrahydrofuran-3-yl}propane-2-sulfonamide (PF-04958242)". J. Med. Chem. 58 (10): 4291–308. 2015. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00300. PMID 25905800.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "Attenuation of ketamine-induced impairment in verbal learning and memory in healthy volunteers by the AMPA receptor potentiator PF-04958242". Mol. Psychiatry 22 (11): 1633–1640. 2017. doi:10.1038/mp.2017.6. PMID 28242871.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "PF 4958242". http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800032498.
- ↑ "The Safety and Efficacy of PF-04958242 in Age-Related Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141 (7): 607–13. 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2015.0791. PMID 25997115.
- ↑ "Cognitive enhancers (nootropics). Part 1: drugs interacting with receptors". J. Alzheimers Dis. 32 (4): 793–887. 2012. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-121186. PMID 22886028.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Inhibition of glycine transporter 1: The yellow brick road to new schizophrenia therapy?". Curr. Pharm. Des. 21 (26): 3771–87. 2015. doi:10.2174/1381612821666150724100952. PMID 26205290.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Early investigational drugs for hearing loss". Expert Opin Investig Drugs 24 (2): 201–17. 2015. doi:10.1517/13543784.2015.960076. PMID 25243609.

