Earth:Vallis (planetary geology)
Vallis or valles /ˈvælɪs/ (plural valles /ˈvæliːz/)[1] is the Latin word for valley. It is used in planetary geology to name landform features on other planets.
Scientists used vallis for old river valleys they discovered when they sent the first probes to Mars. The Viking Orbiters caused a revolution in our ideas about water on Mars; finding huge river valleys in many areas. Space craft cameras showed that floods of water broke through dams, carved deep valleys, eroded grooves into bedrock, and traveled thousands of kilometers.[2][3][4] Some valles on Mars (Mangala Vallis, Athabasca Vallis, Granicus Vallis, and Tinjar Valles) clearly begin at graben. On the other hand, some of the large outflow channels begin in rubble-filled low areas, called chaos or chaotic terrain. It has been suggested that massive amounts of water were trapped under pressure beneath a thick cryosphere (layer of frozen ground), then the water was suddenly released, perhaps when the cryosphere was broken by a fault.[5][6]
Nirgal Vallis and sapping
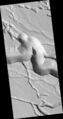
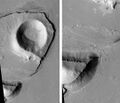
Nirgal Vallis is one of the longest valley networks on Mars. It is so large that it is found on more than one quadrangle. Scientists are not sure about how all the ancient river valleys were formed. There is evidence that instead of rain or snow, the water that formed the valleys originated underground. One mechanism that has been advanced is sapping.[7] In sapping, the ground just gives away as water comes out. Sapping is common in some desert areas in America's Southwest. Sapping forms alcoves and stubby tributaries. These features are visible in the picture from the Coprates quadrangle of Nigal Vallis taken with Mars Odyssey's THEMIS.
Nirgal Vallis that runs in two quadrangles has features looking like those caused by sapping. Picture taken with THEMIS.
Kasei Valles
One of the most significant features of the Lunae Palus region, Kasei Valles is one of the largest outflow channels on Mars. Like other outflow channels, it was carved by liquid water, probably during gigantic floods.
Kasei is about 2,400 kilometers (1,500 mi) long. Some sections of Kasei Valles are 300 kilometers (190 mi) wide. It begins in Echus Chasma, near Valles Marineris, and empties into Chryse Planitia, not far from where Viking 1 landed. Sacra Mensa, a large tableland divides Kasei into northern and southern channels.
Scientists suggest it was formed by several episodes of flooding and maybe by some glacial activity.[8]
Map of Lunae Palus with labels. Kasei Valles is a very large ancient river valley.
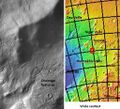
Area around northern Kasei Valles, showing relationships among Kasei Valles, Bahram Vallis, Vedra Valles, Maumee Valles, and Maja Valles. Map location is in Lunae Palus quadrangle and includes parts of Lunae Planum and Chryse Planitia.
Kasei Valles, as seen by THEMIS.
Other valles in the Lunae Palus quadrangle
Hypanis Vallis in the Lunae Palus quadrangle of Mars, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
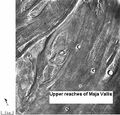
Streamlined islands seen by Viking showed that large floods occurred on Mars. Image is of a small part of Maja Valles and is located in Lunae Palus quadrangle.
Scour patterns were produced by flowing water from Maja Valles, which lies just to the left of this mosaic. Detail of flow around Dromore crater is shown on next image. Image is located in Lunae Palus quadrangle and was taken by Viking Orbiter.
Great amounts of water were required to carry out the erosion shown in this Viking image of a small part of Maja Valles. Image is located in Lunae Palus quadrangle.
Vedra Valles, Maumee Valles, and Maja Valles flow from Lunae Planum on the left to Chryse Planitia on the right. Image is located in Lunae Palus quadrangle and was taken by Viking Orbiter.
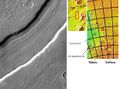
Bahram Vallis, as seen by Viking. Valley is located in Northern Lunae Planum and the Lunae Palus quadrangle. It lies nearly midway between Vedra Valles and lower Kasei Valles
Bahram Vallis in the Lunae Palus quadrangle of Mars, as seen by HiRISE. Rotational landslides (slumps) are visible at the base of north wall.
Maja Valles streamlined island in the Lunae Palus quadrangle of Mars, as seen by HiRISE. Island formed behind the impact crater at the lower right.
Nanedi Valles, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see more details.
Valles in the Syrtis Major quadrangle
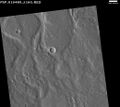
Auqakuh Vallis. At one time a dark layer covered the whole area, now only a few pieces remain as buttes. Image was taken with THEMIS.
Huo Hsing Vallis in Syrtis Major, as seen by THEMIS. Straight ridges may be dikes in which liquid rock once flowed.
Huo Hsing Vallis Ridges, as seen by HiRISE. Ridges may be caused by water moving along faults.
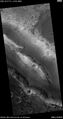
Arnus Vallis layers, as seen by HiRISE.
Valles in the Hellas quadrangle
Mad Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Picture on right is an enlargement of part of the other picture.
Lineated Floor Deposits
The floors of some channels have features called lineated floor deposits. They are ridged and grooved materials that seem to deflect around obstacles. Scientists believe they are ice-rich. Some glaciers on the Earth show such features. Lineated floor deposits may be related to lobate debris aprons, which have been proven to contain large amounts of ice. Reull Vallis, as pictured below, displays these deposits.[9]
Drainage features in Reull Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship of Reull Vallis to other features.
Reull Vallis with lineated floor deposits, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship to other features.
Layers in Reull Vallis, as seen by THEMIS.
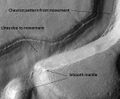
Niger Vallis with features typical of this latitude, as seen by HiRISE. Chevon pattern results from movement of ice-rich material. Click on image to see chevron pattern and mantle.
Origin of Dao Vallis
Dao Vallis begins near a large volcano, called Hadriaca Patera, so it is thought to have received water when hot magma melted huge amounts of ice in the frozen ground. The partially circular depressions on the left side of the channel in the image below suggests that groundwater sapping also contributed water.[10]
Hellas quadrangle map showing Dao Vallis in the upper middle of the map.
Dao Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Click on image to see relationship of Dao Vallis to other nearby features.
Vallis in Elysium quadrangle
Wide view of Iberus Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Imagine taking a walk in these canyons and looking up at the layers.
Patapsco Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Patapsco Vallis is a valley in the Elysium quadrangle of Mars. Scale bar is 1000 meters long.
Lethe Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Flow was from southwest to northeast. Wider part of Lethe Vallis had less erosive power, so mesas are left behind from pre-existing material. Lethe Vallis is a valley in the Elysium quadrangle. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
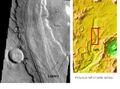
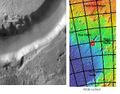
Athabasca Valles, showing source of its water, Cerberus Fossae. Note streamlined islands that show direction of flow to south. Athabasca Valles is in the Elysium quadrangle.
Athabasca Valles Streamlined Form, as seen by HiRISE. Athabasca Valles is in the Elysium quadrangle.
Ituxi Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Ituxi Vallis is a lava channel that lies east of Elysium Mons.
Vallis in Oxia Palus quadrangle
Close-up of Simud Valles, as seen by HiRISE. Simud Valles is found in the Oxia Palus quadrangle.
Ares Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Ares Valles is found in the Oxia Palus quadrangle.
Channels in Ares Vallis region (Oxia Palus quadrangle), as seen by HiRISE.
Tear-drop shaped islands caused by flood waters from Maja Valles, as seen by Viking Orbiter. Image is located in Oxia Palus quadrangle.
Vallis in Memnonia quadrangle
Samara Vallis in the Memnonia quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
Padus Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Padus Vallis is in the Memnonia quadrangle.
Close-up of Padus Vallis, as seen by THEMIS. Padus Vallis is in the Memnonia quadrangle.
Other examples of valles
Frento Vallis in Noachis quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image to see better view of Dust Devil Tracks. In the Arcadia quadrangle on Mars, its exact location is centered at 37 degrees north latitude and 93.1 degrees west longitude. It is 357 km long and was named after a classical river.[11]
Enipeus Vallis in the Arcadia quadrangle, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
Scamander Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Click on image to see dark slope streaks in a variety of shades. The darker the streak the younger it is. is an ancient river valley in the Amenthes quadrangle. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
Her Desher Vallis, as seen by HiRISE. Her Desher Vallis is found in the Coprates quadrangle.
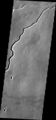
Branched channels in Thaumasia quadrangle, as seen by Viking Orbiter. Networks of channels like this are strong evidence for rain on Mars in the past.
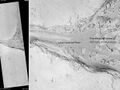
Ravi Vallis, as seen by Viking Orbiter. Ravi Vallis was probably formed when catastrophic floods came out of the ground to the right (chaotic terrain). Image located in Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle.
Small meandering channel in the stream bed of a larger channel. Water probably eroded the two channels at different times. Image from HiRISE under the HiWish program. Image located in Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle.
See also
- Astronomy:List of valles on Mars – Valley-like topographical features
- Astronomy:List of geological features on Mercury – None
- Astronomy:Outflow channels – Long, wide swathes of scoured ground on Mars
- Astronomy:Peace Vallis – Martian valley
- Astronomy:Valley network (Mars) – Branching networks of valleys on Mars
References
- ↑ In Latin, the singular is valles (with a short 'e') or vallis, and the plural is valēs with a long 'e'.
valles. Charlton T. Lewis and Charles Short. A Latin Dictionary on Perseus Project. - ↑ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=NoDvAAAAMAAJ. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ↑ Raeburn, P. 1998. Uncovering the Secrets of the Red Planet Mars. National Geographic Society. Washington D.C.
- ↑ Moore, P. et al. 1990. The Atlas of the Solar System. Mitchell Beazley Publishers NY, NY.
- ↑ Carr, M. 1979. Formation of martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 84: 2995-3007.
- ↑ Hanna, J. and R. Phillips. 2005. Tectonic pressurization of aquifers in the formation of Mangala and Athabasca Valles on Mars. LPSC XXXVI. Abstract 2261.
- ↑ "Nirgal Vallis - Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS". http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20030916a.
- ↑ "The Cataracts of Kasei - Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS". http://themis.asu.edu/node/5672.
- ↑ "Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS: Image of the Day". http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20021022a.
- ↑ "Dao Vallis - Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS". http://themis.asu.edu/zoom-20020807a.
- ↑ "Planetary Names: Welcome". http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov.