Chemistry:Leelamine
From HandWiki
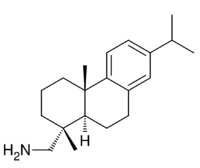
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Abieta-8,11,13-trien-18-amine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-[(1R,4aS,10aR)-1,4a-Dimethyl-7-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,4a,9,10,10a-octahydrophenanthren-1-yl]methanamine | |
| Other names
(+)-Dehydroabietylamine; Amine D
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H31N | |
| Molar mass | 285.475 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Leelamine (dehydroabietylamine) is a diterpene amine that has weak affinity for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, as well as being an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.[1] Optically active leelamine is also used as a chiral resolving agent for carboxylic acids.[2][3] Leelamine has been shown to be effective against certain cancer cells, independent from its activity on CB receptors or PDK1 - it accumulates inside the acidic lysosomes leading to disruption of intracellular cholesterol transport, autophagy and endocytosis followed by cell death.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Leelamine - Dehydroabietylamine - Cayman Chemical". https://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/Product.vm/catalog/10006148.
- ↑ US patent 3454626
- ↑ US patent 4559178
- ↑ Kuzu, O. F.; Gowda, R.; Sharma, A.; Robertson, G. P. (2014). "Leelamine Mediates Cancer Cell Death through Inhibition of Intracellular Cholesterol Transport". Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 13 (7): 1690–703. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0868. PMID 24688051.
External links
 |

