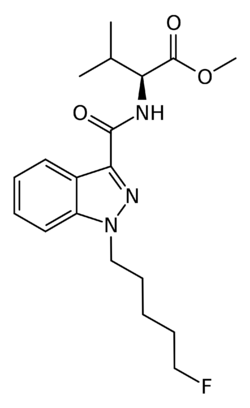
Chemistry:5F-AMB
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H26FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 363.433 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
5F-AMB (also known as 5F-MMB-PINACA and 5F-AMB-PINACA) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid from the indazole-3-carboxamide family,[1] which has been used as an active ingredient in synthetic cannabis products. It was first identified in Japan in early 2014.[2][3] Although only very little pharmacological information about 5F-AMB itself exists,[4] its 4-cyanobutyl analogue (instead of 5-fluoropentyl) has been reported to be a potent agonist for the CB1 receptor (KI = 0.7 nM).[5][6]
Side effects
5F-AMB intoxication caused one fatality on its own,[7] another through ketoacidosis in combination with AB-CHMINACA, AB-FUBINACA, AM-2201, 5F-APINACA, EAM-2201, JWH-018, JWH-122, MAM-2201, STS-135 and THJ-2201 and another fatality in combination with AB-CHMINACA and Diphenidine.[8][9]
Legality
In the United States, 5F-AMB is a Schedule I controlled substance.[10]
5F-AMB is an Anlage II controlled substance in Germany as of May 2015.[11]
Sweden's public health agency suggested classifying 5F-AMB as hazardous substance on November 10, 2014.[12]
The state of Louisiana banned 5F-AMB through an emergency rule after it was detected in a synthetic cannabinoids product called "Kali Berry 2" on 3 June 2014.[13]
5F-AMB is controlled by the Fifth Schedule of the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDA) in Singapore as of May 2015.[14]
5F-AMB was also scheduled in Japan on July 25, 2014.[15]
As of October 2015 5F-AMB is a controlled substance in China.[16]
In December 2019, the UNODC announced scheduling recommendations placing 5F-MMB-PINACA as a Schedule II controlled research chemical.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ "5-Fluoro-AMB". Cayman Chemical. https://www.caymanchem.com/Product.vm/catalog/15489.
- ↑ "Chemical analysis of a benzofuran derivative, 2-(2-ethylaminopropyl)benzofuran (2-EAPB), eight synthetic cannabinoids, five cathinone derivatives, and five other designer drugs newly detected in illegal products". Forensic Toxicology 32 (2): 266–281. August 2014. doi:10.1007/s11419-014-0238-5.
- ↑ "Identification and analytical characteristics of synthetic cannabinoids with an indazole-3-carboxamide structure bearing a N-1-methoxycarbonylalkyl group". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 407 (21): 6301–6315. August 2015. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8612-7. PMID 25893797.
- ↑ "Metabolic profiling of new synthetic cannabinoids AMB and 5F-AMB by human hepatocyte and liver microsome incubations and high-resolution mass spectrometry". Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 30 (8): 1067–1078. April 2016. doi:10.1002/rcm.7538. PMID 27003044. Bibcode: 2016RCMS...30.1067A.
- ↑ Buchler IP, Hayes MJ, Hegde SG, Hockerman SL, Jones DE, Kortum SW, Rico JG, Tenbrink RL, Wu LL, "Indazole derivatives", WO patent 2009106980, published 3 September 2009, assigned to Pfizer Inc.
- ↑ "Pharmacology of Valinate and tert-Leucinate Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-AMBICA, 5F-AMB, 5F-ADB, AMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA, and Their Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 7 (9): 1241–1254. September 2016. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00137. PMID 27421060.
- ↑ "Death after use of the synthetic cannabinoid 5F-AMB". Forensic Science International 262: e21–e24. May 2016. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.03.004. PMID 27017174.
- ↑ "Death due to diabetic ketoacidosis: Induction by the consumption of synthetic cannabinoids?". Forensic Science International 257: e6–e11. December 2015. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.08.012. PMID 26363623.
- ↑ "Postmortem distribution of AB-CHMINACA, 5-fluoro-AMB, and diphenidine in body fluids and solid tissues in a fatal poisoning case: usefulness of adipose tissue for detection of the drugs in unchanged forms". Forensic Toxicology 33 (1): 45–53. January 2015. doi:10.1007/s11419-014-0245-6.
- ↑ "Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Six Synthetic Cannabinoids (5F-ADB, 5F-AMB, 5F-APINACA, ADB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA and MDMB-FUBINACA) Into Schedule I". Drug Enforcement Administration. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/rules/2016/fr1221.htm.
- ↑ "Gesetz über den Verkehr mit Betäubungsmitteln (Betäubungsmittelgesetz - BtMG) Anlage II (zu § 1 Abs. 1) (verkehrsfähige, aber nicht verschreibungsfähige Betäubungsmittel)" (in de). http://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/btmg_1981/anlage_ii.html.
- ↑ "Cannabinoider föreslås bli klassade som hälsofarlig vara" (in sv). Folkhälsomyndigheten. https://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/nyheter-och-press/nyhetsarkiv/2014/november/cannabinoider-foreslas-bli-klassade-som-halsofarlig-vara/.
- ↑ "DHH Adds Two New Synthetic Marijuana Compounds to Banned List". Louisiana Department of Health and Hospitals. 3 June 2014. http://dhh.louisiana.gov/index.cfm/newsroom/detail/3059.
- ↑ "CNB NEWS RELEASE". Central Narcotics Bureau (CNB). 30 April 2015. http://www.cnb.gov.sg/Libraries/CNB_Newsroom_Files/CNB_NR_-_30_Apr_2015.sflb.ashx.
- ↑ "指定薬物一覧" (in ja). Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/iyakuhin/yakubuturanyou/dl/meisho.pdf.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in zh). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
- ↑ "December 2019 – WHO: World Health Organization recommends 12 NPS for scheduling". https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Announcement/Details/021820a0-8746-42a4-9ee3-47ce50b30ca3.
 |
