Chemistry:AM-2233
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
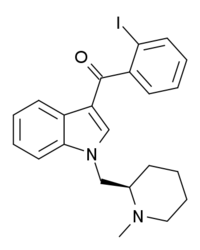 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23IN2O |
| Molar mass | 458.343 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
AM-2233 is a drug that acts as a highly potent full agonist for the cannabinoid receptors, with a Ki of 1.8 nM at CB1 and 2.2 nM at CB2 as the active (R) enantiomer.[1] It was developed as a selective radioligand for the cannabinoid receptors and has been used as its 131I derivative for mapping the distribution of the CB1 receptor in the brain.[2][3][4][5][6][7] AM-2233 was found to fully substitute for THC in rats, with a potency lower than that of JWH-018 but higher than WIN 55,212-2.[8]
It is notable for inducing tinnitus,[9] though the reasons for this are unclear and may provide valuable insight into tinnitus research.
Legal Status
As of October 2015 AM-2233 is a controlled substance in China.[10]
See also
- AM-679
- AM-694
- AM-1220
- AM-1221
- AM-1235
- AM-1241
- AM-2232
- Cannabipiperidiethanone
- FUBIMINA
- JWH-018
- List of AM cannabinoids
- List of JWH cannabinoids
- List of HU cannabinoids
- List of designer drugs
References
- ↑ Hongfeng Deng (2000). Design and synthesis of selective cannabinoid receptor ligands: Aminoalkylindole and other heterocyclic analogs (PhD Dissertation). University of Connecticut. ProQuest 304624325.
- ↑ "Potent cannabinergic indole analogues as radioiodinatable brain imaging agents for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48 (20): 6386–6392. October 2005. doi:10.1021/jm050135l. PMID 16190764.
- ↑ "Cannabinoid chemistry: an overview". Cannabinoids as Therapeutics. Milestones in Drug Therapy MDT. 2005. pp. 23–46. doi:10.1007/3-7643-7358-X_2. ISBN 978-3-7643-7055-8.
- ↑ "F200A substitution in the third transmembrane helix of human cannabinoid CB1 receptor converts AM2233 from receptor agonist to inverse agonist". European Journal of Pharmacology 531 (1–3): 41–46. February 2006. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.026. PMID 16438957.
- ↑ "Evaluation of the in vivo receptor occupancy for the behavioral effects of cannabinoids using a radiolabeled cannabinoid receptor agonist, R-[125/131I]AM2233". Synapse 60 (2): 93–101. August 2006. doi:10.1002/syn.20277. PMID 16715483.
- ↑ "R-2-[131I]Iodophenyl-(1-(1-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)methanone". Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Dec 12, 2006. PMID 20641836.
- ↑ "Ligand-binding architecture of human CB2 cannabinoid receptor: evidence for receptor subtype-specific binding motif and modeling GPCR activation". Chemistry & Biology 15 (11): 1207–1219. November 2008. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.10.011. PMID 19022181.
- ↑ "Cannabinergic aminoalkylindoles, including AM678=JWH018 found in 'Spice', examined using drug (Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol) discrimination for rats". Behavioural Pharmacology 22 (5–6): 498–507. September 2011. doi:10.1097/FBP.0b013e328349fbd5. PMID 21836461.
- ↑ "AM-2233 INDUCED TINNITUS: COLLECTED REPORTS" (in en). 30 September 2014. http://hamiltonmorris.blogspot.com/2014/09/am-2233-induced-tinnitus-collected.html.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in zh). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
 |

