Chemistry:BML-190
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
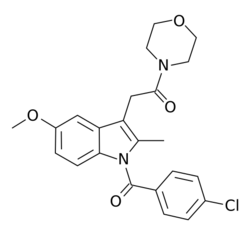 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H23ClN2O4 |
| Molar mass | 426.892 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
BML-190 (Indomethacin morpholinylamide) is a drug used in scientific research that acts as a selective CB2 inverse agonist.[1] BML-190 is structurally derived from the NSAID indomethacin but has a quite different biological activity.[2] The activity produced by this compound is disputed, with some sources referring to it as a CB2 agonist rather than an inverse agonist;[3][4] this may reflect an error in classification, or alternatively it may produce different effects in different tissues, and more research is required to resolve this dispute.
Lead optimization of the parent structure resulted in L-768,242 & L-759,787.
References
- ↑ "BML-190 and AM251 act as inverse agonists at the human cannabinoid CB2 receptor: signalling via cAMP and inositol phosphates". FEBS Letters 536 (1–3): 157–60. February 2003. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00048-6. PMID 12586356.
- ↑ "Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor". British Journal of Pharmacology 139 (4): 775–86. June 2003. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705304. PMID 12813001.
- ↑ "Suppression of nerve growth factor Trk receptors and prolactin receptors by endocannabinoids leads to inhibition of human breast and prostate cancer cell proliferation". Endocrinology 141 (1): 118–26. January 2000. doi:10.1210/endo.141.1.7239. PMID 10614630.
- ↑ "Cannabinoids stimulate fibroblastic colony formation by bone marrow cells indirectly via CB2 receptors". Calcified Tissue International 80 (1): 50–9. January 2007. doi:10.1007/s00223-006-0171-7. PMID 17205329.
 |
