Biology:Band 3 anion transport protein
 Generic protein structure example |
| solute carrier family 4 (anion exchanger), member 1, adapter protein | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SLC4A1AP |
| NCBI gene | 22950 |
| HGNC | 13813 |
| OMIM | 602655 |
| RefSeq | NM_018158 |
| UniProt | P02730 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 2 p23.3 |
Band 3 anion transport protein, also known as anion exchanger 1 (AE1) or band 3 or solute carrier family 4 member 1 (SLC4A1), is a protein that is encoded by the SLC4A1 gene in humans.
Band 3 anion transport protein is a phylogenetically-preserved transport protein responsible for mediating the exchange of chloride (Cl−) with bicarbonate (HCO3−) across plasma membranes. Functionally similar members of the AE clade are AE2 and AE3.[1]
Function
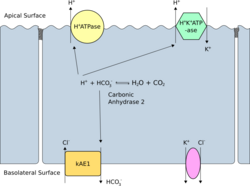
Band 3 is present in the basolateral face of the α-intercalated cells of the collecting ducts of the nephron, which are the main acid-secreting cells of the kidney. They generate hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions from carbon dioxide and water – a reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase. The hydrogen ions are pumped into the collecting duct tubule by vacuolar H+ ATPase, the apical proton pump, which thus excretes acid into the urine. kAE1 exchanges bicarbonate for chloride on the basolateral surface, essentially returning bicarbonate to the blood. Here it performs two functions:[citation needed]
- Electroneutral chloride and bicarbonate exchange across the plasma membrane on a one-for-one basis. This is crucial for CO2 uptake by the red blood cell and conversion (by hydration catalysed by carbonic anhydrase) into a proton and a bicarbonate ion. The bicarbonate is then excreted (in exchange for a chloride) from the cell by band 3.
- Physical linkage of the plasma membrane to the underlying membrane skeleton (via binding with ankyrin and protein 4.2). This appears to be to prevent membrane surface loss, rather than having to do with membrane skeleton assembly.
Distribution
It is ubiquitous throughout the vertebrates. In mammals, it is present in two specific sites:[citation needed]
- the erythrocyte (red blood cell) cell membrane and
- the basolateral surface of the alpha-intercalated cell (the acid secreting cell type) in the collecting duct of the kidney.
Gene products
The erythrocyte and kidney forms are different isoforms of the same protein.[2]
The erythrocyte isoform of AE1, known as eAE1, is composed of 911 amino acids. eAE1 is an important structural component of the erythrocyte cell membrane, making up to 25% of the cell membrane surface. Each red cell contains approximately one million copies of eAE1.[citation needed]
The kidney isoform of AE1, known as kAE1 (which is 65 amino acids shorter than erythroid AE1) is found in the basolateral membrane of alpha-intercalated cells in the cortical collecting duct of the kidney.[citation needed]
Clinical significance
Mutations of kidney AE1 cause distal (type 1) renal tubular acidosis, which is an inability to acidify the urine, even if the blood is too acidic. These mutations are disease causing as they cause mistargetting of the mutant band 3 proteins so that they are retained within the cell or occasionally addressed to the wrong (i.e. apical) surface.[citation needed]
Mutations of erythroid AE1 affecting the extracellular domains of the molecule may cause alterations in the individual's blood group, as band 3 determines the Diego antigen system (blood group).[citation needed]
More importantly erythroid AE1 mutations cause 15–25% of cases of hereditary spherocytosis (a disorder associated with progressive red cell membrane loss), and also cause the hereditary conditions of hereditary stomatocytosis[3] and Southeast Asian ovalocytosis.[4]
Interactions
Band 3 has been shown to interact with CA2[5][6][7][8] and CA4.[9]
Discovery
AE1 was discovered following SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) of erythrocyte cell membrane. The large 'third' band on the electrophoresis gel represented AE1, which was thus initially termed 'Band 3'.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ "Molecular physiology and genetics of Na+-independent SLC4 anion exchangers". Journal of Experimental Biology 212 (11): 1672–1683. 2009. doi:10.1242/jeb.029454. PMID 19448077.
- ↑ "Co-clustering of denatured hemoglobin with band 3: its role in binding of autoantibodies against band 3 to abnormal and aged erythrocytes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (16): 6137–41. August 1986. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.16.6137. PMID 3461480. Bibcode: 1986PNAS...83.6137S.
- ↑ "Monovalent cation leaks in human red cells caused by single amino-acid substitutions in the transport domain of the band 3 chloride-bicarbonate exchanger, AE1". Nat. Genet. 37 (11): 1258–63. 2005. doi:10.1038/ng1656. PMID 16227998.
- ↑ "Deletion in erythrocyte band 3 gene in malaria-resistant Southeast Asian ovalocytosis". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (24): 11022–6. 1991. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.24.11022. PMID 1722314. Bibcode: 1991PNAS...8811022J.
- ↑ "A transport metabolon. Functional interaction of carbonic anhydrase II and chloride/bicarbonate exchangers". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (51): 47886–94. Dec 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105959200. PMID 11606574.
- ↑ "Carbonic anhydrase II binds to the carboxyl terminus of human band 3, the erythrocyte C1-/HCO3- exchanger". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (43): 28430–7. October 1998. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.43.28430. PMID 9774471.
- ↑ "Localization of the Cl-/HCO3- anion exchanger binding site to the amino-terminal region of carbonic anhydrase II". Biochemistry 39 (44): 13344–9. November 2000. doi:10.1021/bi0015111. PMID 11063570.
- ↑ "Identification of the carbonic anhydrase II binding site in the Cl(-)/HCO(3)(-) anion exchanger AE1". Biochemistry 39 (18): 5527–33. May 2000. doi:10.1021/bi992564p. PMID 10820026.
- ↑ "The extracellular component of a transport metabolon. Extracellular loop 4 of the human AE1 Cl-/HCO3- exchanger binds carbonic anhydrase IV". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (28): 25239–46. July 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202562200. PMID 11994299.
- ↑ Alberts, Bruce; Johnson, Alexander; Lewis, Julian; Raff, Martin; Roberts, Keith; Walter, Peter. Molecular Biology of the Cell (Fourth ed.). Garland Science. p. 604. ISBN 0815332181.
Further reading
- "Molecular and cellular biology of the erythrocyte anion exchanger (AE1)". Semin. Hematol. 30 (1): 34–57. 1993. PMID 8434259.
- "Studies on the structure of a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic loop of the human red cell anion exchanger (band 3, AE1)". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26 (3): 516–20. 1998. doi:10.1042/bst0260516. PMID 9765907.
- "[Band 3: expanding knowledge on its functions]". Seikagaku 73 (12): 1431–5. 2002. PMID 11831035.
- "Band 3 anion exchanger and its involvement in erythrocyte and kidney disorders". Curr. Opin. Hematol. 9 (2): 133–9. 2002. doi:10.1097/00062752-200203000-00009. PMID 11844997.
- "Defects in processing and trafficking of the AE1 Cl−/HCO3− exchanger associated with inherited distal renal tubular acidosis". Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 8 (1): 1–11. 2004. doi:10.1007/s10157-003-0271-x. PMID 15067510.
External links
- Diego blood group system at BGMUT Blood Group Antigen Gene Mutation Database at NCBI, NIH
- Band+3+Protein at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Chloride-Bicarbonate+Antiporters at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human SLC4A1 genome location and SLC4A1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
 |