Chemistry:5F-PB-22
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
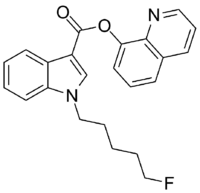
| Formula | C23H21FN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 376.431 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
5F-PB-22 (5F-QUPIC or quinolin-8-yl 1-pentyfluoro-1H-indole-3-8-carboxylate) is a designer drug which acts as a cannabinoid agonist.[1] The structure of 5F-PB-22 appears to have been designed with an understanding of structure–activity relationships within the indole class of cannabinoids.[2]
Pharmacology
5F-PB-22 acts as a full agonist with a binding affinity of 0.468 nM at CB1 and 0.633 nM at CB2 cannabinoid receptors.[3]
Legal status
As of October 2015 5F-PB-22 is a controlled substance in China.[4]
In January 2014, 5F-PB-22 was designated as a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States after several deaths were associated with its use.[5][6]
In the United Kingdom, 5F-PB-22 is now classified and controlled as a Class B drug, following the November 2016 amendment to the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. Several other synthetic cannabinoids structurally related to JWH-018, like 5F-PB-22, were also classified in this amendment.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ "Effects of bioisosteric fluorine in synthetic cannabinoid designer drugs JWH-018, AM-2201, UR-144, XLR-11, PB-22, 5F-PB-22, APICA, and STS-135". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 6 (8): 1445–58. August 2015. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00107. PMID 25921407. https://zenodo.org/record/47750.
- ↑ "5F-PB-22". Forendex. http://forendex.southernforensic.org/index.php/detail/index/1233.
- ↑ "Pharmacological evaluation of synthetic cannabinoids identified as constituents of spice". Forensic Toxicology 34 (2): 329–343. 1 July 2016. doi:10.1007/s11419-016-0320-2. PMID 27429655.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
- ↑ "Four postmortem case reports with quantitative detection of the synthetic cannabinoid, 5F-PB-22". Journal of Analytical Toxicology 38 (8): 559–62. October 2014. doi:10.1093/jat/bku048. PMID 24876364.
- ↑ "Synthetic Cannabinoid-Related Illnesses and Deaths". The New England Journal of Medicine 373 (2): 103–7. July 2015. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1505328. PMID 26154784.
- ↑ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Amendment) Order 2016" (in en). http://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2016/1109/made.
 |
