Chemistry:Perrottetinene
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 348.486 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
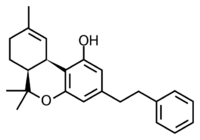
Perrottetinene is a naturally occurring cannabinoid compound found in liverworts from the genus Radula native to Japan, New Zealand and Costa Rica, namely Radula perrottetii, Radula marginata and Radula laxiramea,[1][2] along with a number of similar compounds.[3][4] Its chemical structure closely resembles that of THC, the main active component of marijuana but with a cis rather than trans conformation and a bibenzyl tailchain instead of pentyl.[5] The absolute configuration of perrottetinene was established in 2008 by an enantioselective total synthesis.[6]
Pharmacology
In 2018, a study showed that perrottetinene is mild to moderately psychoactive through activation of the cannabinoid receptor 1. (-)-cis-PET was found to have a binding affinity of 481nM at CB1 and 225nM at CB2 while the unnatural (-)-trans-PET was found to have a binding affinity of 127nM at CB1 and 126nM at CB2, both acting as partial agonists. In terms of binding affinity this study found cis-PET to be over 22x weaker than Delta-9-THC. The same study also reported significantly reduced prostaglandin D2 and E2 brain concentrations in mice after perrottetinene administration.[7]
Perrottetinene is structurally related to Machaeriol A and other Machaeriols found in Machaerium species.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "Transcriptional profiling of lung cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension". Pulmonary Circulation 10 (1): 147–150. 1999-04-01. doi:10.1515/znc-1999-3-401. PMID 32166015.
- ↑ "Cannabimimetic plants: are they new cannabinoidergic modulators?". Planta 249 (6): 1681–1694. June 2019. doi:10.1007/s00425-019-03138-x. PMID 30877436.
- ↑ "Bibenzyl cannabinoid and bisbibenzyl derivative from the liverwort Radula perrottetii". Phytochemistry 37 (3): 859–862. 1994. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)90371-6.
- ↑ "New bibenzyl cannabinoid from the New Zealand liverwort Radula marginata". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 50 (10): 1390–1392. October 2002. doi:10.1248/cpb.50.1390. PMID 12372871.
- ↑ "Shared Binding Mode of Perrottetinene and Tetrahydrocannabinol Diastereomers inside the CB1 Receptor May Incentivize Novel Medicinal Drug Design: Findings from an in Silico Assay". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 11 (24): 4289–4300. December 2020. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00547. PMID 33201672.
- ↑ "Stereoselective total synthesis of (-)-perrottetinene and assignment of its absolute configuration". Organic Letters 10 (2): 269–271. January 2008. doi:10.1021/ol702692q. PMID 18085788.
- ↑ "Uncovering the psychoactivity of a cannabinoid from liverworts associated with HAVOK". Science Advances 4 (10): eaat2166. October 2018. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aat2166. PMID 30397641. Bibcode: 2018SciA....4.2166C.
- ↑ "Machaeriol A". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Machaeriol-A.
 |

