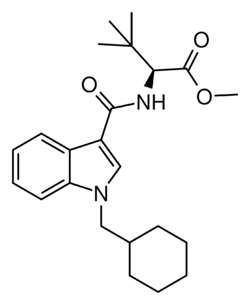
Chemistry:MDMB-CHMICA
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H32N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 384.520 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
MDMB-CHMICA[3] is an indole-based synthetic cannabinoid that is a potent agonist of the CB1 receptor and has been sold online as a designer drug.[2][4][5][6] While MDMB-CHMICA was initially sold under the name "MMB-CHMINACA", the compound corresponding to this code name (i.e. the isopropyl instead of t-butyl analogue of MDMB-CHMINACA) has been identified on the designer drug market in 2015 as AMB-CHMINACA.[7]
Chemistry
Several commercial samples of MDMB-CHMICA were found to exclusively contain the (S)-enantiomer based on vibrational and electronic circular dichroism spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography.[8] An (S)-configuration for the tert-leucinate group is unsurprising since MDMB-CHMICA is likely synthesized from the abundant and inexpensive "L" form of the appropriate tert-leucinate reactant.
Pharmacology
MDMB-CHMICA acts as a highly potent full agonist of the CB1 receptor with an efficacy of 94% and an EC50 value of 0.14 nM, which is approximately 8 times lower than the EC50 of JWH-018 (1.13 nM) and twofold lower than AB-CHMINACA (0.27 nM).[2][9][10]
Metabolism
MDMB-CHMICA's main metabolic reactions comprise mono-hydroxylations and hydrolysis of the carboxylic ester function. In total, 31 metabolites could be identified in vivo.[11][12][13]
Side effects
Seventy-one serious adverse events, including 42 acute intoxications and 29 deaths (Germany (5), Hungary (3), Poland (1), Sweden (9), United Kingdom (10), Norway (1)) that occurred in nine European countries between 2014 and 2016 have been associated with MDMB-CHMICA.[2][14][15][16][17]
Side effects such as unconsciousness or coma, hyperemesis, nausea, seizures, convulsions, tachycardia, bradycardia, mydriasis, syncope, spontaneous urinating and defecating, shortness of breath, somnolence, respiratory acidosis, metabolic acidosis, collapse, lower limbs paralysis, chest pain, aggression and severe disturbance of behaviour were reported.[2][18][19][20][21][22]
Legal status
In the United States, MDMB-CHMICA is a Schedule I controlled substance.[23]
MDMB-CHMICA is illegal in Austria, Canada, China,[24] Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Louisiana,[25] Luxembourg, Norway, Portugal, Turkey, the UK, Sweden and Switzerland.[2]
In August 2016 the European Commission proposed a ban on MDMB-CHMICA across the European Union. [26] In 27 February 2017 the Commission adopted an implementing act in banning MDMB-CHMICA, and Member States shall take the necessary measures to subject it to control measures and criminal penalties no later than by 4 March 2018. [27]
Seizures
Over 3600 MDMB-CHMICA seizures between 2014 and 2016 in 19 member states of the European Union have been reported to the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA),[2] including a 40 kg seizure [sic] in Luxembourg in December 2014.[28]
See also
References
- ↑ "Substance Details MDMB-CHMICA". https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Substance/Details/37d19d4e-77cc-434e-ab4d-f95134871426.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 European Monitoring Centre for Drugs Drug Addiction; European Police Office (July 2016). EMCDDA–Europol Joint Report on MDMB-CHMICA. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). doi:10.2810/08132. ISBN 978-92-9168-925-5. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/2873/2016.4528_WEB.pdf.
- ↑ Pulver, Benedikt; Fischmann, Svenja; Gallegos, Ana; Christie, Rachel (March 2023). "EMCDDA framework and practical guidance for naming synthetic cannabinoids". Drug Testing and Analysis 15 (3): 255–276. doi:10.1002/dta.3403.
- ↑ "MDMB-CHMICA". Cayman Chemical. https://www.caymanchem.com/product/16965.
- ↑ "MDMB-CHMICA". Southern Association of Forensic Scientists. http://forendex.safs1966.org/index.php/detail/index/1305.
- ↑ "Pharmacology of Valinate and tert-Leucinate Synthetic Cannabinoids 5F-AMBICA, 5F-AMB, 5F-ADB, AMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA, and Their Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 7 (9): 1241–54. September 2016. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00137. PMID 27421060.
- ↑ "Identification and analytical characteristics of synthetic cannabinoids with an indazole-3-carboxamide structure bearing a N-1-methoxycarbonylalkyl group". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 407 (21): 6301–15. August 2015. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8612-7. PMID 25893797.
- ↑ "Absolute configuration of the synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA with its chemical characteristics in illegal products". Forensic Toxicology 34 (2): 344–352. 1 June 2016. doi:10.1007/s11419-016-0321-1.
- ↑ "Identification and quantification of synthetic cannabinoids in "spice-like" herbal mixtures: update of the German situation for the spring of 2015". Forensic Toxicology 34 (1): 94–107. January 2016. doi:10.1007/s11419-015-0292-7.
- ↑ "MDMB-CHMICA induces thrashing behavior, bradycardia, and slow pressor response in a CB1- and CB2-receptor-dependent manner in conscious rats". Forensic Toxicology 36 (2): 313–319. 2018. doi:10.1007/s11419-018-0405-1. ISSN 1860-8965.
- ↑ "Metabolism and urine analysis of the new synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA". Toxichem Krimtech 82: 192. 2015. https://www.gtfch.org/cms/images/stories/media/tb/tb2015/Franz_et_al_2015.pdf.
- ↑ "Human urinary metabolite pattern of a new synthetic cannabimimetic, methyl 2-(1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoate". Forensic Toxicology 34 (2): 316–328. July 2016. doi:10.1007/s11419-016-0319-8.
- ↑ "Phase I metabolism of the highly potent synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA and detection in human urine samples". Drug Testing and Analysis 9 (5): 744–753. May 2017. doi:10.1002/dta.2049. PMID 27504870.
- ↑ "Derby legal high confusion prompts police warning". BBC. 29 April 2015. https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-derbyshire-32477643.
- ↑ "Drug Alert: Dangerous Synthetic Cannabinoid MMB-CHMINACA Causing Hospitalizations, Deaths in Europe". TalkingDrugs. 2 July 2015. http://www.talkingdrugs.org/drug-alert-dangerous-synthetic-cannabinoid-mmb-chminaca-causing-hospitalizations-deaths-in-europe.
- ↑ "Sudden Cardiac Death Following Use of the Synthetic Cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA". Journal of Analytical Toxicology 40 (1): 86–7. February 2016. doi:10.1093/jat/bkv110. PMID 26353925.
- ↑ "Fatal intoxication with synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA". Forensic Science International 261: e5-10. April 2016. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.02.024. PMID 26934903.
- ↑ "Analysis and clinical findings of cases positive for the novel synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist MDMB-CHMICA". Clinical Toxicology 54 (8): 632–7. September 2016. doi:10.1080/15563650.2016.1186805. PMID 27213960. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/119581/7/119581.pdf.
- ↑ "Clinical toxicity following analytically confirmed use of the synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist MDMB-CHMICA. A report from the Identification Of Novel psychoActive substances (IONA) study". Clinical Toxicology 54 (8): 638–43. September 2016. doi:10.1080/15563650.2016.1190980. PMID 27251903. https://eprint.ncl.ac.uk/fulltext.aspx?url=228493/557F779B-1B52-49C9-BB95-63214A108798.pdf&pub_id=228493.
- ↑ "A systematic review of adverse events arising from the use of synthetic cannabinoids and their associated treatment". Clinical Toxicology 54 (1): 1–13. 2 January 2016. doi:10.3109/15563650.2015.1110590. PMID 26567470.
- ↑ "Poisoning due to MDMB-CHMICA, a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist". Clinical Toxicology 55 (2): 151–152. February 2017. doi:10.1080/15563650.2016.1227832. PMID 27635694.
- ↑ "Analytically Confirmed Intoxications Involving MDMB-CHMICA from the STRIDA Project". Journal of Medical Toxicology 13 (1): 52–60. March 2017. doi:10.1007/s13181-016-0584-2. PMID 27638057.
- ↑ "Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of Six Synthetic Cannabinoids (5F-ADB, 5F-AMB, 5F-APINACA, ADB-FUBINACA, MDMB-CHMICA and MDMB-FUBINACA) Into Schedule I". Drug Enforcement Administration. https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/fed_regs/rules/2016/fr1221.htm.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
- ↑ "Gov. Jindal and State Officials Ban New Synthetic Marijuana Compound". http://dhh.louisiana.gov/index.cfm/newsroom/detail/3161.
- ↑ "New psychoactive substances: Commission proposes new ban and strengthens the EU's Early Warning System and risk assessment". Lisbon: European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). 31 August 2016. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/news/2016/NPS-Commission.
- ↑ "COUNCIL IMPLEMENTING DECISION (EU) 2017/369". Brussels: European Commission. 27 February 2017. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32017D0369&from=EN.
- ↑ "Global SMART update". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. 13 March 2015. https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Global_SMART_Update_13_web.pdf.
 |

