Chemistry:BZO-CHMOXIZID
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
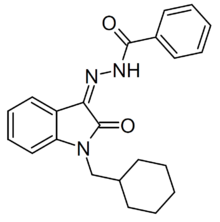
| Formula | C22H23N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 361.445 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
BZO-CHMOXIZID (CHM-MDA-19) is a synthetic cannabinoid compound first reported in 2008 in the same series as the better known derivative MDA-19.[1] It started to be widely sold as an ingredient in grey-market synthetic cannabis blends in 2021 following the introduction of legislation in China which for the first time introduced general controls on various classes of synthetic cannabinoids,[2] but did not include the group to which MDA-19 and BZO-CHMOXIZID belong. While BZO-CHMOXIZID is the most potent compound at CB1 from this so-called "OXAZID" series, it is still markedly CB2 selective and of relatively low potency at CB1, with an EC50 of 84.6 nM at CB1 compared to 2.21 nM at CB2.[3][4]
Legality
In the United States, As of May 22, 2023 BZO-CHMOXIZID is legal at the federal level, but may be considered illegal if intended for human consumption under the federal analogue act.[5]
North Dakota has placed BZO-CHOMXIZID (CHM-MDA-19) (along with BZO-HEXOXIZID (MDA-19), BZO-POXIZID (Pentyl MDA-19), 5F-BZO-POXIZID (5F-MDA-19) and BZO-4en-POXIZID (4en-pentyl MDA-19) into Schedule I on 04/27/23.[6]
In China, the May 2021 ban on specific synthetic cannabinoid core classes does not include the class of cannabinoids BZO-CHMOXIZID belongs to.[7][8]
References
- ↑ "Design and synthesis of a novel series of N-alkyl isatin acylhydrazone derivatives that act as selective cannabinoid receptor 2 agonists for the treatment of neuropathic pain". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51 (16): 4932–47. August 2008. doi:10.1021/jm8002203. PMID 18666769.
- ↑ "关于将合成大麻素类物质和氟胺酮等18种物质列入《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品管制品种增补目录》的公告" (in Chinese). Ministry of Public Security of the People's Republic of China. 12 May 2021. https://app.mps.gov.cn/gdnps/pc/content.jsp?id=7881703.
- ↑ "Cannabinoid receptor activation potential of the next generation, generic ban evading OXIZID synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists". Drug Testing and Analysis 14 (9): 1565–1575. September 2022. doi:10.1002/dta.3283. PMID 35560866. https://biblio.ugent.be/publication/01GQ74V7ZKBG7AK8QKJWSP5FAV.
- ↑ "Identification of Optimal Urinary Biomarkers of Synthetic Cannabinoids BZO-HEXOXIZID, BZO-POXIZID, 5F-BZO-POXIZID, and BZO-CHMOXIZID for Illicit Abuse Monitoring". Clinical Chemistry 68 (11): 1436–1448. November 2022. doi:10.1093/clinchem/hvac138. PMID 36175111.
- ↑ "21 U.S. Code § 813 - Treatment of controlled substance analogues". https://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/text/21/813.
- ↑ "AN ACT to amend and reenact sections 19-03.1-05, 19-03.1-11, and 19-03.1-13 of the North Dakota Century Code, relating to the scheduling of controlled substances; and to declare an emergency.". Sixty-eighth Legislative Assembly of North Dakota in Regular Session. 3 January 2023. https://www.ndlegis.gov/prod/assembly/68-2023/regular/documents/23-8099-04000.pdf.
- ↑ "关于将合成大麻素类物质和氟胺酮等18种物质列入《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品管制品种增补目录》的公告" (in Chinese). Ministry of Public Security of the People's Republic of China. 12 May 2021. https://app.mps.gov.cn/gdnps/pc/content.jsp?id=7881703.
- ↑ "Details for Country CHINA". https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Country/Details/CN.
 |

