Chemistry:MDMB-CHMINACA
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H31N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 385.508 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
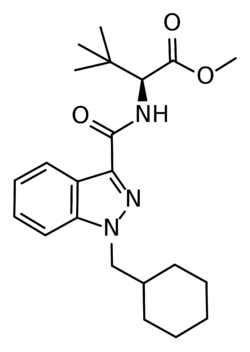
MDMB-CHMINACA[1] (also known as MDMB(N)-CHM) is an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid that acts as a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor,[2] and has been sold online as a designer drug.[3][4][5][6][7] It was invented by Pfizer in 2008, and is one of the most potent cannabinoid agonists known, with a binding affinity of 0.0944 nM at CB1, and an EC50 of 0.330 nM.[8] It is closely related to MDMB-FUBINACA, which caused at least 1000 hospitalizations and 40 deaths in Russia as consequence of intoxication.[9]
Legal status
MDMB-CHMINACA is a Fifth Schedule of the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDA) controlled substance in Singapore as of May 2015.[10]
MDMB-CHMINACA is illegal in Germany, Switzerland as of December 2015.[11]
Sweden's public health agency suggested classifying MDMB-CHMINACA as a hazardous substance, on September 25, 2019.[12]
See also
- AB-CHMINACA
- ADB-CHMINACA
- ADB-FUBINACA
- MDMB-CHMICA
- MDMB-FUBINACA
- PX-3 (APP-CHMINACA)
References
- ↑ Pulver, Benedikt; Fischmann, Svenja; Gallegos, Ana; Christie, Rachel (March 2023). "EMCDDA framework and practical guidance for naming synthetic cannabinoids". Drug Testing and Analysis 15 (3): 255–276. doi:10.1002/dta.3403.
- ↑ "Pharmacology of Valinate and tert-Leucinate Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-AMBICA, 5F-AMB, 5F-ADB, AMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA, and Their Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 7 (9): 1241–54. September 2016. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00137. PMID 27421060.
- ↑ "MDMB-CHMINACA". Cayman Chemical. https://www.caymanchem.com/Product.vm/catalog/16200.
- ↑ "Identification and analytical characteristics of synthetic cannabinoids with an indazole-3-carboxamide structure bearing a N-1-methoxycarbonylalkyl group". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 407 (21): 6301–15. August 2015. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8612-7. PMID 25893797.
- ↑ Prof. SA Savchuk (2014). "Detection methods of psychoactive substances and liquid chromotograoghy detection of metabolites." (in ru). Russian Ministry of Health. http://www.nncn.ru/objects/nncn01/1406569417.pdf.
- ↑ "Идентификация синтетических каннабимиметиков MDMB-CHMINACA, MDMB-FUBINACA и их метаболитов" (in ru). CTS "SCIENCE". http://scientific-technology.ru/khromatomass-spektrometriya/obnaruzhenie-i-identifikatsiya-sinteticheskikh-kannabimimetikov/166-identifikatsiya-sinteticheskikh-kannabimimetikov-mdmb-chminaca-mdmb-fubinaca-i-ikh-metabolitabolitov-2.
- ↑ "Simultaneous detection of 93 synthetic cannabinoids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and retrospective application to real forensic samples". Drug Testing and Analysis 9 (5): 721–733. May 2017. doi:10.1002/dta.2030. PMID 27400642.
- ↑ Buchler IP et al, INDAZOLE DERIVATIVES. WO 2009/106980
- ↑ "Очередная жертва спайса" (in ru). Federal Drug Control Service of the Russian Federation. 17 March 2015. http://www.fskn.gov.ru/includes/periodics/news/2015/0317/205035975/detail.shtml.
- ↑ "CNB NEWS RELEASE". Central Narcotics Bureau (CNB). 30 April 2015. http://www.cnb.gov.sg/Libraries/CNB_Newsroom_Files/CNB_NR_-_30_Apr_2015.sflb.ashx.
- ↑ "Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien" (in de). Der Bundesrat. https://www.admin.ch/opc/de/classified-compilation/20101220/index.html.
- ↑ "Tretton ämnen föreslås klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara" (in sv). Folkhälsomyndigheten. 25 September 2019. https://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/nyheter-och-press/nyhetsarkiv/2019/september/tretton-amnen-foreslas-klassas-som-narkotika-eller-halsofarlig-vara/.
 |
