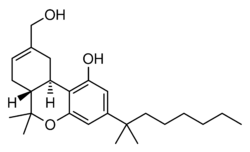
Chemistry:HU-210
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1,1-Dimethylheptyl- 11-hydroxy- tetrahydrocannabinol |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H38O3 |
| Molar mass | 386.576 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
HU-210 is a synthetic cannabinoid that was first synthesized in 1988 from (1R,5S)-myrtenol[1] by a group led by Raphael Mechoulam at the Hebrew University.[2][3][4] HU-210 is 100 to 800 times more potent than natural THC from cannabis and has an extended duration of action.[5] HU-210 has a binding affinity of 0.061 nM at CB1 and 0.52 nM at CB2 in cloned human cannabinoid receptors[6] compared to delta-9-THC of 40.7 nM at CB1. [7] HU-210 is the (–)-1,1-dimethylheptyl analog of 11-hydroxy- Δ8- tetrahydrocannabinol; in some references it is called 1,1-dimethylheptyl- 11-hydroxytetrahydrocannabinol. The abbreviation "HU" stands for Hebrew University.
Effects and research
HU-210, the (–) enantiomer of 11-OH-D8-THC-DMH, has almost all of the cannabinoid activity, while the (+) enantiomer, known as HU-211, is inactive as a cannabinoid and instead acts as an NMDA antagonist having neuroprotective effects.[8][9]
HU-210 has an oral LD50 of 5,000 mg/kg in rats and 14,200 mg/kg in rabbits.[10] HU-210 has an LDLO (Lowest Lethal Dose amount) of 143 mg/kg in humans.[10] Delta-8-THC LD50 has not been confirmed. In a 1973 study monkeys and dogs given 9,000 mg/kg of delta-8-THC was nonlethal.[11][12]
Chemistry
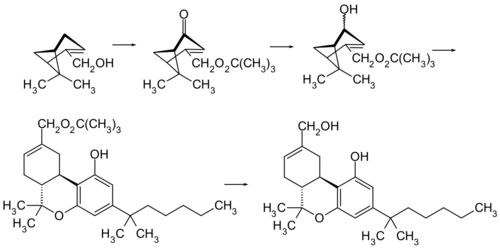
HU-210 is the enantiomer of HU-211 (dexanabinol). The original synthesis of HU-210 is based on an acid-catalyzed condensation of (–)-Myrtenol and 1,1-Dimethylheptylresorcinol (3,5-Dihydroxy-1-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)benzol).[1]
Legal status
HU-210 is not listed in the schedules set out by the United Nations ' Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs from 1961 nor their Convention on Psychotropic Substances from 1971,[13] so the signatory countries to these international drug control treaties are not required by said treaties to control HU-210.
New Zealand
HU-210 is banned in New Zealand as of 8 May 2014.[14]
United States
HU-210 is not explicitly listed in the list of scheduled controlled substances in the USA.[15] A brief profile of HU-210 written and published by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) in 2009, but removed in later years, stated that HU-210 is a Schedule I controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act due to being similar to THC.[16] A version of the document (updated in 2013), now in PDF form, exists on the DEA Office of Diversion Control's website.[17] In that PDF, DEA reasserts that HU-210 is a Schedule I substance. DEA currently considers HU-210 a Schedule I controlled substance under the umbrella of ‘tetrahydrocannabinols’. HU-210’s DEA No. is 7370; the same number assigned to dronabinol and synthetic Delta-8-THC.[18]
Alabama
HU-210 is a Schedule I controlled substance in Alabama.[19]
(4)a. A synthetic controlled substance that is any material, mixture, or preparation that contains any quantity of the following chemical compounds, their salts, isomers and salts of isomers, unless specifically excepted, whenever the existence of these salts, isomers and salts of isomers is possible within the specific chemical designation or compound:...
9. (6aR, 10aR)-9-(hydroxymethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(2-methyloctan-2-yl)-6a,7,10,10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromen-1-ol, some trade or other names: HU-210.
Florida
HU-210 is a Schedule I controlled substance, categorized as a hallucinogen, making it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in the state of Florida without a license.[20]
| “ | (c) Unless specifically excepted or unless listed in another schedule, any material, compound, mixture, or preparation that contains any quantity of the following hallucinogenic substances or that contains any of their salts, isomers, including optical, positional, or geometric isomers, homologues, nitrogen-heterocyclic analogs, esters, ethers, and salts of isomers, homologues, nitrogen-heterocyclic analogs, esters, or ethers, if the existence of such salts, isomers, and salts of isomers is possible within the specific chemical designation or class description:
... 47. HU-210 [(6aR,10aR)-9-(Hydroxymethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(2-methyloctan-2-yl)-6a,7,10,10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromen-1-ol]. |
” |
Vermont
Effective January 1, 2016, HU-210 is a regulated drug in Vermont designated as a "Hallucinogenic Drug."[21]
Other HU Cannabinoids
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Synthesis of the individual, pharmacologically distinct, enantiomers of a tetrahydrocannabinol derivative". Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1 (5): 315–318. January 1990. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(00)86322-3.
- ↑ "Enantiomeric cannabinoids: stereospecificity of psychotropic activity". Experientia 44 (9): 762–4. September 1988. doi:10.1007/BF01959156. PMID 3416993.
- ↑ "Stereochemical effects of 11-OH-delta 8-THC-dimethylheptyl in mice and dogs". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 32 (3): 661–6. March 1989. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(89)90014-2. PMID 2544901.
- ↑ "Stereospecificity of the discriminative stimulus functions of the dimethylheptyl homologs of 11-hydroxy-delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats and pigeons". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 250 (3): 1000–5. September 1989. PMID 2550611.
- ↑ "A novel probe for the cannabinoid receptor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35 (11): 2065–9. May 1992. doi:10.1021/jm00089a018. PMID 1317925.
- ↑ "Medicinal chemistry endeavors around the phytocannabinoids". Chemistry & Biodiversity 4 (8): 1707–1728. August 2007. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200790149. PMID 17712816.
- ↑ "The Structure-Function Relationships of Classical Cannabinoids: CB1/CB2 Modulation". Perspectives in Medicinal Chemistry 8: 17–39. 2016. doi:10.4137/PMC.S32171. PMID 27398024.
- ↑ "Stereochemical effects of 11-OH-delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol-dimethylheptyl to inhibit adenylate cyclase and bind to the cannabinoid receptor". Neuropharmacology 29 (2): 161–5. February 1990. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(90)90056-w. PMID 2158635.
- ↑ "Dexanabinol: a novel cannabinoid with neuroprotective properties". IDrugs 6 (10): 976–9. October 2003. OCLC 112453448. PMID 14534855.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "HU-210". Material Safety Data Sheet. Cayman Chemical. https://www.caymanchem.com/msdss/90083m.pdf.
- ↑ "Comparison of acute oral toxicity of cannabinoids in rats, dogs and monkeys". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 25 (3): 363–72. July 1973. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(73)90310-4. PMID 4199474.
- ↑ "delta-8-Tetrahydrocannabinol". ChemIDplus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/5957-75-5.
- ↑ "International Drug Control Conventions". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/commissions/CND/conventions.html.
- ↑ "Synthetic cannabinoids: What they are". New Zealand Drug Foundation. https://www.drugfoundation.org.nz/synthetic-cannabinoids/what-they-are.
- ↑ "PART 1308 - Section 1308.11 Schedule I". Office of Diversion Control. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. Department of Justice. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/cfr/1308/1308_11.htm.
- ↑ "Spice Cannabinoid - HU-210". Office of Diversion Control. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. Department of Justice. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drugs_concern/spice/spice_hu210.htm.
- ↑ "HU-210". Office of Diversion Control. Drug Enforcement Administration, U.S. Department of Justice. January 2013. http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/drug_chem_info/spice/spice_hu210.pdf. "6aR,10aR)-9-(hydroxymethyl)-6,6-dimethyl-3-(2-methyloctan-2-yl)-6a,7,10,10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c] chromen-1-ol)] [Purported Ingredient of “Spice”"
- ↑ "HU-210" (in en). 2001-01-01. https://www.lipomed-usa.com/en/hu-210.
- ↑ "Controlled substances, Schedule I, additional synthetic controlled substances and analogue substances included in, trafficking in controlled substance analogues, requisite weight increased, Secs. 13A-12-231, 20-2-23 am'd.". Alabama Senate Bill 333. March 2014. https://legiscan.com/AL/text/SB333/2014.
- ↑ "Chapter 893: Drug Abuse Prevention and Control". The 2020 Florida Statutes. The Florida Legislature. http://leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=0800-0899/0893/0893.html.
- ↑ "Chapter 8 – Alcohol and Drug Abuse Subchapter 9: Regulated Drug Rule". Code of Vermont Rules. Vermont Department of Health. 15 July 2017. http://www.healthvermont.gov/sites/default/files/documents/2017/01/REG_regulated-drugs.pdf. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
Further reading
- "Marijuana may make your brain grow". Nature. 13 October 2005. doi:10.1038/news051010-12.
- "Update: Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits Involving Synthetic Cannabinoids". The CBHSQ Report (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality). 16 October 2014. PMID 27030867. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/SR-1378/SR-1378.pdf.
 |
