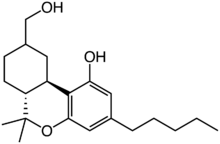
Chemistry:11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 332.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol (11-OH-9α-HHC and 11-OH-9β-HHC, or alternatively 7-OH-HHC under the monoterpenoid numbering system) is an active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and a metabolite of the trace cannabinoid hexahydrocannabinol (HHC).[1][2][3]
In a pathway that parallels the metabolism of the THC family of cannabinoids, following ingestion HHC undergoes hepatic metabolism by cytochrome p450 (predominantly the CYP3A4 isozyme, with some contribution from CYP2C9 and CYP2C19) to a multitude of oxygenated derivatives, including 8-OH-HHC and 11-OH-HHC. C11-oxidation is the major pathway of THC and HHC metabolism.[4]
Like other 11-OH cannabinoid metabolites, 11-OH-9β-HHC retains activity comparable to HHC itself while the 9α-isomer is significantly less active.[5] However, upon formation it is rapidly metabolized further to the inactive 11-carboxylates, producing a shortened half-life within the body and lowering its bioavailability considerably through first-pass metabolism.[6][7]
The 11-OH-9β-HHC isomer is the structurally related methylene homologue of 11-Nor-9β-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol also known as 9-Nor-9β-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol.[8][9]
HU-243 is a synthetic analog of 11-OH-9β-HHC in which the natural n-pentyl side chain is replaced with a geminal-dimethylheptyl substitution. This significantly increases HU-243s binding affinity for the CB1 and CB2 receptors.[10]
See also
- 9-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol
- 9-Nor-9β-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol
- 11-Hydroxycannabinol
- HU-210
- 8-hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol
References
- ↑ "Cannabimimetic activity (delta 1-THC cue) of cannabidiol monomethyl ether and two stereoisomeric hexahydrocannabinols in rats and pigeons". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 25 (2): 393–399. August 1986. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(86)90015-8. PMID 3020594.
- ↑ "Comparative in vivo Metabolism of Δ1-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ1-THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabinol (CBN) by Several Species" (in en). Recent Developments in Mass Spectrometry in Biochemistry and Medicine. Boston, MA: Springer US. 1978. pp. 161–184. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-3991-5_13. ISBN 978-1-4613-3993-9.
- ↑ Falck Jørgensen, Christian; Schou Rasmussen, Brian; Linnet, Kristian; Thomsen, Ragnar (2023). "Evidence of 11-Hydroxy-hexahydrocannabinol and 11-Nor-9-carboxy-hexahydrocannabinol as Novel Human Metabolites of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol". Metabolites 13 (12): 1169. doi:10.3390/metabo13121169. PMID 38132851.
- ↑ "Metabolomics of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: implications in toxicity". Drug Metabolism Reviews 48 (1): 80–87. 2016-01-02. doi:10.3109/03602532.2015.1137307. PMID 26828228.
- ↑ "Stereochemical requirements for cannabinoid activity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 23 (10): 1068–1072. October 1980. doi:10.1021/jm00184a002. PMID 7420350.
- ↑ "Human cannabinoid pharmacokinetics". Chemistry & Biodiversity 4 (8): 1770–1804. August 2007. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200790152. PMID 17712819.
- ↑ "Rapid elimination of Carboxy-THC in a cohort of chronic cannabis users". International Journal of Legal Medicine 130 (1): 147–152. January 2016. doi:10.1007/s00414-015-1241-z. PMID 26233612.
- ↑ "9-Hydroxy-9-norhexahydrocannabinol". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6452587#section=Structures.
- ↑ "7-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/127684#section=Structures.
- ↑ "A novel probe for the cannabinoid receptor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35 (11): 2065–2069. May 1992. doi:10.1021/jm00089a018. PMID 1317925.
 |

